The honored science and education member of the RANS,
corresponding-member of the IAS of HS, Dr.S. (eng.). Professor, Pil E.A. Russia, Saint-Petersburg,
Saint-Petersburg State Marine Technical University
Classification of evolution of variables et
and pt
Economic
growth or recession are affected by a large number of factors one of which is
growth or decrease in population for objective reasons. In order to find out
the interconnection between theoretical economic growth or recession et and theoretical growth or decrease in
population pt respectively, we developed special Table, where
possible variants of interconnection of variables et
and pt in question
are presented. In this work and for our case the word economy will be
understood as GDP in the country in question.
As a result of
the analysis of the whole Table the presented dependences of variables et
and pt can be for
our purpose divided into the following 23 types:
1. et and pt
nonintersecting lines;
2. et and pt
intersecting lines;
3. et and pt
nonintersecting line and curve;
4. et and pt
nonintersecting lines;
5. et and pt
intersecting lines;
6. et and pt
nonintersecting line and curve ;
7.
et and pt nonintersecting lines changing into a curve
and curves;
8. et and pt
intersecting line and curve;
9. et and pt
nonintersecting curves changing into lines;
10. et and pt
nonintersecting curves;
11. et and pt
nonintersecting curves symmetrical in relation to one axis parallel to axis Qt as with same Tptmax = Tetmax
and Tptmin = Tetmin values, so with
different Tetmin, Tptmin, Tetmax and
Tptmax values;
12. et and pt
nonintersecting curves symmetrical in relation to two axes parallel to axes Qt
and t;
13. et and pt
curves intersecting in one point;
14. et and pt
curves intersecting in two points;
15. et and pt
tangent line and curve;
16. et and pt
tangent curves;
17. et and pt
tangent curves symmetrical in relation to axis parallel to axis Qt
;
18. et and pt
tangent curves symmetrical in relation to axis parallel to axis t and symmetrical in relation to axes t и Qt ;
19.
et and pt joining lines;
20.
et and pt joining curves;
21.
et and pt curves changing into
joining lines ;
22.
et and pt joining lines
changing into diverging curves;
23.
et and pt joining and diverging curves.
Using the calculations which were
made we developed a classification of dependences of variables et
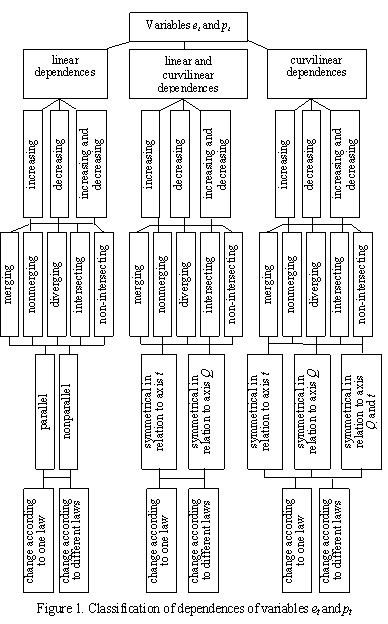
and pt, which is shown in Figure 1. As
we can see on Figure 1, variables et and pt
can be divided into three classes: the linear dependence class, the linear and
curvilinear dependence class and the curvilinear dependence class. These
classes in their turn are divided into three subclasses: increasing,
decreasing, and increasing and decreasing. The subclasses are divided into the
following five kinds: merging, nonmerging, diverging, etc. These kinds
themselves are divided into five subkinds depending on the kind in question,
such as: parallel, nonparallel, etc. On the last level variables et
and pt are divided into two types depending on the law or
laws according to which they change.
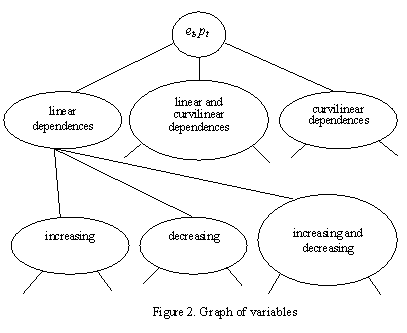
The
classification shown in Figure 1 can be represented as the graph shown in Figure 2, where the graph’s peaks are linear, curvilinear dependences or their
combinations, which can go up or down, be symmetrical, etc., and the branches
are their characteristics. Thus, the better we know the parameters of peak
branch characteristics, the easier it is to make right conclusions while
analyzing the economic state of a country and its population.
This classification allows us to
quickly relate specific variables et and pt
in question to their class, subclass, etc.