Master student Tsyplakova D.D., Professor Ushakov I.V., Ph.D.
Dyakov I.A.
Tambov State Technical University, Russia
THE METHOD OF COMPUTING SHORT-CIRCUIT CURRENTS
Short-circuit (SC) is
any unintended normal operating conditions, circuit between phases, and in
systems with earthed neutral (or four) as the closure of one or more phases on
the ground (or neutral).
To select the devices
and conductors, to determine the effect on the load-bearing structures in the
calculation of short circuit currents based on the following provisions: all
the sources that feed the point under consideration, working with rated load;
synchronous machines have automatic voltage regulators and high-speed devices
forcing excitation; fault occurs at the time point when the fault current has a
maximum value; electromotive force all power supplies are in phase; rated
voltage of each step taken by 5% above the nominal voltage.
Take into account the
impact on the short-circuit currents connected to the network synchronous
compensators, synchronous and asynchronous motors. Effect of induction motors
to short-circuit currents are not taken into account when:
a) unit capacity of
100 kW electric motors, electric motors if the fault location remote from one
stage of transformation;
b) any power when
they are remote from the fault position by two or more stages of
transformation, or if the current from them can come to a place of RS only
through those elements through which the main circuit current from the network,
which have significant resistance (line transformers, etc. .d.).
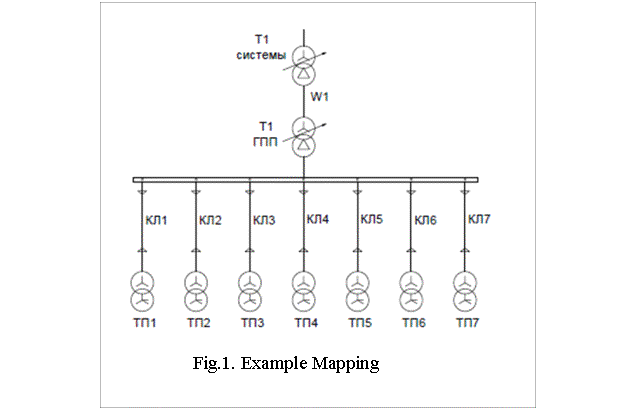
The calculation
scheme for determining the fault current is a diagram in one-line version,
which introduced generators and motors, affecting short-circuit current, as
well as elements of the system power supply (line, transformer), connecting
power sources to the short circuit.
By design scheme
constitute an equivalent circuit in which the transformer is replaced by the
electrical connection (Figure 1). Elements of the power supply system (PSS),
connecting power sources to the short circuit is introduced into the equivalent
circuit impedances, and power sources - resistance and EMF. Resistance and EMF
equivalent circuit must be brought to the same voltage level.
The calculation is
usually carried out in basic terms: basic
full power Sá; the base
voltage of the first level Uá1.
Then the
the base current of the first level: 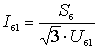 .
.
The
basic voltage and current of the second stage:
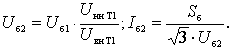
The
basic voltage and current of the third level:
![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
Resistance
element equivalent circuit SES at the following stages of calculation
determined by baseline value.
Find
the resistance of the main elements of the equivalent circuit of the power
supply system (the system of overhead lines, cable lines, transformers,
asynchronous motors):
System:
resistance of the system referred to the power system Sá:
xñmin =![]() ñmin
ñmin![]() , xñmax
=
, xñmax
=![]() ñmax
ñmax![]() .
.
Electromotive
force system: ![]()
Air
line: the reactance of the overhead line: ![]() , where x0 - specific reactance of the
overhead line, Ohm km; L - length of lines, km. Resistance of overhead lines:
, where x0 - specific reactance of the
overhead line, Ohm km; L - length of lines, km. Resistance of overhead lines: ![]() .
.
Transformer:
reactance transformer load tap
changer:![]() ,
, 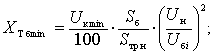
![]() ,
, 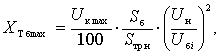 where Uê – Voltage short circuit%; Sòð í – nominal
capacity of the transformer, MBA; Uí – ated voltage of the transformer, kV.
where Uê – Voltage short circuit%; Sòð í – nominal
capacity of the transformer, MBA; Uí – ated voltage of the transformer, kV.
Resistance without
transformer tap changer: 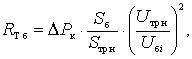 where DÐê – short-circuit power, MW. Impedance transformer:
where DÐê – short-circuit power, MW. Impedance transformer: ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
Cable
line: reactance: ![]() , where XÊË – reactance cable line, Ohm; active
resistance:
, where XÊË – reactance cable line, Ohm; active
resistance: ![]() , where RÊË – active resistance cable line, Ohm. Impedance
cabling ÊË:
, where RÊË – active resistance cable line, Ohm. Impedance
cabling ÊË: ![]()
Calculation
is carried out for the current three-phase short-circuit (SC), as This mode is
heaviest.
Short-circuit
current is given by:![]() , where Åýêâ – equivalent
electromotive force; Zýêâ – the
equivalent resistance circuit faults.
, where Åýêâ – equivalent
electromotive force; Zýêâ – the
equivalent resistance circuit faults.

Short-circuit
current is given by: ![]() ,
,
![]() where Åýêâ – equivalent electromotive force; Zýêâ – the equivalent
resistance circuit faults.
where Åýêâ – equivalent electromotive force; Zýêâ – the equivalent
resistance circuit faults.
After finding the fault
current to the basic values of the value transferred to the named unit. For
example, we find the fault current at the point K1. Design scheme for the
calculation of short-circuit current is as follows (Figure 2).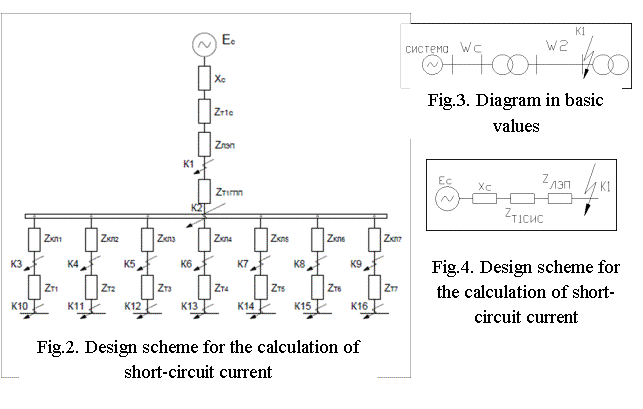

For
further calculation we transform design scheme into an equivalent circuit
diagram in basic values (Figure 3).
We find the
equivalent electromotive force: ![]()
Equivalent
resistance: ![]()
![]()
Short-circuit
current: 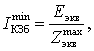
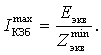
Short-circuit current in the named values: ![]()
![]()
The calculation of short circuit currents for the remaining points of
the circuit to a high voltage runs similarly.