Строительство
Совершенствование
экспериментально-лабораторной базы исследования сцепления
бетона с опалубкой
Жайлаубеков Алмас
Шариханулы
Студент-магистрант 2
курс
Казахский национальный технический университет имени К.И. Сатпаева,
г.Алматы, Республика Казахстан
E-mail: almaszhailaubekov@mail.ru
a
candidate for a Master's degree Zhailaubekov A.Sh.
Kazakh National Technical Univercity after K.I. Satpayev
Almaty, Republic of Kazakhstan
E-mail: almaszhailaubekov@mail.ru
Improvement
of experimental and laboratory research base of concrete adhesion with
formwork.
ABSTRACT.
In this article from the standpoint of
manufacturability, cost and complexity of pilot plants presented allowing for
experimental studies of different types of lubricants, in order to identify and
reduce the adhesion of least effort vouchers, including at low temperatures.
Keywords.
Designing pilot plants, concrete formwork adhesion,
adhesion and cohesion of the concrete, the plane of contact with the concrete
formwork, breakout force when removing the formwork.
From an economic point of view, the complex process of
monolithic construction of basic structures, is the dominant method of
construction, as it requires considerably lower energy consumption, consumption
of concrete and formwork, and as a result, more than 15% lower financial costs.
The most time-consuming technological conversion there are formwork. Their
labor intensity varies from 40 to 55% of the total labor input, and the cost is
estimated at 30-45%, respectively. For every cubic meter of monolithic
structures necessary to install and remove from 3.0 to 8.0, and in thin-walled
structures to 12.0 m2 of formwork. Application of lubricants inefficient
shuttering or general application, as often happens in practice that increases
complexity demolding 70-100%, while because of the high clutch Stripping large
effort and mechanical action on the formwork at its purification 70% of
premature formwork building and faces after stripping require mnogozatratnoy
posleraspalubochnoy finishing. It is worth noting that the work is aimed at
addressing the potential of reducing the cost of stripping and improving the
quality of construction can not be relevant.
In this connection, the problem of underestimating the
importance of technological operation lubrication on the formwork, attributing
it to the category of minor, and sometimes unnecessary, (the period of contact
with the concrete formwork creates favorable conditions for the manifestation
of the clutch) and the predetermined goal of theoretical and experimental
studies of the influence of adhesive and cohesive properties of the concrete
formwork with the forming surface during its removal.
Based on the above, it sets the main goal - the
determination of indicators affecting the construction of monolithic high-rise
buildings, with step by step solution to the underlying problem of the design
of experimental facilities for future studies grip concrete formwork.
The authors have designed and prepared for the
experimental setup in experimenting pioneer (Figure 1) intended for holding the
samples in specific conditions of real structures, allowing for experimental
studies of various types of lubricants in order to identify and reduce adhesion
least vouchers effort, including greases used in zero temperatures:
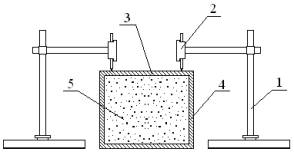
The experimental apparatus №1 consists
of two side fastened together tayrotami and two face sheets of plywood deck
pretreated with inner surfaces, various types of lubricants. The main elements
of the module and are loading devices, guide blocks, the site of attachment,
traction ropes and measuring the load.
The experimental
apparatus №1
251658240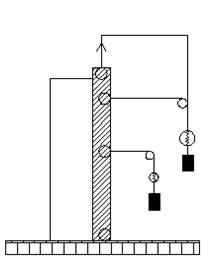
To measure the shrinkage humid offered special unit
number 2, where linear (three-dimensional) deformation of concrete is
determined using dial gauges. To this end, during vibration of the concrete in
the form of a 10cm edge on the surface of the plate stacked polished aluminum
1mm thick. Deformation of each sample was determined by two dial gauges every
4h in the first day from mixing with the mixture, and then twice a day for 14
days.
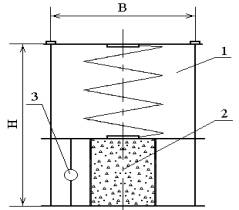
In the case study species expanding
concrete be used in an experimental setting number 4 is a torque jig,
consisting of three cross-pieces - the lower, middle and upper interconnected
rods which serve to support the spring, which creates a strain related linear
expansion of concrete. Measurements of strain as a result of expansion of the
concrete produced in the conductor set a dial indicator. To produce the samples
used cylinders GOST 10180 D = 71,4 mm, h = 143 mm. After dialing the stripping
strength of a sample of extruded through a die cylinder on the press with
metering in special place pull force.
|
The experimental apparatus № 2 251658240 1-stand; 2 - indicator of hour type ; 3-aluminum plate; 4-metallic form; 5 – concrete. |
The experimental apparatus № 3
2-
cylinder; 3- indicator. |
The experimental apparatus № 4
251658240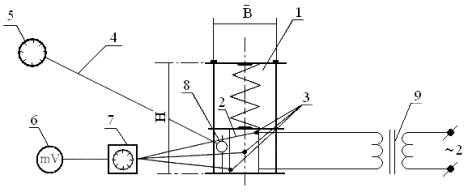
1 – dynamometric conductor; 2 - electric cylinder; 3 –
sensors of temperature control in section of sample; 4 – sensot of
temperature control in mode; 5 - potentiometer; 6 -
micro-voltmeter; 7 – ten point switch; 8 - indcator; 9 –
laboratory transformer.
In order to simulate the contact heating concrete (for
lubricants used at low temperatures below -s ° C.) Developed an experimental
setting number 4, the prototype of which was the installation № 3. What metal
molds (cylinders) were converted into the electric cylinder (by winding the
layer of asbestos spiraling output 350B, which in turn is protected by a second
layer of asbestos). The specified temperature and humidity conditions of
keeping the samples were maintained test equipment. The sensors monitor the
temperature of the regime were Chromel-Copel thermocouple fastened on the deck
of cylinders.
The advantage of these methods for
determining strain detachable effort strength and methods of holding the
samples, in addition to simplicity lies also in the fact that the samples in
the required amount may be in the conditions of curing concrete structures,
thus providing a real picture of the material.