Doctor of Technical
Sciences, professor Omirserik Zhortuylov
Kazakh
National Agrarian University, Kazakhstan
Master of Agricultural
Sciences Aizhan Sarsembayeva, Zhambyl Duisebayev
Taraz
State University named after M.Kh.Dulati , Kazakhstan
WAYS OF IMPROVEMENT PICK
UP MECHANISMS OF HARVESTING MACHINE
One of the many important decisions made
by forage and livestock producers in selection of a forage-handling system. The
system must be geared to meet needs of the current operation. Just as
important, however, is that it must also match future plans. To make this
decision intelligently, a number of questions must be asked and the proper
information must be obtained in order to analyze each of the alternatives. The
number of possible alternatives may be reduced by carefully considering the
needs of a particular operation. Two factors are crucial in planning : Will the
system provide the proper quality in the stored feeds? Does it match the labor
and capital resources available on the ranch or farm?
Balers have evolved from stationary
machines when they were first introduced in the last part of the 19th
century to highly mobile machines of today. These first stationary balers
produced bales of low density consisting of a series of compressed flakes.
Initially, bales were rectangular, of varying lengths and density, but of a
size a man could handle. Round balers were later introduced, followed by large
rectangular balers. Balers in common use today in the United States form bales
that are one of the following types: small rectangular, large rectangular,
small round, and large round[1].
One of the most
promising technologies to mechanize complex forage is cleaning round baler.
With balers can make hay, silage, straw, flax and hemp, and with the use of
units for hermetic packaging rolls in plastic film, silage [2].
Storing silage in wrapped bales is a very
popular technique in many countries (Wilkinson &Toivonen, 2003) since it
offers advantages over hay production, such as a more flexible harvest date,
less weather dependency, and a greater flexibility in ration formulation
(Savoie&Jofriet, 2003; Shinners, Huenink, Muck, & Albrecht, 2009a).
Bale silage making is based on a well-established procedure that usually
consists of wilting forage up to 600 g dry matter (DM) kg1, baling and then
wrapping it with 4e6 layers of a stretch polyethylene film. Compared to silage
stored in horizontal silos the bale silage technique is particularly prone to
spoilage, and because of the proximity of most of the silage to the plastic
film and the thinness of the film, the threat to the oxygen barrier is much
greater than with conventional silage (Forristal&O’Kiely, 2005). Recently,
the stretch polyethylene wrapping system has shown some limits with regards to
sealing efficiency (Jacobsson, Lingvall, &Jacobsson, 2002); notably the
high permeability to oxygen of the stretch film (Borreani &Tabacco,2008;
2010), and the non-uniform distributionof the plasticfilm between the ends and
the curved surface of the bale (Borreani, Bisaglia, & Tabacco, 2007). These
problems have lead to undesirable air exchange over the conservation period and
has been suggested that an increasing number of plastic film layers are
required. Increasing the number of film layers from four to six, or even eight,
often improves the airtightness of the bale coverage and can improve silage
conservation quality by reducing mould development (Borreani & Tabacco,
2008; Mu¨ ller, 2005), but it can involve prohibitive increases in costs
and plastic usage and also increases in working time. There are also
environmental concerns over the disposal of the additional plastic (Lingvall,
1995). Tying bales with netting has become the usual procedure instead of twine
tying (Shinners, Huenink, Muck, & Albrecht, 2009b; Taylor, 1995), but this
does not provide any sealing effect when preparing round bales for making
silage (Harrigan&Rotz, 1994). The commercial availability of round balers
equipped with film-tying attachments, suggests the possibility of replacing the
standard net-tying system with a film-tying system, in order to improve the
airtightness of the coverage on the bale curved surface (Bisaglia, Borreani,
& Tabacco, 2007)[3].
Increased
productivity may forage machines by increasing machine speed and width pick-up.
Performance balers also depends on the work of the pick mechanism. For the
selection of rolls of grass, hay, straw and grain mass used balers: drum
Managed fingers and fixed cover; drum driven fingers and rotating shroud, or
slatted chain- slatted with articulated or rigid mounting brackets.
In forage
machines: the pick- grinder, roll baler, truck - pick- used drum driven fingers
and fixed cover.
Drum Wagons
Managed fingers pick plants spring fingers 1 fixed to the tubular shaft 2
(Figure 1a). Tubular shafts pivotally connected with the disc mounted on the
shaft of the pick 3. On one side end of the tubular shaft 4 has a crank with a
roller that moves along a guide track 5. Profile track provides the trajectory
of finger movement, in which there is no pulling gleaned mass gap in the
housing (ring - skates) 6 [4].
Quality of work
is determined by the purity of the pick roll selection, continuous and uniform
crop flow for the next working bodies, free from the weight of the output
fingers without pulling it under the drum and minimal impact on power plants in
the selection. Pick-up width is always greater than the width of the roll.
Scientists
designers and specialists of the CIS, the results of theoretical experimental
studies justified values of the optimal design parameters drum
picker (width, diameter of the rings - rays, fingers fly over the ring - ramps
, step of their placement ) . Determine the impact of spring fingers on the
plant in the selection of rolls of alfalfa, wheat grass, herbs and spring wheat
[5, 6].
Selection with minimal losses shall be subject to the conditions [5]:
![]() (1)
(1)
Where![]() - the height of the
roll, m;
- the height of the
roll, m;
![]() - crest height in meters;
- crest height in meters;
![]() - the minimum gap between the ends of the fingers and the
surface of the soil, m.
- the minimum gap between the ends of the fingers and the
surface of the soil, m.
The dependences of establishing the connection between the district and the
translational velocities, the design parameters of the drum picker (![]() ) and height of the
crest
) and height of the
crest ![]() [4]:
[4]:
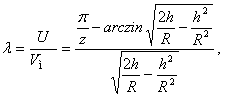 (2)
(2)
Where
![]() - number of tubular shafts pieces;
- number of tubular shafts pieces;
![]() - distance from the
end of the finger to the drum axis.
- distance from the
end of the finger to the drum axis.
Baler works without stripping and immersion
in the roll if the horizontal component of the absolute velocity of the point A
in the middle of serving the housing portion of the finger which is in the
upper position is zero. The relationships District and translational velocity
end of the pin that is in the upper position. [6].
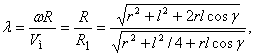 (3)
(3)
Where ![]() - the angular velocity of rotation of the drum, rad / s;
- the angular velocity of rotation of the drum, rad / s;
![]() - distance from the center of the shaft to the end of the
pin, m;
- distance from the center of the shaft to the end of the
pin, m;
![]() - distance from the center axis of the tubular shaft to shaft,
m;
- distance from the center axis of the tubular shaft to shaft,
m;
![]() - the length of the fingers, m;
- the length of the fingers, m;
![]() - the angle of deviation from the radial position of the
finger;
- the angle of deviation from the radial position of the
finger;
![]() - pick-up speed, m / s;
- pick-up speed, m / s;
![]() - distance from the center of the shaft to the middle
finger, m.
- distance from the center of the shaft to the middle
finger, m.
It was established experimentally that
the deflection angles of fingers from the radial direction in the direction
opposite to the rotation![]() , the pick-up work proceeds normally with minimal losses;
wide angle fingers work deteriorates because broken connection with finger
roll. [5]
, the pick-up work proceeds normally with minimal losses;
wide angle fingers work deteriorates because broken connection with finger
roll. [5]
Experience shows that when the
translational velocities 1,6/ 2,7 m / s steady work the pick and minimal crop
losses reached at ![]() [4].
[4].
Free exit of the fingers mass gleaned
without pulling it into the drum is provided when the angle ![]() between the plane of the fingers and the housing is more than
the sum of the angles of friction on the stem pins and shroud.
between the plane of the fingers and the housing is more than
the sum of the angles of friction on the stem pins and shroud.
Desired angle output pins (at least 700)
provided the corresponding profile of the guide track. [4]
Shaft speed pick-determined by the
formula [6]:
![]() QUOTE n=
QUOTE n=![]() M
M![]() hz
hz![]() (4)
(4)
Where ![]() - the crop flow to a single tubular shaft that path traversed
by the pickup during entry or exit of stubble fingers two adjacent tubular
shafts, m. On the basis of long-term operation of existing drum pickers with
spring fingers, the average shaft speed is 107 rev / min at
- the crop flow to a single tubular shaft that path traversed
by the pickup during entry or exit of stubble fingers two adjacent tubular
shafts, m. On the basis of long-term operation of existing drum pickers with
spring fingers, the average shaft speed is 107 rev / min at![]() ;
; ![]() .
.
GSKB in machinery for harvesting crops
and self-propelled chassis (city Taganrog) recommended range of the shaft speed
pick-up within 72-190 rev / min. But, it is recommended not to exceed the speed
of 125 rev / min, as parts wear out quickly pick-up.
Analysis of the main parameters of
pickers CIS and foreign countries has shown that the width of their capture
fluctuate accordingly from 1.4 to 1.6 m and from 1.4 to 2.1 m [7, 8, 9].
Diameters of the rings - ramps up 220 ... 500 mm, number of tines 4 ... 6
units, the distance between the rods fingers from 60 ... 105mm diameter rod
finger 4 ... 6mm, length of spring fingers departure for ring - rays 110...120
mm.
Small width 1.4 ... 1.6m roll - baler CIS
: PR -145 (1.2 m ) Ltd "Buryatfermash ", PR- 400 , PR- 200 (1.5 m )
of " Bezhetskselmash "; PCP -1, 5 (1.5 m) of "Pskovmash" and square balers PT-
165 (1.6 m) KLA GOMSELMASH, PT- 160 (1.6 m) KazNIIMESKH , PPR- 041
"Turkan" (1 , 5 m ) city Morozovsk etc. does not allow qualitatively
pick rolls of hay and straw , formed a broad forage harvester and combine
harvesters. To clean the rollers cleaning requires repeated passage balers.
Although grounded basic parameters drum picker, but the drawback is the
complexity of its design and low reliability.
The complexity of design due to the fact
that one of the sidewalls of the guide track is mounted on a special profile,
which are rolled by rollers mounted on the cranks toolholders.
Low reliability work due to the fact that
when the pick-up on the field in spring fingers pick hay roll and move it over
the surface of the ring - up ramp . In contact with an obstacle the pickup
fingers deformed teeth spring fingers and crushed through rollers and cranks on
the treadmill, and the rollers, rolling on the surface of the guide track with
a speed of the central shaft 70 ... 120 min -1, wearing a track guide surface,
resulting in service to deformation and failure.
In addition, to reduce the deformation
and deterioration of the ground spring fingers practice, the diameter is
increased from 5 to 6 mm. When working harder spring fingers press on the
rollers and the treadmill that wear rapidly, which leads to breakage.
In this connection, to eliminate from the
construction of the pick-up crank, rollers and treadmill KazNIIMESKH first in
the CIS in 1995 developed a pickup mechanism mounted in the pick- grinder [7].
Pick -crusher (Figure 1b) contains: 1 crossmember with 2 brackets that are
running 3 ramps having a concave ring and associated straight section. The drum
located in front of the cross member and consists of discs 4 and 5 of the main
shaft, which is mounted on the holder with spring fingers 6 arranged radially.
Concave portion sloping boards made with a variable radius of
curvature , turning a straight surface. Over the drum between the supply
authority intermediate conveyor machines installed as pressing beater with 7 pins
, rotating in the opposite direction to the rotation of the drum. Test pick-
chopper shown that the absence of the treadmill, cranks and pulleys allowed to
increase the frequency of rotation of the drum by 30% and improve the
performance of the pick-up chopper.
Company «Class» (Germany) - one of the
world leaders in the production of forage machines. Since 1958 she produces
machines for hay, straw and silage, salable in various regions of the planet.
Company «Class» also produces baler press camera with constant volume series
«Rollant». The pressing mechanism - steel rollers located conjugated spiral
roll that increases the strength of [8]. In round baler «Rollant» company
«Class», having no grinding device "Roto - Kat" for pick- installed
units and rotary lever (Figures 1c, 1d). They are actively involved in the
transportation of hay and materials. The straw from the pick- uniform flow into
the bale chamber. In addition, they are transported as short hay and straw
length of the stems or slightly dried herb haylage . Pick-up is reliable, never
clogged compressible material. These units , which are installed only in roll
presses «Rollant», are a prerequisite for high performance in continuous
operation when cleaning any different cultures. Wagons with width 1.80m picked
clean, even wide rolls of hay. With such deep Pick- rolls especially dense
pressed on the outer sides of the bale chamber.
Depending on the model balers «Rollant»
pickups can be equipped with a working width of 1.58 m, 1.80 m or 2.0 m. With such
widths can qualitatively select plants or even straw stacked in roll combine
harvester equipped with a wide header. When large width picker’s special augers
move plants to the width of the baling chamber.
Height-adjustable support wheels baler
have its spring tines above the ground at a distance, when you are going to
virtually all plants without a trace. Shock absorbers provide a smooth ride
over the ground. Double elastic spring fingers pick plants are very clean.
Spring fingers can be easily replaced in case of breakage, as they are fixed to
the carrier profiles individually. Raising and lowering the pick is made
hydraulically from the tractor cab. Given the optimal distance between the
pickup and the ground is set after each lifting - lowering automatically.
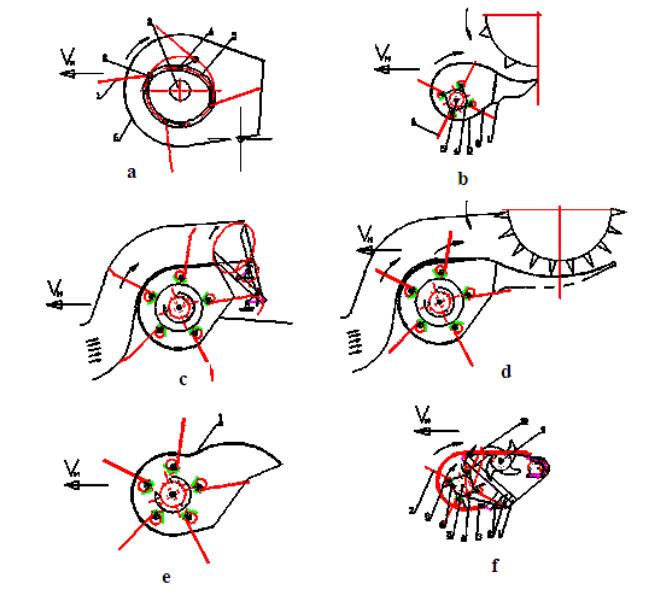
a - with a treadmill, cranks and rollers b -
unmanaged tine equipped beater, c -lever unit mass, d - rotary unit mass, e-
unmanaged tines are fitted with scrapers, f-tine with unmanaged equipped with
feeder masses
Figure - Drum Baler with spring fingers
Round balers firm «Krone» with chain-
slatted conveyor releases since 1977. This technique ensures maximum
performance when compressed hay and silage, as well as ease of maintenance and
service. Wide demand of cars produced today provides leadership firm «Krone» in
many countries. Depending on the type of the press chamber may be compressed
rolls of a diameter of 1.25 m or 1.55 [9].
Company «Krone» first of the
manufacturers put into production with unmanaged pick tine «Easy Flow», which
operates without complicated control mechanism spring fingers. The main
difference between «Easy Flow» is undulating design guillemot 1 (Figure 1e).
This design provides a continuous flow of the cleaning teeth weight when immersed
in close and low location of the receiving authority. Compared to conventional
pickups, shaft speed pick- developed increased by 30 %. Accordingly, the baler
may be aggregated with the higher speed achieving high productivity.
New baler has far fewer moving parts and
operates quietly and smoothly. A little wear and tear requires correspondingly
lower maintenance costs, reduced energy costs, as there are no curved guide
grooves. Large width of 2.15 m is allowed to work baler with large rollers and
without loss of plants during cornering. Serial presser roller provides a
continuous flow of material, even when the uneven rolls. With five tine tine
spacing of 55 mm carry clean selection of rolls. Guide wheels mounted in front
of the pick-up allow pick hay clean even in soft soil [9].
The disadvantage is a reduction in the
reliability of designs picker where the receiving authority is far and its
level exceeds the height and the selection of different types of moisture and
forage plants.
Due to the load being selected before
receiving body mass inevitable happens when loading crumbling and spilling on
the ground sheet of the most nutritious plants and their losses.
To eliminate the load weight between the
drum and the receiving authority, working to improve the contact with different
body mass materials are selected, better preservation of its nutritional value
in KazNIIMESKH designed to drum baler to agricultural harvesting machines [10].
Drum baler has a similar structure, but has the following differences: the
three annular portions skates have constant curvature, but mounted
eccentrically relative to the axis of the drum 5, the holder 6 of the spring
fingers 7 formed as a centrifugal fan blade 8, the intermediate conveyor is
made as a shaft with the impellers 9 and 10, and the guide surface 9 is
described by an Archimedean spiral (Figure 1e).
This pick-up mounted on a round baler PR-
400V baler PT- 160, which passed acceptance tests with the recommendation for
the construction of an experimental batch.
During the trial found that technological
selection of plants is carried out safely and provides reliable transportation
stems of various plant. This eliminates pulling stalks between the fingers and
the impeller blades and the receiving authority, even in excess of the height
of the receiving body and the level of pick-up. They never clog gleaned weight,
which improves performance.
The new design improves the pick shaft
speed by 30%, thereby improving performance balers; spring fingers to set the
pick 6 mm in diameter, increasing their longevity.
Conclusions
While perfecting the pick sweepers
considered theoretical and experimental studies the pickup arrangements. Based
on the analysis of design features and components picker they perform
manufacturing operations (firms «Krone», «Class» (Germany), KazNIIMESKH
(Kazakhstan) prepositional structure must be different mechanisms without the
treadmill , cranks and pulleys.
Company «Krone» first of the
manufacturers put on production pickup with unmanaged tine spring fingers «Easy
Flow». The main difference lies in an undulating design guillemot. Pick has far
fewer moving parts and operates quietly and smoothly. Less wear parts requires
correspondingly lower maintenance costs, reduced energy costs, as there are no
curved guide grooves. This design provides a continuous flow of mass immersion
retractable teeth and near the location of the receiving authority.
Firms «Class» and KazNIIMESKH
proposed sorters equipped units to eliminate load different materials gleaned
mass between the drum and the receiving authority in excess of the height of
the last level and pick-up. They never clog gleaned weight, which improves
performance.
Compared to conventional pickups, shaft
speed pickers developed more by 30%, respectively balers can be aggregated at a
high speed, achieving high productivity.
Pick-up width CIS exceed the swath width
of not less than 200 mm and shall be 1.6 ... 2.1 m.
List of used literature
1.
R. Dwain Horrocks, John
F. Vallentine.
Forage-Harvesting Equipment.
Harvested Forages, 1999, Pages 293-314.
2. Ñîëîâüåâà Í.Ä.
Îñîáåííîñòè êîíñòðóêöèè çàðóáåæíûõ ðóëîííûõ ïðåññ-ïîäáîðùèêîâ. //Òðàêòîðû è
ñåëüñêîõîçÿéñòâåííûå ìàøèíû.– 2002.– ¹2.– Ñ. 37-38.
3.
C. Bisaglia, E. Tabacco, G.
Borreani.The use of plastic film instead of netting when tying round bales for
wrapped baled silage. Biosystems Engineering, Volume 108, Issue 1, January
2011, Pages 1-8.
4. Ñåëüñêîõîçÿéñòâåííûå è
ìåëèîðàòèâíûå ìàøèíû / ïîä.îáù.ðåä. Ã.Å. Ëèñòîïàäà.– Ì: .Êîëîñ, 1976.–
Ñ.156-157.
5. Êëåíèí Í.È., Ïîïîâ È.Ô.,
Ñàêóí Â.À. Ñåëüñêîõîçÿéñòâåííûå ìàøèíû.– Ì.: Êîëîñ, 1970.– Ñ. 255-259.
6. Òåîðèÿ êîíñòðóêöèè è
ðàñ÷åò ñåëüñêîõîçÿéñòâåííûõ ìàøèí /ïîä.ðåä Å.Ñ.Áàñîãî.– Ì: Ìàøèíîñòðîåíèå,
1978.– Ñ.322-326.
7. Ïàò.9472 Ðåñïóáëèêà Êàçàõñòàí, ÌÏÊ7 À01D 89/00, 43/08, À01F29/00, 29/06.
Ïîäáîðùèê-èçìåëü÷èòåëü /Әá³ëæàíұëû Ò.;
Ñåèòáåêîâ Ë.Ñ.; Ðçàëèåâ À.Ñ.; Ëîêøèí À.Ë.; Æîðòóûëîâ Ө.; çàÿâèòåëü è
ïàòåíòîîáëàäàòåëü ÊàçÍÈÈÌÝÑÕ.–çàÿâë. 07.04.9; îïóáë.16.10.2000, Áþë.¹ 10.
8. Ðóëîííûå ïðåññ-ïîäáîðùèêè:
ïðîñïåêò ôèðìû «Class».
9. Ðóëîííûå
ïðåññ-ïîäáîðùèêè: ïðîñïåêò ôèðìû «Krone».
10. Èííîâàöèîííûé ïàò. 24471
Êàçàõñòàí, ÌÏÊ À01D 89/00, À01Ä 90 /00, A01F 15/10, À01F17/02. Áàðàáàííûé ïîäáîðùèê ê óáîðî÷íûì
ñåëüñêîõîçÿéñòâåííûì ìàøèíàì /:Æîðòóûëîâ Î.; Åâòèôååâ À.Ã.; Àëåêñååê À.À.;
Ñîëäàòîâ Â.Ò.; Àáèëæàíóëû Ò.; Áåêåíîâ Ó.Å.; Ñìàãóëîâ Ò.À.; çàÿâèòåëü è
ïàòåíòîîáëàäàòåëü ÊàçÍÈÈÌÝÑÕ .–2010/1371.1; çàÿâë.08.11.2010; îïóáë.15.09.2011,
Áþë.¹9.