Undergraduate Kaldybaev Ò.S.,
c.ò.s., professor RÀS Kolesnikov À.S.,
PhD doctor Zhakipbayev B. E., c.t.s. Kocherov Ye.N., master
Estauova À.À., master Êulmahanova À.N., master Besbaeva N.À., master Àykenova S.Zh.,
master Shegenova G.Ê., master Êàsimova Zh.Zh., student Ayazbekov M.
A study
of aluminum-containing accelerators used for Torbert concreting
At the present time when carrying out concrete work, which require quick
setting and hardening concrete and mortar additives are put accelerators of setting
and hardening. Instead of alkaline additives are increasingly used supplements
boosters that do not contain compounds of alkali metals, with the purpose of
increasing the strength at the later stages of hardening and resistance of
concrete to internal corrosion caused by the interaction of alkalis with
aggregate and thereby increase the durability of structures made of concrete.
Of particular importance supplements boosters have sprayed concreting when the
concrete mix with the concrete spraying machine is supplied under pressure and
compacted under the action of impact. In shotcrete adhesion of concrete or
mortar mix should occur within seconds. As alkali-free accelerators are the
most used aluminium compound is a finely dispersed amorphous modification of
hydroxides and oxides of aluminum, aqueous solutions of sulfates and
hydroxocuprate aluminum. High reactivity of these additives in cement paste
caused by intensive education in the interaction with components of the test
vysokoplotnogo hydrosulphate-minata calcium 3CaO∙Al2O3∙3CaSO4∙32H2O
(ettringite phase).
The rotor is a high - tech way of concrete, which are nowadays solved
various tasks in the construction industry, mining, agriculture. Invented in
the early XX century in the USA, this mechanized method of laying concrete
quickly spread worldwide [1,2]. The rotor allows you to perform special, a
particularly challenging work such as tunnel driving, fastening the coastal
slopes, the device shaft lining and many others. With more than 90% of the
total use of concretestone have to mount mine
workings [2]. The use of this technology in Kazakhstan has received active
development in recent years is that associated with the construction of sports
facilities in Almaty and Astana for holding the Asian games, the development of
the metro. To build infrastructure in the mountainous terrain necessitated the
construction of long transport tunnels.
In shotcrete, the concrete mixture using a
special device (shotcrete machine)is applied to the
surface under pressure and compacted by the impact energy [2]. Layers of Torreblanca, in some cases reaching a thickness of more
than 25cm, and must quickly gain a firm foothold on rough vertical surfaces,
the vaults of tunnels, mines, hard to reach areas and components of the
equipment. In addition, when spraying should be provided with minimum rebound
of the concrete mix. The rotor may be "dry" or "wet"
methods [3-4]. During the "dry" shotcrete
at the nozzle of the gunning apparatus with compressed air is a dry mixture of
components (aggregate, cement, powdery additives), where it is mixed with water
or an aqueous solution of additives and then discharged onto the surface. When
wet spraying in the nozzle of the gunning apparatus is supplied ready concrete
mixture, compressed air and a solution of additives (figure 1).
a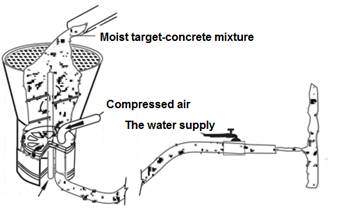
b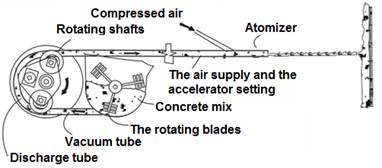
Figure
1 – is a Conventional diagram of the installation for the preparation of
sprayed concrete in the dry (a) wet and (b) methods of production [5].
With its advantages of wet shotcrete method to date, is
most prevalent, especially when performing major works.
As subjects of the study selected highly dispersed
amorphous aluminum hydroxides, one of which is a product of Russian manufacturer (JSC "Boksitogorsky alumina") of AmGA,
another product of the company "Industrias Químicas del Ebro"
(Spain) Geloxal. Chemical composition of aluminum hydroxides according to the
manufacturers is presented in table 2.
Table
2–Chemical composition of aluminum hydroxides
|
¹ Number of indicator |
Íàèìåíîâàíèå ïîêàçàòåëåé |
Name of indicators |
Geloxal |
ÀmGÀ |
|
1. |
Mass fraction of Ñl- |
% by weight. |
not more than 0,5 |
– |
|
2. |
Mass fraction of SO42- |
% by weight. |
not more than 2 |
– |
|
3. |
Mass fraction of SiO2 |
% by weight. |
– |
0,16 |
|
4. |
Mass fraction of Na2O |
% by weight. |
not more than 1 |
0,15 |
|
5. |
Mass fraction of Al2O3 |
% by weight. |
50 |
50 |
Thus,
the requirements of modern accelerators for shotcrete
are not only in the fact that at a moderate cost, they provided almost
immediate grasp of the concrete mix and quick set early strength, but also in
the fact that they do not adversely affect the properties of concrete in
adulthood and did not serve the cause of reduction of its durability.
Bibliography
1.
Yoggy,
G.D. The history of shotcrete / Shotcrete.
2005 (Summer). P. 26–32.
2.
Melbye,
T. Sprayed concrete for rock support / Garshol – MBT
International Underground Construction Group, Division of MBT: Switzerland-
2001. -247 pp.
3.
EFNARC (1999) – Guidelines for Specifiers and Contractors: UK- 1996. – 35 pp.
4.
William, D. Brown. Standard practice
for shotcrete. Engineer Manual No. 1110–2–2005.
Washington – 1993 – 49 pp.
5.
American Concrete Institute ACI
506R–90: Guide to Durable Concrete. Farmington Hills. –1995. – 41 pp.