Технические науки/ 6. Электротехника
и радиоэлектроника
Ph.D. Iryna Zharikova, Oleksandr Botsman
Kharkov National University of Radio Electronics
Intelligent
lighting control system
based on piezoelement
1. Introduction
At
present time there is a requirement
to automate routine actions made by
man. Tasks of this sort are considered during "smart
home" systems design.
One of the most important tasks
during development of a number of
similar projects is to create intelligent
lighting control system. Such systems
can be designed on the base of various sensors that detect sound vibrations and control the "smart house"
lighting according to a predetermined algorithm
using a microcontroller.
2. Task formulation
In
this regard it was decided to
develop a compact intelligent lighting
control system, which should provide:
-
switching on and off of network load
during the detection of double-clapping;
-
minimal false actuations;
- no need for additional power supply;
-
small weight and size of the
finished device in the packaging.
The structure
of such a system includes:
- a microcontroller
– for control all elements of the system;
- a sensor that will detect the acoustic waves;
- an universal
electromagnetic relay – for switching
on and off of network load;
- circuits of power supply formation
from the mains voltage.
It is advisable to start the
development of this device with the selection of the sensor. It must possess
the following features:
- respond
exclusively to sharp splashes of sound vibrations;
- have a resonant frequency close to the frequency of the sound of clapping
hands.
3. A sensor selection
on the basis of the research results analysis
To
provide needed characteristics various types of sensors were investigated.
These researches were based on a measurement
of sensor sensitivity G and bandwidth
depending on the frequency of sound
vibrations f. For
analysis convenience, the data are grouped and presented
as a graph (Fig. 1).
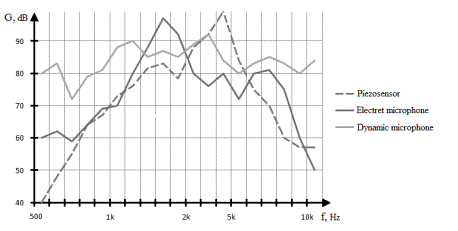
Figure 1. The sensors sensitivity oscillogram
|
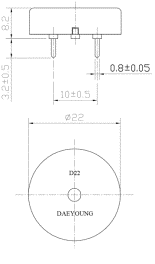
Figure
2. Piezosensor
CBEG2240BP |
Based on the research results analysis
the required sensor was selected. It
was piezosensor CBEG2240BP of Daeyoung
firm (Fig. 2). It has the following parameters: - input voltage –
9 V; - sound pressure level
– 90 dB; - resonant
frequency – 4000 Hz. |
The
use of piezoelectric transducer in the developed device will allow capturing
only acoustic splashes with frequency close to the handclaps, and will ignore other
– more uniform – oscillations of the sound spectrum.
4. The analysis of the
developed system
The
developed device is powered by 220 V and requires no additional power supply.
It is connected in-sequence with the load as any electrical lighting equipment
with power consumption to 1540 watts. Other technical characteristics of the
device are presented in the Tab. 1.
Table
1
|
Device characteristics |
Value |
|
Nominal voltage,
V |
220 |
|
Sensor type |
piezoelectric
element |
|
Work range, m |
10 |
|
Maximum load
current, A |
7 |
|
Maximum load power, W |
1540 |
|
Power
consumption,
W |
not
more 0.2 |
The
schematic circuit diagram of the device is shown in Fig. 3. Electronic
part power built on transformerless power supply [1] consisting of a quenching
circuit C1, R1, where the voltage drops to 70 V. Then, using rectifier VDS1 a
constant voltage is formed, which drops on the stabilizer diode VD1 to 12 V.
This voltage is used to supply the relay K1 coil, and to supply the voltage
regulator structurally made on the integrated circuit chip DD1. After
stabilizer the constant voltage of 5 V powered microcontroller DD2 and one
stage of amplification, made on bipolar transistor VT2. Signal source for the
latest is sound pressure sensor built on the principle of piezoelectric effect.
For a given algorithm when it is necessary to connect the load to the network of
220 V, the microcontroller sets a high logic level, which through resistor R2
closes transistor VT1 switch, thereby connecting the second end of the relay
coil to the ground. This leads to the closure of the power contacts of the
relay and to connection of load to the main network.
This
device is controlled by a single-chip 8-bit FLASH
CMOS microcontroller PIC12F683 of Technology Incorporated company [2]. In this case, the microcontroller used in the package SOIC8.
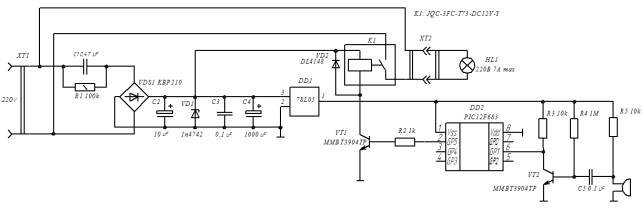
Figure 3. Electrical circuit diagram of lighting control device
The
main functions of the microcontroller are:
-
analysis of the analog input of the internal comparator CIN-;
-
with a sufficient pulse amplitude – recording of this event;
-
control of input pulses by time intervals;
-
at violation of intervals – reset the session and return to the initial standby
mode;
-
at compliance with all requirements of the program logic – setting a high logic
level in output pin GP5, which, in turn, closes the transistor switch VT1,
thereby connect the load HL1 to 220 V.
|
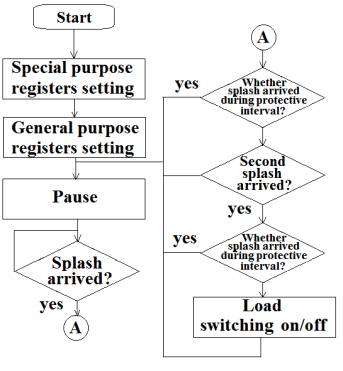
Figure
4. The algorithm of the
microcontroller program |
The
algorithm for microcontroller work is shown in Fig. 4. The
key points of this algorithm are "protected pauses" between the
detection of the input low-frequency splashes. This solution ensures a
correct load control and eliminates most false actuations [3]. |
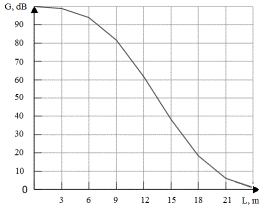
To
confirm the effectiveness of
the chosen technical solution, a series of measurements were performed. Dependences of
the sensitivity of the developed device
from a source of sound splashes remoteness L, and the radiation pattern on the axis of the source of acoustic oscillations are shown in Fig.
6-7.
|
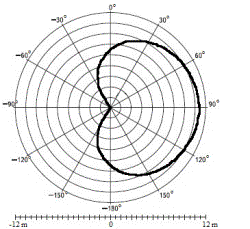
Figure
6. Radiation pattern
of device |
Figure
7. Graph of the sensor sensitivity
from the distance to it |
Conclusions
Thus, in this
paper a method of non-contact control of lighting was proposed. Intelligent
system based on piezoelement allow remote switching on and off a variety of
lighting equipment. The device has a narrow bandwidth tuned to the selective choice
of clapping audio frequency. As can be seen from the radiation pattern (Fig. 6),
the developed system catch sound vibrations even at distance of 10 meters
from the sound source, which allows to place it in most living accommodations,
without fear for the stability of actuations. That is,
the tasks of research were carried out and implemented in the form of finished device.
References
[1] Антипенский Р.В., Фадин А.Г. Схемотехническое проектирование и
моделирование радиоэлектронных устройств. М: Орион, 2007. 128 с.
[2] Предко М.А. Справочник по PIC-микроконтроллерам.
М: ДМК Пресс, 2002. 324 с.
[3] Жарикова И.В., Боцман А.С. Интеллектуальная система управления
освещением на базе пьезоэлемента. Радиотехника. №180. 2015. С. 102-105.