Engineering / Automated control systems in manufacturing
1MN Mukhtarova, 2RB Akhmetkaliev, 1AK Danlybayeva, 1AK Sariyeva, 1EM Zulbukharova
1Al-Farabi Kazakh National University, Kazakhstan Republic
2Almaty University
of Power Engineering and Telecommunications, Almaty, Kazakhstan Republic
Structure
of the technological complex
The mobile technological complex consists of three
main principally new devices : a rotary hydraulic (hydrodynamic) mill (RGDM), a
multicommodity multi-product hydrocluster (CIM) and centrifugal concentrators
(CCC).
The hydrodynamic mill (MHD) is a kind of rotary
hydraulic cavitation mill, designed for finely grinding various materials of
any strength and abrasiveness. The mill can provide grinding of granular
material to a size of 0.1 microns (a characteristic feature - the thinner the
grinding of the raw material is required, the more effectively the hydrodynamic
mill operates), and also for mixing various liquids, liquids with gas and solid
materials.
Experimental-industrial tests of a mill with a
productivity of ~ 100 t / h have confirmed the high efficiency of grinding. At
the same time, it became necessary to increase the wear resistance of the mill
units. This problem was solved by the method of electropulse hardening of the
working surfaces of the mill and the use of special polymeric and metallic
nanopowder materials.
The technical and economic comparison of the rotary
hydraulic cavitation mill (RHCM) with serially produced domestic and foreign
vibro-ball mills indicates that the rotary hydraulic mill with the same degree
of grinding is almost five times less than the energy consumed per 1 ton of the
raw material . Its mass is 30-90 times, and its dimensions are 7-10 times
smaller than in the best vibro-ball mills. In addition, the new mill easily
fits into the technological line for hydraulic processing of granular
materials, since it can suck in and pump up the original pulp to a height of up
to 20 m or more.
Multicommodity shelf hydroclassifier (CGS) provides
effective separation of various granular materials at any size and density,
including fine particles, as well as productive and quality enrichment and
separation of such materials by fractions with different granulometric and
chemical compositions of the incoming slurry.
As a result of studying the process of precipitation
of suspended grains of minerals in laminar flows, it was possible to separate
fine-grained materials with relatively high accuracy, and also to brighten the
polluted waters.
The dependence of the distribution of various
components of the slurry (noble and heavy metal ores, mercury-containing
components, and other toxic products) on the zones of MGC is established. The
distribution is determined by calculation, allowing to establish a qualitative-quantitative
plot of precipitation of various components in different zones of multi-product
hydroclassifier.
The enlarged characteristics of shelf
thickeners-hydroclassifiers of different firms are given in Table. 2.
Advantages of a shelf thickener-thickener: own weight and production cost are
reduced by 1.7-2.0 times, and the simplicity of the design allows it to be
manufactured in small workshops. The latter is achieved due to the transverse
(horizontal) flow direction in the interlam space, when the liquid phase of the
pulp-flows perpendicular to the direction of the sediment movement.
Table. 2
Comparative data of shelf thickeners of hydroassifiers
|
Characteristic, indicator |
Form-developer (manufacturer) |
|||
|
Ecoresources Hydrotechnics |
Uralmashobr |
Research Institute Hydromechanism |
Denver (USA) |
|
|
Output by initial pulp, m3 / h |
165 |
165 |
165 |
165 |
|
Total mass, t |
12.0 |
24.0 |
28.0 |
23.5 |
|
Overall height, m |
3.0 |
6.0 |
9.0 |
11.1 |
|
Cost of production, thousand rubles. |
400 |
780 |
840 |
1600 |
|
Laminarization of the flow
(liquidation of the counterflow) |
stream
laminarity |
missing |
missing |
stream
laminarity |
|
Flow direction |
horizontal |
vertical |
vertical |
combo |
The horizontal arrangement of the thickener with
several bunker discharges of condensed products compared to vertical
single-bunker designs of shelf thickeners made it possible to reduce the
overall overall height of the apparatus by 1.5-2 or more times.
Centrifugal concentrator gives off heavy metals, incl.
And mercury containing, as well as gold and platinoids from technogenic wastes
(tailings) of concentrating plants. With this method, extraction of heavy
metals, incl. Mercury-containing and precious metals, from tailings will be
95-99%. After the recovery of heavy metals, it is possible to use waste as
building materials and, in particular, as a backing material for underground
mining. Land that has been freed from the tailings, after reclamation, can be
used for farmland, construction and other areas of economic development.
The proposed technology makes it possible to use
environmentally friendly solvents for the transfer of precious metals into the
ionic form and to extract them on selective ion-exchange filters having a fiber
base. It is also promising to use ceramic filters.
The proposed technological complex and the equipment
included in it have no analogues in the world practice of hydraulic processing
of granular materials due to their efficiency, low material intensity and cost.
The novelty of technical solutions is protected by more than ten author's
certificates of inventions and patents.
The technological complex works as follows (ðèñ.1): waste (tails) from the tailings (tailing dump)
are transported (2) by road (3) to the receiving hopper through the grate
screen, which releases inclusions of fineness +50 mm. Sand from the bunker with
the help of a belt feeder and a tray (4) is fed to the vibrating screen (6),
mounted above the sump (7). Pulp preparation is carried out by supplying
technical water to a tray, a vibrating screen and a sump in a volume of 3-4 m3
/ t of the starting product. The oversized product of the vibrating screen (+2
mm ... 50 mm) is fed by a conveyor (5) belt to the storage area, and the
sub-product (-2 mm ... +0 mm) from the sump in the form of a slurry flows
through the suction nozzle into the cavitation hydrodynamic rotor mill (8).
Here, grinding (dispersing) occurs, the disclosure of fine-grained materials
due to high-intensity hydrodynamic impacts and cavitation.
![]()
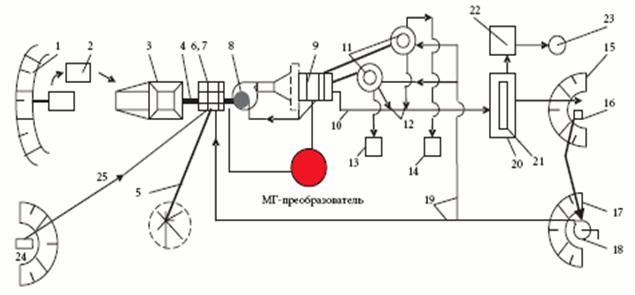
Fig. 1 Diagram of connections of devices of an autonomous mobile
technological complex for processing and utilization of technogenic and
natural-technogenic deposits
The destruction of the intergrowths of the minerals of
heavy metals (Cu, Zn, Pb, Kd, Se, etc.) in noble metals (gold,
platinum, palladium, silver) with quartz and other minerals occurs on weaker
metal contacts with nonmetals Effect of Rebinder),
which to a large extent facilitates the removal from the tails of RP of
mercury, heavy metal toxins and precious metals.
From the mill, the pulp is sent to multi-product
hydrocracker (MGC) (9), where the stream is laminated in a labyrinth of
parallel plates and is divided into fractions characterized by the density and
granulometric composition of the granular material that settle on inclined
surfaces made of special material (lamellas). The fractions (+0.2 mm ... 2.0
mm) are separated in the first compartment of the hydroclassifier, which are
sent to a hydrodynamic mill for re-grinding by a vibrating screen (6). In
subsequent sections, minerals, heavy metals, mercury, harmful components are
released, Cu, Zn, Pb and others.
In the lower storage chambers of MGC (9), precious metals and heavy metals, as
well as other ores, are enriched to a concentration of 10 times or more from
the initial (1st stage). Further (up to 80%), most of the pulp with dissolved
toxins, radionuclides and other fine dispersible harmful inclusions through the
drain pipe of the hydroclassifier is sent to the thin-layer settler (20). From
the accumulating lower chambers of the hydroclassifier, the enriched slurry of
minerals is sent to the second stage of
enrichment in concentrators (11), in which the degree of concentration
of metals increases by 2-3 orders of magnitude (for example, 2-3 kg / t of the
starting product in gold with an annual concentrate output of 8-20 Tons).
From the concentrators (11), the bulk of the pulp in
the form of an obsolete product, the yield of which is more than 90%, with the
toxins and radionuclides dissolved in it through the fixed drainage boxes and
the waste pulpwood (10) is sent to the thin-layer settler (20) with the
coagulator (21). In the settling tank the slurry with finely dispersed
particles (less than 5-40 microns) is condensed with the help of coagulator to
the state T: Æ = 1: 1. The condensed fine suspension with demilitarized
products sent to the storage card – blade (15), which has a dumping well (16).
Clarified water with dissolved toxins and radionuclides is sent to the
radionuclide and toxin (22) release unit, after which they are sent to the
respective disposal facilities of radioactive waste and toxins (23). Purified
from fine particles and harmful impurities, the technical water from the well
enters the sedimentation pond (17), from where it comes from a circulating
water pump (18).
Bibliography
1.
Latyshev, P. N.
Directory CAD. Programs and manufacturers: Catalogue edition. — Moscow: publishing
house of SOLON-PRESS, 2006, 2008, 2011. — 608, 702, 736 S. — ISBN
5-98003-276-2, 978-5-91359-032-9, 978-5-91359-101-2.
2.
Muromtsev Yu.
l., Muromtsev D. Yu., Tyurin I. V., etc. Information technology in the design
of electronic equipment: proc. a manual for students. ouch. uchebn.
institutions. — M.: Publishing center "Akademiya", 2010. — 384 p. —
ISBN 978-5-7695-6256-3.
3.
Norenkov I. P.
fundamentals of CAD: proc. for higher education institutions. — 4-e Izd., Rev.
and extra — M.: Izd-vo MGTU im. N. E. Bauman, 2009. — 430 p. — ISBN
978-5-7038-3275-2.
4.
Norenkov I. P.
computer-aided design. Tutorial. — M.: Izd-vo MGTU im. N. E. Bauman, 2000. —
188 p