Physiological And biochemical mechanisms
of herbs adaptation in conditions of Lake Baikal
M.A. Zhivetyev,
I.A. Graskova, V.K. Voinikov
Siberian Institute
of Plant Physiology and Biochemistry SD RAS, Irkutsk, 664033, Russia
The research of state of ecological systems
both Lake Baikal and area, testing climate-generate influence of this lake, was
actually. The plant adaptation to unfavorable factors of environment, including a low temperature, touch on
protein, lipids, carbohydrate metabolism. Some signal molecule is necessary to
switching on adaptive process. One of them are oxygen active forms. So long as
active forms of oxygen play the important role in beginnings of adaptation, the
peroxidase is attract attention of researcher. Peroxidase is enzyme, which
participate in metabolism of hydrogen peroxide end execute the major function
in oxidation stress.
We was research leafs of plants of three
species, growing in Irkutsk and on the southeastern shore of Lake Baikal. These
species are Achillea asiatica Serg., Taraxacum officinale Wigg., Plantago major L. These species are
medicinal herbs. In leafs of it we was identify the activity of peroxidase, the
content of fatty acids, sugars, stress-induced proteins.
The variation of activity of weak-associated
with plant cell wall and soluble peroxidases of three species of medicinal
herbs has been identified for the first time subject to thermal regime and subject
to place of growth.
In October the coming of negative temperature led
to slump of peroxidase activity of plants, growing in Irkutsk. Inversely,
plants, sprouting on shores of Lake Baikal, were intensifying activity of this ferment.
All described above can be evidence of
initiation of unlike adaptation mechanisms in Irkutsk end at Baikal shores
subject to environmental conditions.
Termostability and optimal pH of
weak-associated with plant cell wall and soluble peroxidases was shown to
change in relation to natural conditions and season of year. Also the activity
of peroxidase was variable during vegetation period.
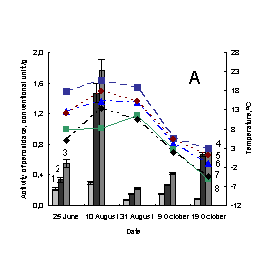
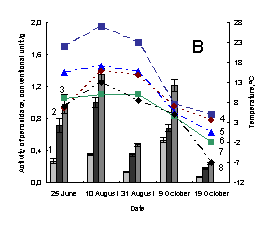
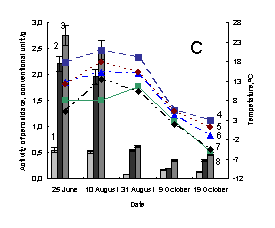
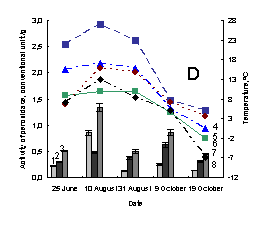
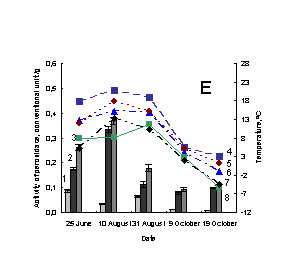
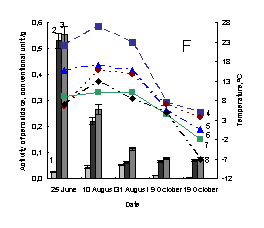
Pic. 1. The variation of activity of
weak-associated with plant cell wall and soluble peroxidases of medicinal herbs:
1 – activity of weak-associated with plant cell wall peroxidase; 2 – activity of
soluble peroxidase; 3 –activity of total peroxidase; 4 – minimum of air tempetature in day of sampling; 5 – soil
tempetature in five centimeter depth; 6 – average daily air tempetature; 7 – maximum
of air tempetature in day of sampling; 8 – minimum of air tempetature in day before
sampling; À – Taraxacum officinale, settlement Vydrino,
shore of Lake Baikal, 2009; Â – Taraxacum officinale, town
Irkutsk, 2009; Ñ – Achillea asiatica, settlement Vydrino,
shore of Lake Baikal, 2009; D - Achillea
asiatica, town Irkutsk, 2009; E – Plantago
major, settlement Vydrino, shore of Lake Baikal, 2009; F – Plantago major, town Irkutsk, 2009.
Dehydrine expression was followed by spike of
peroxidase activity (and, a priori, an increase of hydrogen peroxide
concentration).
Increase of content of
sugar, doing cryoprotector function, was shown to end of vegetation period. The accumulation of sugars on shores
of Lake Baikal was going on greater than it in Irkutsk.
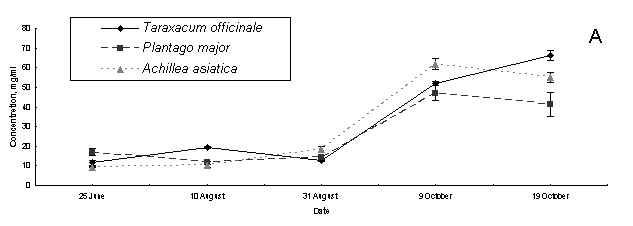
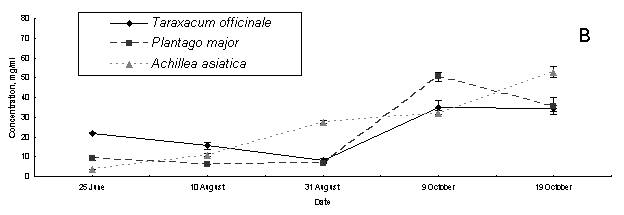
Pic. 2. Content of sugar of medicinal
herbs: À – settlement
Vydrino, shore of Lake Baikal; Â – town Irkutsk.
In autumn, the accumulation of sugars,
stressful proteins (stress-induced proteins) end unsaturated fatty acids in
leafs of plants have been registered in Lake Baikal larger then in Irkutsk.
This complex of adaptation mechanisms can be used in the capacity of marker of
state of plants in natural conditions of habitation.