History \2. General history.
Vyrezkova
A. V.
Irkutsk
National Research Technical University
Theory of development of town planning
Since ancient times people learned to build the dwelling. The
surrounding district was rich natural materials which people used. A lot of
houses formed the city.
For defense against enemies cites were enclosed
walls. Therefore the Russian word "city" originally meant
"strengthening". Planning and a city building is one of architecture
areas, it received the name "town planning".
Planning
of the cities of Antiquity, the Middle Ages, Renaissance, the Old Russian
cities had many differences. For example special type of a
state system of Ancient Greece — the policy. It was represented by the
city-state which reflected special outlook of Greeks. The person citizen was
considered as the supreme value in Ancient Greece. The ancient Greek cities had
irregular, free planning. It submitted to a natural land relief. The majority
of the cities settled down on the sea coast at a mountain foot, and rose uphill
sometimes. Rigid planning grids of the antique cities fitted into the difficult
coastline, without breaking picturesqueness of building.
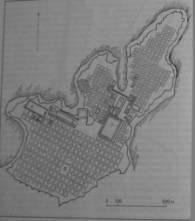
Pic. 1. The
policy.
In Antiquity on the
strong hill built the temple complex. However the biggest and the best-known of
all cities of Ancient Greece — Athens — has not a regular plan.
Planning of the
cities of Ancient Rome goes back to the structure of military camp. The characteristic rectangular
grid of quarters of the small cities was cut by perpendicular streets:
"kardo", laid from the North to the South, and "decumanus",
conducting with the West to the East.
The medieval cities
differed in the high density of building, the small population and the small
sizes which were caused by need as much as possible to reduce perimeter of defensive
city walls. Each medieval city was protected with mighty stone walls with teeth
and towers. The city had defensive value, and to seize its gate meant to seize
all city.
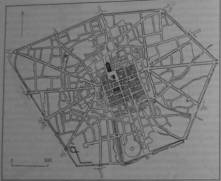
Pic. 2. The
medieval city.
Use of
historically developing radial and ring planning system was the most
outstanding achievement of medieval town-planning art. The medieval cities
differed in an art harmony, and even ordinary building possessed high esthetic
value.
Architects
of the Renaissance were skillfully arranged to made their predecessors. They
not only broadened the medieval cities, but also put forward ideas of
improvement of separate elements of their internal device.
The cathedral was the center of the West European city. Office building
of a town hall and market square were located nearby. Streets were located at
an angle to city gate. The feudal castle settled down outside the city limits.
Unlike the West European city which was concluded in the high stone
walls, the city of medieval Russia was merged with the nature and a rural
environment. The important role in a place choice for future city was played by
esthetic preference of people. The city usually grew on a sublime place. The
central place in its composition was
occupied by detinets (it was Kremlin). It was an internal kernel of city. In
the Kremlin the biggest, monumental constructions — a cathedral and the palace
were concentrated.
Architects of baroque created
large-scale, solemn city ensembles. They sought for spatial association of
interiors of buildings, streets and areas. In Renaissance there were works about the ideal
cities.
The Old Russian cities as the plan were subdivided on round,
semicircular, segment, and sector. Generally they had three-part structure:
fortress, bargaining, posad. Over time it got a circular form.
The theory of town planning passed a long way of transformations. It
developed consistently and logically.
Reference list:
3.Yargina Z. N. "Bases of the theory of town
planning"