Ph.D., Ziyadullaev O.E.,
lecturer Abdurakhmanovà S.S.
Tashkent Chemical
Technological Institute, Uzbekistan
SYNTHESIS OF AROMATIC ACETYLENIC ALCOHOLS
AND THEIR VINYL ESTERS
Acetylene
hydrocarbons and various derivatives thereof, due to their high reactivity and
availability is widely used in organic synthesis.
Homogenous-catalytic vinylation reaction on the basis of aromatic
acetylene alcohols (AAÀ) MeOH-DMSO (MeOH- LiOH, NaOH and KOH) has been
carried out and it was exposed that vinyl ethers (VE) synthesized desirable in
the interval of 40-60% [1, 2].
When industrial implementation of heterogeneous catalytic processes have
to adjust the speed and direction of chemical reactions, the mechanism of which
is known only in the most general terms, and the catalysts are complex solids,
properties which are still not fully understood, and that may include almost
all the elements of the periodic the periodic system [3, 4].
In this study of heterogeneous catalytic process to synthesize certain
vinyl esters of aromatic acetylenic alcohols in relatively high yields in the
presence of MOH (MOH- LiOH, NaOH and KOH) systems impregnated activated carbon.
The active component of the catalyst used hydroxides of sodium and potassium.
The process carried out at different temperatures and reaction time.
In reaction Grinyara- Iotsicha using croton aldehyde and ketones
(acetone, methyl ethyl ketone, methyl isopropyl ketone, pinokaline and
acetophenone) phenyiacetylene by their interaction with the organomagnesium
compound synthesized in the following respective compounds AAA- 1-phenyl-3-methylbutyn-1-ol-3 (I) 1-phenyl-3-methylpentyn-1-ol-3 (II) 1-phenyl-3,4-dimethylpentyn-1-ol-3 (III), 1-phenyl-3,4,4-trimethylpentyn-1-ol-3 (IV) 1,3-diphenylbutyn-1-ol-3 (V) and
1-phenylgekcyn-4-in-1-ol-3(VI). The scheme of the reaction has been offered as following [5].
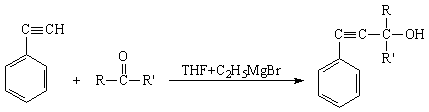
here: R= -CH3, R'= -CH3; R=
-CH3, R'= -C2H5; R= -CH3, R'= izo -C3H7,
R= -CH3, R'= -C(ÑH3)3; R= -CH3, R'=
-Ñ6H3, R= -H, R'= -ÑH=CH-CH3.
Synthesis
process AAA method Grinyara- Iotsicha conducted at a temperature range -5-10 °C
in the presence of solvents DEE and THF. The starting materials were taken in
equimolar amounts. The results are shown in the table 1.
Table1.
Influence of the nature and
duration of the reaction solvents
on the yield of AAA
(temperature0– 5 oC)
|
ÀÀA |
Products,% |
|||
|
solventDEE |
solventTHF |
|||
|
ÀÀA |
intermediate connections |
ÀÀA |
intermediate connections |
|
|
Duration of reaction, 2 hour |
||||
|
I |
75,0 |
18,3 |
87,4 |
6,5 |
|
II |
68,4 |
23,4 |
83,5 |
10,2 |
|
III |
56,4 |
29,5 |
74,5 |
15,3 |
|
IV |
53,0 |
34,7 |
69,3 |
18,4 |
|
V |
50,0 |
39,6 |
66,0 |
21,0 |
|
VI |
64,3 |
26,4 |
79,0 |
14,1 |
|
Duration of reaction, 4 hour |
||||
|
I |
78,6 |
13,2 |
89,6 |
4,5 |
|
II |
71,8 |
17,4 |
85,0 |
7,6 |
|
III |
60,6 |
21,6 |
75,2 |
13,0 |
|
IV |
55,9 |
25,0 |
71,0 |
15,5 |
|
V |
54,7 |
28,0 |
68,7 |
18,2 |
|
VI |
68,0 |
20,0 |
81,2 |
12,2 |
|
Duration of reaction, 6 hour |
||||
|
I |
67,3 |
24,8 |
82,2 |
11,4 |
|
II |
62,4 |
27,0 |
77,6 |
17,0 |
|
III |
52,4 |
37,0 |
69,5 |
18,4 |
|
IV |
45,2 |
41,6 |
63,2 |
21,0 |
|
V |
42,7 |
44,0 |
57,3 |
23,7 |
|
VI |
58,6 |
35,6 |
70,6 |
17,4 |
here: I- 1-phenyl-3-methylbutyn-1-ol-3; II- 1-phenyl-3-methylpentyn-1-ol-3; III- 1-phenyl-3,4-dimethylpentyn-1-ol-3; IV-1-phenyl-3,4,4-trimethylpentyn-1-ol-3; V- 1,3-di-phenylbutyn-1-ol-3; VI- 1-phenylgecyn-4-in-1-ol-3.
The
table shows that when using THF as solvent, increasing the reaction time from 2
to 4 hours, an increase yield. However, with increasing duration of synthesis
up to 6 hours, a sharp fall of efficiency AAA exit.
The
table shows that when the reaction is carried out in solvents DEE and THF in
AAA is formed with a high yield. For example, with a reaction time 4 hours
temperature -5- 0 oC in a solvent DEE, yield AAA: I- 78,8; II- 71,8;
III- 60,6; IV- 55,9; V- 54,7 and VI- 68,0%, and in case of replacement solvent
THF respectively 89,6; 85,0; 75,2; 71,0; 68,7 and 82,2%. Comparing the reaction
results in different solvents shows that the average selectivity output y THF
solvent by 13,0% more than the DEE. This reaction is due to the greater
polarity of THF molecule compared to DEE.
Hence,
vinylation reaction on the basis of AAÀ acetylene with higher base-catalytic
system, The scheme of the reaction has been offered as following:
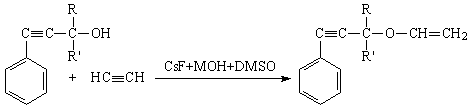
here: R= -CH3, R'= -CH3; R=
-CH3, R'= -C2H5; R= -CH3, R'= izo -C3H7, R= -CH3,
R'= -C(ÑH3)3; R= -CH3, R'= -Ñ6H3,
MOH= LiOH, NaOH, KOH.
It has
been observed the relatively maximum yield synthesis of VE AAÀ in the presence
of MeOH-CsF-DMSO with higher base-system on the experiment's results.
The gained results show that
as LiOH, NaOH and KOH are used in the system of CsF-MOH-DMSO as MOH, in each
particular state the yield of product goes through maximum while the
temperature is rising. It has been determined the increase of AAÀ on the series
LiOH·CsF<KOH·CsF<NaOH·CsF in the selected catalytic systems. As
temperature rose from 80 to 120 oC, the yield raised appreciably.
The selectivity of temperature
100oC state has been meant as the highest system for the process.
It can be explained that
catalytic activity of presented system with the formation of CsOH and NaF in
the system and its less solubility with the higher base-property of CsOH. In
LiOH and KOH systems, the solubility of the formed LiF and NaF is higher, and
in the system they are existed in the state of ion in the system, the balance
specifies. Hereon, CsOHcouldn't perform completely activity. Owing to this
LiOH+CsOH+LiF+CsF system is in charge of catalyst.
Table 2.
The influence of nature and temperature of catalysts
on the yield of VE AAÀ (duration of reaction is 6 hours, solvent DMSO)
|
Catalyst |
Temperature, oC |
I |
II |
III |
IV |
|
LiOH·CsF |
80 |
44,3 |
38,2 |
33,3 |
56,0 |
|
100 |
49,0 |
46,6 |
42,9 |
59,4 |
|
|
120 |
51,1 |
48,4 |
46,3 |
58,0 |
|
|
KOH·CsF |
80 |
49,6 |
45,2 |
40,2 |
57,4 |
|
100 |
57,4 |
52,0 |
40,7 |
66,4 |
|
|
120 |
58,3 |
55,7 |
49,6 |
67,3 |
|
|
NaOH·CsF |
80 |
74,2 |
73,2 |
67,3 |
79,6 |
|
100 |
84,8 |
77,1 |
72,3 |
88,0 |
|
|
120 |
86,0 |
79,7 |
75,0 |
89,5 |
here: I- VE 1-phenyl-3-methylpentyn-1-ol-3; II- VE 1-phenyl-3,4-dimethylpentyn-1-ol-3; III- VE 1-phenyl-3,4,4-trimethylpentyn-1-ol-3; IV- VE 1,3-diphenylbutyn-1-ol-3.
It has been observed,
vynilation process on the AAÀ higher base-system, reaction undergoes under top
level along with the formation of polycomponent mixtures on the some stages.
Herein, moving hydrogen of acetylene goes on base of stereo-regioselectivity,
also its exchanging process does easily. Although investigations on the
vinylation process of organic compounds including members of various classes
hydroxyl group containing in their molecules have been carried out for years,
reaction mechanism hasn't enough researched scientifically yet. At present
having formed catalytic active center, reactions being carried out in the
system MeO-CsF-DMSO, formation of metal solvates and having become interval
metal complex possessing active center, counterbalances the function of
catalyst.
The optimal conditions for the
synthesis of AAA: equimolar ratio of the starting materials; temperature -5- 0oC,
the solvent THF, the reaction time of 4 hours. In this case it has been determined that very maximum yield of product is
I synthesized AAA – I- 89,6; II- 85,0; III- 75,2; IV- 71,0; V- 68,7 and
VI- 81,2%.
On the basis of experimental studies identified the following series of
reactions reactivity of ketones Grinyara- Iotsicha acetophenone < pinokalin
< methylisopropylketone < crotonaldehyde < methylethyl ketone
<acetone.
Conclusion,
in order to synthesize VE AAÀ with
higher yield 6 hour's process at 100 oC temperature in the system of
NaOH-CsF-DMSO has been chosen. In this case it has
been determined that very maximum yield of product is I=84,8%; II=77,1%;
III=72,3% and IV=88,0%.
Literature
1. WeilT.F., SchreinerP.R.
Organo catalytic alkynylation of aldehydes and ketones under phase-transfer
catalytic conditions // European Journalof Organic Chemistry,V.24(237). 2005 pp. 2213-2219.
2. Ziyadullaev O.E., Turabjanov
S.M., Ikramov A., Mahatova G.B. Theoretical foundations reaction homogeneously
catalytic vinylation of acetylene alcohols. ÕV International scientific
conference «High-Tech in Chemical
Engineering-2014» 2014, Moscow (Russia). pp. 124.
3. Schmidt E.Y., Trofimov
B.A., Zorina N.V., Mikhaleva A.I., Ushakov I.A., Alexandrov G.G., DyachenkoO.A.
Synthesis of functionalized 3,4-dihydropyrans via rearrangement of the products
of a one-pot diastereoselective assembly of ketones and acetylene // European
Journal of Organic Chemistry,V.35
(482). 2010. pp. 6727-6730.
4. Ziyadullaev O.E. Synthesis
Reactions Vinyl Ethersof Aromatic Acetylene Alcohols In The Alkali Phase// International Journal Of Engineering Sciences &
Research Technology, V.4.(5).Ìày, 2015, ðð. 633-637.
5.
Ziyadullaev O.E., Turabdjanov S.M., Juraev R.S.,
Abdurakhmanovà S.S. Synthesis of aromatic acetylene alcohols of the methods
Grinyara-Iotsicha ÕI Miedzynarodowej naukowi-praktycznej
konferencji «Europejskanauka XXI Powieka»
Przemysl, Poland. 2015. V.15, pp. 88-91.