Economics / 3. Financial Relations
Ovchinnikova I.V., senior lecturer, Kortyukova A.S.,
Minakova E.A., students 4th year
T.F. Gorbachev Kuzbass StateTechnical University
Tax planning in the system of financial planning
budgetary institutions
At
the present stage of development of economic relations between the financial
management of all institutions, without exception, it becomes the most acute
problem. One of the components of financial policy is tax planning and optimization
of tax liabilities.
In
the literature, for example in scientific work Barulin SV, the following definition
of tax planning: "Tax planning - is based on the forecast parameters of
the process of determining the most effective directions of motion and
optimizing the volume and structure of incoming and outgoing flows for the
coming fiscal year and (or) the prospects of the state and economic entities
"[3].
Thus,
we can identify tax planning as a systematic activity of the taxpayer aimed not
only to analyze the tax implications of certain business transactions, but also
proactive in order to optimize the taxation of the economic entity to achieve
the desired result.
Most
non-profit organizations, in spite of the implementation of the mostly
non-commercial activities are also major payers of taxes and fees.
Thus,
in accordance with the Federal Law of 12.01.1996 g №7-FZ "On non-profit
organizations" (as amended on 07.13.2015) budget authority admits:
"non-profit organization established by the Russian Federation, subject of
the Russian Federation or a municipal entity for works and services in order to
ensure the implementation of laws of the Russian Federation authority,
respectively public authorities (government agencies) and local authorities in
the fields of science, education, health, culture, social protection,
employment, physical culture and sports, as well as other areas "[2].
Budgetary
institution carries out its activities in accordance with the state (municipal)
tasks, the fulfillment of which he has no right to refuse. However, budgetary
institutions shall be entitled to carry out other activities not related to its
core business for a fee. As a result, this leads to a broadening of the tax
base and the tax burden, respectively.
Even
if the budget institution carries out only non-commercial activities, may be
subject to taxation: property nonprofit organization, transport, land,
salaries, etc.
In
this connection it is necessary to release additional financial resources for
the implementation of statutory activity of public institutions through
efficient tax planning.
The
problem of planning of tax payments is that it is limited to the development of
methods of reducing the legitimate tax deductions managers, accountants,
economists on taxes. Thus, the basic principles of tax planning, defining the
nature and basis of the tax planning of public institutions are:
1)
The principle of legality - is in compliance with current legislation. According
Bryzgalina A .: "This is a fundamental principle in tax planning, as it
separates the observance of tax planning activities of tax evasion". [4]
2)
The principle of profitability - is to use the tools of tax planning to reduce
the tax liabilities of budget institutions.
3)
Principle of effectiveness - is the most effective use of legislation and planning
tools available to your organization. The application of this principle leads
to achieve tax savings in the future.
4)
The principle alternative - is to review and select the most effective options
for tax planning in relation to a particular organization.
5)
The principle of efficiency - is a timely response to changes in the legislation
of the Russian Federation and the subsequent adjustment of tax planning procedures.
6)
The principle of clarity and validity - is the economic and legal
justification, and clear scheme procedure of tax planning.
Tax
planning for budgetary institutions should be based on the following rules [2]:
1)
The study and use of all kinds of benefits and tax exemptions in the
implementation of budget institutions.
2)
The study and application of special tax regimes.
3)
Development of accounting policy with all the features of taxation of budgetary
institutions.
4)
Control over timely payment of taxes.
The
process of tax planning can be divided into several stages. To start with it is
advisable to analyze the objects of taxation, study their specifics and
possible preferential terms.
The
next step is to evaluate the tax risks associated with the use of tax
incentives.
The
final step is to monitor the implementation of the tax budget. To evaluate the
effectiveness of tax planning.
In
his article, Ovchinnikov IV leads the algorithm implementation of tax planning
in the budget institutions (Figure 1). [5]
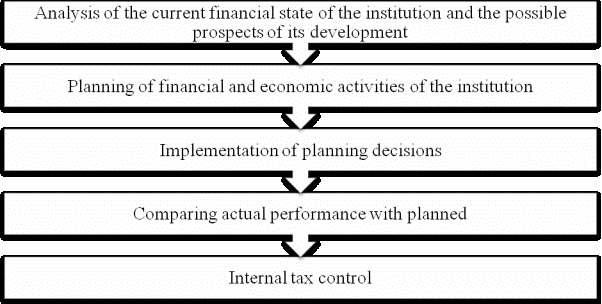
Fig.
1. Algorithm for tax planning in budgetary institutions
Tax
planning in budgetary institutions - a system of tax administration in the
budget process using the optimum legal tax methods and techniques to reduce tax
liabilities.
Thus,
tax planning has an impact on the effectiveness of the non-profit organization,
to optimize cash flow, liquidity and financial liquidity.
References
1.
Tax Code of the Russian Federation of July 31, 1998 № 146-FZ (in the action.
Ed.).
2.
Federal Law "On non-profit organizations" of 12.01.1996 №7-FZ (in
red. On 07.13.2015).
3.
Barulin SV, EA Ermakova, VV Stepanenko Tax management / Tutorial. -
"Omega-L". - 2007.
4.
Bryzgalin AV Golovkin A. Complex operations and transactions: taxation and
accounting (part one). - "Tax and Financial Law." - 2010.
5.
Ovchinnikov IV, especially financial planning in the state educational
institutions of higher education / Collected materials of the international
economic forum "Socio - economic problems of old industrial
materials." - KuzGTU, Kemerovo. - 2015.