Technical
science /10. Mining
Associate professor Turymbetov
T.A., graduate student Madenov A.N., undergraduate Aitbayev N.T.
Caspian State University of Technologies and
Engineering named after
Sh. Yessenov, Aktau,
Kazakhstan
The stress-strain state of underground structures in
the form shtreks
In this case investigated the static elastic stress and strain state of
two shallow cavities laying in heavy transtropic
massif depending on the degree of discontinuity conform to small sloping layers
at an angle ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() denote the
depth of the workings of the distance between their centers
denote the
depth of the workings of the distance between their centers ![]() .
.
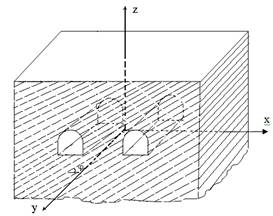
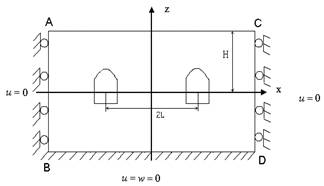
à) three dimensional view; b) two
dimensional view;
Fig.1. The computational domain
Anisotropic doubly periodic massif of
slits systems are replaced with solid transtropic
body, equivalent stiffness basic structure, by solving the problem of
reduction.
The plane of the cross-sectional areas
with anisotropic in plane deformation slits; efforts are at infinity [1].
By
solving the problem of bringing to an anisotropic body with the boundary
conditions. Elastic parameters ![]() , transtropic solid body, equivalent stiffness anisotropic
massif with slots are given [2].
, transtropic solid body, equivalent stiffness anisotropic
massif with slots are given [2].
Hooke's law of anisotropic massif with cavities with generalized plane
strain relative to the Cartesian coordinate system ![]() (see Figure 1):
(see Figure 1):
![]() ; (1)
; (1)
were ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ; - deformation coefficients defined by the formulas [2].
; - deformation coefficients defined by the formulas [2].
Here ![]() - effective elastic constants transtropic massif equivalent stiffness anisotropic massif with slits, which depends on the elastic constants of the last
- effective elastic constants transtropic massif equivalent stiffness anisotropic massif with slits, which depends on the elastic constants of the last ![]() and the geometry of the slits
and the geometry of the slits ![]() .
.
The cross-section in plane
ABCD shtrek planes of deformation using ![]() units to
units to ![]() isoparametric
calculation elements (Figure 1b). Constitute the basic resolution of the system
of algebraic equations finite element method’s
isoparametric
calculation elements (Figure 1b). Constitute the basic resolution of the system
of algebraic equations finite element method’s ![]() - order relative to the projections of moving points
and it can be solved with the following boundary conditions [3]:
- order relative to the projections of moving points
and it can be solved with the following boundary conditions [3]:
base BD calculation area ABCD non-deformable –
![]() ; (2)
; (2)
sides ÀÂ and ÑD under the weight of rocks moved only in the vertical
direction due to a lack of influence of cavities –
![]() . (3)
. (3)
The study estimated the area with cavities is automatically split into isoparametric elements using program FEM_3D in
object-oriented environment program.
Solution of the fundamental system of
equations with to finite element method’s displacement components with the
boundary conditions (2), (3) rigorous methods is difficult; therefore it can be
solved in an iterative method of Gauss-Seidel-relaxation factor with a given
accuracy. An attractive feature of this method is as follows: firstly prepared
only once and the system stiffness ![]() matrix used when iterating its elements and
column elements of the matrix
matrix used when iterating its elements and
column elements of the matrix ![]() ; secondly, when
; secondly, when ![]() - iteration for unknown
- iteration for unknown ![]() , need values
, need values ![]() when
when ![]() - iteration, and for
- iteration, and for ![]() - their values for
- their values for ![]() -iteration.
-iteration.
Applying a method of finite elements, we
determine moving ![]() and
and ![]() as linear function [4].
as linear function [4].
Where factors ![]() is received from [5]. Now shall determine
connection between
is received from [5]. Now shall determine
connection between ![]() and
and ![]() . Where
. Where ![]() and
and ![]() Matrix of element
rigidity
Matrix of element
rigidity
![]() (4)
(4)
Thus,
the system linear algebraic equation is formed [5]:
![]() (5)
(5)
At an angle
of inclination of the plane of isotropy ![]() (and the plane of the slits) slots massif with cavities, ceteris paribus both stress and displacement are distributed symmetrically around the vertical axis
(and the plane of the slits) slots massif with cavities, ceteris paribus both stress and displacement are distributed symmetrically around the vertical axis ![]() and increase with the depth of emplacement of structures; reduces stress, increasing
displacement with reduction w/a; when
and increase with the depth of emplacement of structures; reduces stress, increasing
displacement with reduction w/a; when ![]() both the stress and the displacement are asymmetric about a vertical axis
both the stress and the displacement are asymmetric about a vertical axis ![]() . When the length of the brattice 5D and more, where D-cavities of the largest diameter,
interference structures is negligible.
. When the length of the brattice 5D and more, where D-cavities of the largest diameter,
interference structures is negligible.
REFERENCES
1. Erzhanov Zh.S, Aytaliev Sh.M., Masanov Zh.K. Stability of horizontal caves in the
pan-layered massif. Alma-Ata, Science, 160p, 1971.
2. Erzhanov Zh.S, Kaidarov
K.K., Tusupov M.T. Mountain range with a discontinuous layer coupling
(plane problem). "Mechanical processes in the rock mass." Alma-Ata,
"Nauka", 189p, 1969.
3. Turymbetov T., Azhikhanov N., Zhunisov N., Aimeshov Zh. Stress-strain state of two diagonal cavities weighty
inclining layered massif system with slots in terms of elastic-creep
deformations. - World
conference on technology, innovation and entrepreneurship, pp. 2263-2271,
Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, Volume 195, ISSN: 1877-0428, Istanbul,
Turkey, 2015.
4. Turymbetov T., Ozbay U, Massanov Zh, Aimeshov
Zh. Modeling
of underground
developments
in anisotropic structure on the basis of the finite elements method. The 4th International Sciences Congress "Science
and Education in the Modern
World"., pp.989-993, Vol. II, New Zealand, Auckland, 5-7
January,
2015.
5. Azhikhanov N., Turymbetov T., Aimeshov Zh. The shtrek well type fluid
filtration simulation in the tense heterogenous
layer. Yale Journal of Science and Education. Pp. 434-440. No.1. (18), Volume
X, January-June, 2016.