Shuykin
S. A., Ballod B. A., Koltsova
E. A.
Ivanovo State Power Engineering University, Russia
Automation Method Analysis of
Sentiment in Social Media Messages
The article considers one of the
aspects of text analysis of natural language, namely, sentiment analysis. The
study findings have a wide range of possible applications in different spheres,
for instance in marketing, sociology, politics, etc. In these areas, it is
important to have an idea about the mood of customers / society / electorate and
their attitude to certain events or phenomena in social media. Besides, there exists
an urgent need to increase the accuracy and rate of message processing as the
mood and opinions of social network users are constantly changing. The results
of the undertaken research could allow following and controlling these
opinions.
Thus, the present paper aims to
introduce the new methodology for sentiment analysis which is able to increase
the speed and accuracy of data processing.
To begin with, let us have a look at
the methods and models employed for sentimental processing. The currently
existing models of data processing have proved to be unsuitable and
inefficient, not meeting modern requirements. At present, all existing models
of sentimental determination can be divided into 2 categories.
The first category includes methods for
vector analysis of text. The text is represented as a vector of words or their
combinations (n-grams). A number of algorithms such as SVM (support vector
method), Naive Bayesian Classifier, decision trees and some others are used for
this purpose.
The second category refers to the
search for emotive vocabulary (words that are responsible for the overall tonality
of the text) according to pre-compiled dictionaries.
For
the primary goal to be achieved, a number of methods have been applied like tokenisation, TF-IDF analysis and machine learning. These
methods demonstrate the best ratio of accuracy and speed that were the key
aspects for data processing and proved to be timesaving. The system developed was
tested on posts in Vk.com social media. The tests were performed and the conclusion
about emotional message of those text was made whether they are positive,
negative or neutral.
Turning to the analysis itself, the
main steps and terms are to be distinguished. The input is text from social
network. The first step is separation of lexemes and determining their
properties such as part of speech and morphological features. Then, stop-words are
separated that is those not causing evaluation of the overall tone. The second
step is the evaluation of the tone by the TF-IDF method.
![]()
where Vt,d is the width of the word t in a post d; Сt,d is a count of the word t occurring in a post d; |P| is a count of the
posts with positive tone; |N| - a count of the posts with negative tone; Pt – a
count of positive posts where t word occurs and Nt is
a count of the negative posts where t word occurs.
Thus, most frequent elements in
positive and negative texts are determined. To function correctly, the initial stage
requires manual posts evaluation for algorithm verification.
The next stage is constructing a
sentence structure in the form of a hierarchy of binary relationships based on
semantic rules.
good
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
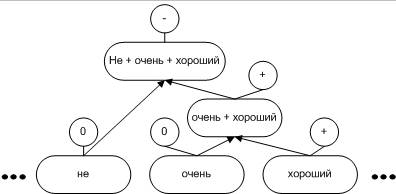
Fig. 1. An example of estimating the tonality of
binary links.
The
example above shows that the word "very" reinforces the positive significance
of the word "good" and "no" inverts the design behind it,
thereby establishing a negative tone.
The program was implemented in Python
programming language using Django framework for the frontend.
As a result, the information system that
automates the work on analytical text processing to determine the key element
has been developed. This development is aimed at improving the existing methods
of processing in order to increase the efficiency. Increasing efficiency means
reducing the time for processing the message, and, therefore, affecting the
timeliness of the submission of the required data. In the future it is planned
to introduce the developed method into the social media monitoring system.