Shtabinskaya T.T.
Grodno State Medical University, Belarus
Influence of clinical, morphological and
immunohistochemical parameters on the survival of patients with colorectal
cancer
The increase in the incidence of cancer of the
distal portions of the gastrointestinal tract and mortality, complicated and
expensive treatment is not sufficient and satisfactory immediate results are
separated by reason of unflagging interest to this area of practical medicine
[1]. Purpose: To evaluate the value of clinical, morphological and
immunohistochemical parameters for forecasting adjusted progression-free
survival (APFS) with colorectal cancer (CRC).
Materials and methods:
the study was performed on paraffin sections using antibodies to VEGFА, CD 105, MMP-2, Erk2, iNOS, TGF-β, NRP1, MMP-9 according to standard procedure [2]. Quantitation of
the level of expression was described in the previous article [3]. Statistical analysis was performed using
STATISTICA 10.0 (SNAXAR207F394425FA-Q). Construction of multi-factor models
predict the 5-year outcome was performed using Cox regression direct
incremental method based on analysis of 72 CRC observations, remote in the
Grodno Regional Oncology Center (Belarus). Grouped attribute the outcome of
cancer after 5 years from the time of surgery, estimated by APFS has been
selected. Due to the fact that the distribution was different from the normal
(p <0.05), to check the variables to calculate the mutual correlation of
Spearman's rank correlation. Independent clinical and morphological variables
weakly correlated and therefore can be used as independent variables in the
regression. For immunohistochemical of interrelated factors (parenchymal and
stromal levels of expression of each of the markers) as a regressor used the
product of interrelated variables. When building a model predicting disease
outcome 59 clinical, morphological and immunohistochemical index were used.
Results: found that significantly affect the five-year APFS only five of them.
The values of the likelihood function and criteria for each of the two steps of
the regression are presented in Table 1.
Table
1 - The universal criterion of model coefficients
|
|
||||||||||
|
Step |
-2 Log
Likelihood |
Overall
(score) |
Change
From Previous Step |
Change
From Previous Blstromalk |
||||||
|
Chi-square |
df |
Sig. |
Chi-square |
df |
Sig. |
Chi-square |
df |
Sig. |
||
|
1a |
286,057 |
28,555 |
3 |
,000 |
18,846 |
3 |
,000 |
18,846 |
3 |
,000 |
|
2b |
277,087 |
36,539 |
4 |
,000 |
8,970 |
1 |
,003 |
27,817 |
4 |
,000 |
|
3c |
272,047 |
41,264 |
5 |
,000 |
5,040 |
1 |
,025 |
32,857 |
5 |
,000 |
|
4d |
267,530 |
48,790 |
6 |
,000 |
4,518 |
1 |
,034 |
37,374 |
6 |
,000 |
|
5e |
263,447 |
54,013 |
7 |
,000 |
4,082 |
1 |
,043 |
41,457 |
7 |
,000 |
|
Примечание: a. Variable(s) Entered
at Step Number 1: Stage |
||||||||||
|
b.
Variable(s) Entered at Step Number 2: iNOSstromal*iNOSparenchymal |
||||||||||
|
c.
Variable(s) Entered at Step Number 3: Erk2parenchymal*Erk2stromal |
||||||||||
|
d.
Variable(s) Entered at Step Number 4: MMP2parenchymal*MMP2stromal |
||||||||||
|
e.
Variable(s) Entered at Step Number 5: Grade |
||||||||||
As
can be seen from Table 1, the coefficients of the model are significant and
their numerical values will help to interpret the result. The numerical value
of the coefficient of proportionality, as well as the rest of the regression
parameters are presented in Table 2.
Table
2 - Characteristics of the variables included in the model prediction of five
APFS
|
|
|
B |
SE |
Wald |
df |
р |
Exp(B) |
|
Step 5 |
Grade |
-,955 |
,455 |
4,404 |
1 |
,036 |
,385 |
|
Stage |
|
|
22,760 |
3 |
,000 |
|
|
|
Stage(1) |
-3,189 |
,756 |
17,777 |
1 |
,000 |
,041 |
|
|
Stage(2) |
-1,779 |
,599 |
8,809 |
1 |
,003 |
,169 |
|
|
Stage(3) |
-2,242 |
,542 |
17,146 |
1 |
,000 |
,106 |
|
|
MMP2par*strom |
47,686 |
15,717 |
9,205 |
1 |
,002 |
5,124E20 |
|
|
iNOSstrom*par |
2,336 |
,926 |
6,361 |
1 |
,012 |
10,343 |
|
|
Erk2par*strom |
192,152 |
94,257 |
4,156 |
1 |
,041 |
2,821E83 |
As
can be seen from Table 2, Grade adenocarcinoma and stage of the disease -
negative factors. Increasing grade reduces patient survival 0.385, and stages -
in 0.041, 0.169 and 0.106 times, respectively. Positive factors are the
parenchymal and stromal expression of MMP2, iNOS and Erk2.
251658240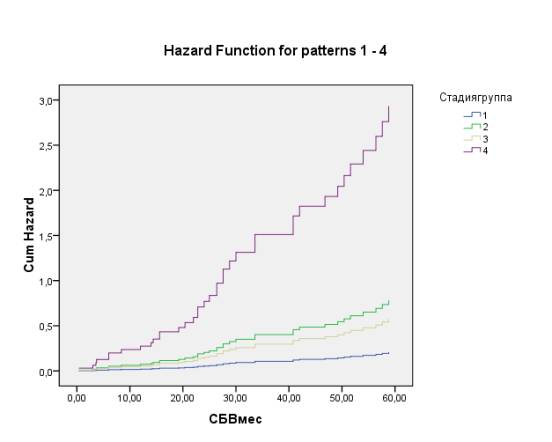
Figure 4 - Hazard Function
for stage disease 1-4
Conclusion: with
initially high expression of MMP-2, and iNOS Erk2 and low grades and stages of
the disease can be predicted APFS more than 5 years.
Literature:
1. Loftus W.K. Ultrasound, CT and colonoscopy of colonic cancer
/ W.K.Loftus C.
Metreweli, J J. Sung et al. // Br. J. Radiol. - 1999. - Vol. 72, № 1. -
P. 144-148.
2. Коржевский, Д.Э. Основы
гистологической техники / Д.Э. Коржевский, А.В. Гиляров. – Спб.: СпецЛит, 2010.
– 95 с.
3. Штабинская, Т.Т.
Прогностическое значение уровня экспрессии фактора роста эндотелия сосудов в
колоректальном раке / Т.Т. Штабинская [и др.] // Научно-практический журнал УО
«Гродненский государственный медицинский университет». – 2015. - № 3(51). - С.
64-69.