Ermolaev V. A, Komarova N.A., Sosnina O.B.
The Kemerovo technological institute of the food
industry
Changes of a microstructure of products of an animal
origin in the course of freezing
Freezing
of a product is the most widespread method of conservation of a product, and
also the integral stage in many technological operations applied in the
food-processing industry at which in fabrics of a product there are the
essential physical and chemical changes reflected finally on its quality. Thus
distinguish the freezing occurring in separate freezing chambers and
self-freezing, occurring under vacuum as a result of tap of warmth by
evaporation at fall of temperature more low криоскопической
points and formations in a product of crystals of ice. Process of self-freezing
under vacuum is caused by intensive evaporation of a moisture in a product.
For
the majority of materials the most comprehensible is the method of
self-freezing that is caused by more uniform and fast cooling of a product on
all volume. Such a frost allows to avoid formation of large crystals of the ice
adversely operating on structure of fabrics of a product. Thus self-freezing is
favourable in the power plan.
Firm
cheeses on power and food value take a special place among foodstuff that is
caused by the high maintenance in them of fibers, dairy fat, vitamins and
mineral salts. Cheeses are a source of irreplaceable amino acids [1]. For
research of influence on a microstructure of cheese of freezing and
self-freezing in vacuum cheese "Dutch" was used. Preliminary a frost
of cheese it was made in the refrigerating chamber at temperature -40OC.
Self-freezing was carried out in the vacuum chamber.
|
|
|
|
a |
d |
|
|
|
|
b |
e |
|
|
|
|
c |
f |
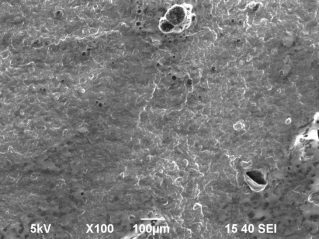
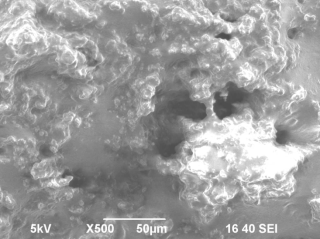
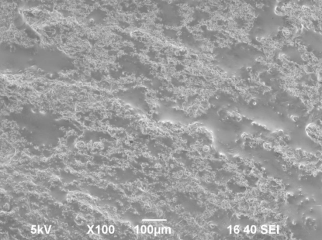
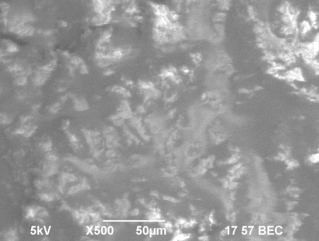
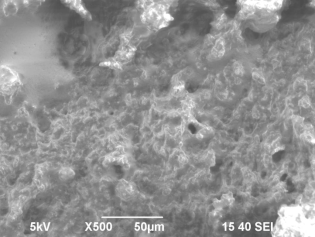
Fig.
1. A microstructure of the "Dutch" cheese: a, d - before frosts; b, e
- after self-frosts under vacuum; c, f - after frosts in the freezing chamber
On
fig. 1 cheese microphotos "Dutch" before and after frosts are
presented. After self-freezing cheese was characterized by an equal, smooth
surface (fig. 1 b, e) with characteristic cellular structure and capillaries,
the size 100 microns.
Formation
of crystals of ice in the course of self-freezing occurs by gradual deepening
of a zone of crystallization. A sign of end of process of self-freezing is
achievement in the middle of cheese particles of temperature-20 …-30OC.
Duration of self-freezing varies within 20-30 minutes. Increase of duration of
this process conducts to formation of too large crystals of ice that can be at
the bottom of destruction of cages of fabrics and deterioration of quality
indicators of the defrosted cheese.
At
fast freezing more uniform formation кристалликов
ice in cages and in intercellular space is observed. In a case with slow
freezing are formed кристаллики the large sizes, the cheese structure is thus broken, the surface
becomes rough with chaotic сколами (fig. 1 c, f). The
difference in distribution of crystals of ice at fast and slow freezing speaks
diffusion processes.
Thus,
on the basis of the spent experimental researches the expediency of application
of self-freezing under vacuum at which more uniform structure with small
crystals of ice in comparison with заморозкой
in the freezing chamber is observed has been established that directly affects
quality of cheese.
The
list of references:
1.
Majors, A.A. Formation of structurally-mechanical properties of cheese / А.А. Majors, Е.А. Nikolaev. – Barnaul, 2005. – 223 P.