Krasovska H.V.
Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv
Izmailova O.V.
Kyiv National University of Construction and
Architecture
Krasovska K.K.
Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv
Prototyping of intellectual decision support system for organizational
and technological trainings in construction
The main goal of the organizational and technological
training (OTT) is decision-making in organization and production technology of
works at the construction object. These questions are usually discussed within the
project in organization of construction (POC) and the project of works
performance (PWP). One of the most significant levers in the improving of OTT’s
efficiency is multivariate development of organizational and technological
solutions at all stages of the construction of the facility. In the theory and
practice of OTT in construction is stored the positive experience of using of
the organizational and technical modelling and multivariate approach to
processing of construction decisions. The great contribution to OTT is usage of
computer systems, which took into account restrictions in terms of works; ensure
rational use of resources; follow specifications and requirements in works
performance and accidents prevention; coordinate decisions with production
capacity of building organizations and enterprises of construction industry,
with the possibilities of providing external material resources and
technological equipment. However, in the field of organizational and technical
training of construction important reserves of efficiency improvement are
hidden. Their usage requires the development of the decision support system,
which is based on computer technology and ensures varied designing and planning
of organizational and technological solutions based on their relationship;
flexible system of forming of the decisions variants and estimating their
relative efficiency; grounded choice considering to various alternative
criteria and their combination; reliability analysis of the decisions and plans
of construction. It is necessary to guarantee the possibility of preparing and
making decisions in weakly structured situations, the varying degree of
availability and clarity of data, ensure efficiency of decision making,
reasonable complexity and difficulty of processes. [2, 3]
Today one of the most promising directions in matters
of collecting and analyzing large amounts of data for decision-making in
complex management decisions, usage of models with different aspects and
methods of multi-criteria analysis and choice of effective decisions in
conditions of uncertainty are decision support systems (DSS). Technologies
which are the basis of DSS are priority areas of research in information
technology, and at the same time they are well-developed. [1, 4]
The main goal of this research is to build a
conceptual model of DSS to support organizational and technological preparation
of construction (DSS OTP). The building of conceptual model is considered as an
initial experimental part of system planning and lays in creation (as primary
product of the conceptualization) of the system’s prototype as the starting
point of spiral life cycle model of the system.
Construction of the prototype, even in schematic way, will
let the developer to determine operational inconveniences, difficulties in
realization, completeness or redundancy in functionality, performance,
complexity and flexibility of the system through the dialog with the client.
Prototype as a conceptual model of the system allows you to determine the need
for further research or establish clear requirements for the new system design
spiral steps.
While building of the conceptual model, DSS OTP is
regarded as a computer system, which by collecting and analyzing large amounts
of information at different stages of OTP, on the basis of its large analytical
skills, can help the user (a person who decides (PWD)), to increase decision’s
validity, efficiency of formation and analysis.
DSS OTP is focused on solving decision-making problems
in conditions of weak structurization and is led to ensure application of
scenario approach based on the models of situation analysis. During the process
of situation several aspects have to be counted analysis hierarchical
structures with different aspects of the system (e.g. conditions of strategical
or tactical decision-making, level of processes specification and their
regulatory base), problems and targets of decision-making, measure of
information’s availability, conditions of decision-making. The last ones are
supposed to have alternatives as follows: data preparation for user due to the
characteristics of every decision; choice of the best decision from the
diversity of others; forming of optimal decisions; sorting of optimal decisions
by advantage (ranking). These situational conditions must be counted during the
iterative modelling process of the interdependent and mutually influencing
architecture and planning, constructive, technical and organizational factors
multivariate decisions of OTP, their complex estimation based on many criteria,
estimation of the optimization ways.
Principal moment of the system construction with
different conditions of decision-making is choosing a set of criteria, which
will be used in estimation and decision-making. DSS OTP is built on forming of
the information platform of estimation criteria, which has hierarchical
structure, herewith PWD, in interactive mode, can choose criteria, which will
be counted, update criteria’s structure.
Different models and methods are used for the analysis
and fabrication of variants of OTP in DSS. These models and methods are aimed
at information retrieval, intelligent data analysis, knowledge search in
databases, alternative determined and stochastic organizational and technical
modelling, imitational modelling, methods of hierarchical analysis,
multicriteria optimization methods and decisions estimation, situational
analysis, methods of expert estimation etc. intelligent data analysis,
knowledge search in databases are developed within artificial intelligence that
can be attributed to a class of intelligent decision support systems (IDSS). [1, 4]
This prototype of DSS is considering one of the main
functional components of OTP – preparation and analysis of solutions based on
aggregate deterministic and stochastic deterministic alternative network
models. Alternative network modelling, while maintaining the advantages of
canonical networks, is their effective modification. On the basis of
alternative networks is possible to display in a single model in the
relationship of the full range of production options construction and
installation works (CIW), do their information description, according to
established criteria and selection policy, search for the most effective option
for their implementation. Thus the information saturation of the model is based
on varying degrees of certainty, analytic comprehensive assessment of options
is based on many criteria using the analytic hierarchy process, linear
convolution of criteria and method of concessions, the final decision is the
prerogative of the PWD.
Based on the four basic components IDSS we offer the
following DSS OTP architecture (Fig. 1).

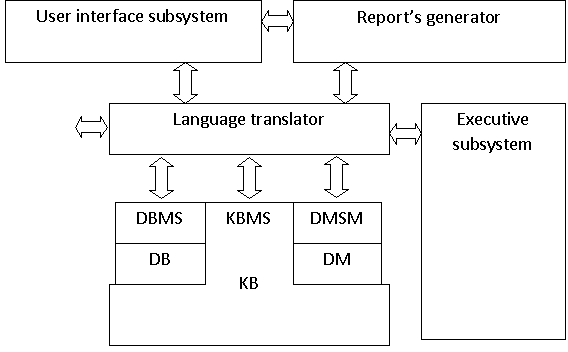

Figure 1. DSS OTP architecture
The sub-system of the user interface in DSS OTP is
oriented on organization of interaction with primary categories of users:
system analyst, PWD and expert. Analyst forms informational platform of the
system, provides the opportunity of analysis of the sensitivity embedded models
and opportunities for their development, etc. In the process of analysis and
selection of options for their evaluation in conditions of data uncertainty
(e.g., forming of criteria structure, determination of their significance,
establishing quality of criteria values) expert is invited. The main user role
belongs to PWD, who determines the content of the problem of decision making,
situational terms of analysis and decision-making to solve the problem. All
information about the sub-set of the best variants is granted to PWD. The final
decision in selecting of effective option remains for PWD.
Executive subsystem decides OTP generation options,
analysis and calculation options, the choice of effective option. During the
analysis and selection of options records set (subsystem of reports) is formed
and provided to experts, analysts and PWD.
Data management subsystem. Data management subsystems
can be divided in several components: database and DBMS, interface subsystem
with external information source. As external sources are considered
computerized systems, that are used in the enterprise, as well as sectoral and
cross-sectoral classificators, industry regulations, resource base, etc.
Model management subsystem consists of database models
and database management system models. Base of models includes models and
methods of multivariate OTP (alternative determined and stochastic
organizational and technical modelling, imitational modelling), the hierarchy
analysis methods, multi-objective optimization techniques and evaluation of
solutions, analytical and heuristic methods of optimization solutions at the
established criteria, models and methods of scheduling. System of management of
models database, in addition to the tools management model provides flexibility
of search and choice of models and their integration.
Knowledge management subsystem. The knowledge base
contains semantic (ontological) model of construction project, a description of
which is served in three interconnected spaces: structural decomposition, works
decomposition (decomposition technology) and presentation of the basic
structural and technological modules. In order to organize flexible models
management knowledge about system’s models is included to the KB, and also
semantics of their use.
Language translator, which allows using object-oriented
programming language (Domain-specific language, DSL) to develop scenarios
according to data models using knowledge.
In conclusion, the architecture of intellectual
decision support system of organizational and process modeling includes the
following subsystems: management interface subsystem; executive subsystem;
subsystem of reports; data management subsystem; model management subsystem;
knowledge management subsystem; language translator.
Literature:
1. Bidyuk P. I., Hozhyy O. P., Korshevnyuk L. O. Computer decision support
systems: manual. guidances. / Nat. Sc. University of Ukraine "Kyiv.
Politehn. Inst." Chernomor. State. University of Them. Piotr Mohila. -
Mykolayiv. - K., 2012. - 379 c.
2. Dron E. A. Automated decision support system for construction management
based on expenses model: Dis. candidate. Sc. Sciences: 05.13.06 - Ufa, 2003. - 186 p.
RSL OD, 61: 03.5/3619-2
3. Safonov K. A. Desicion support system in automation of designing of
organizational and technological preparation in Construction: Dis. Candidate.
Sc. Sciences: 05.13.12 - Nizhny Novgorod, 2002 109 p. RSL OD, 61: 03.05 /
1767-8
4. Sytnyk V.F. Decision Support Systems: Training. guidances. - K .: KNEU,
2004. - 614 p.