ÓÄÊ 338.24
Abdildinova M.N., Rayeva M.K.,
ROLE OF INNOVATION IN
DEVELOPMENT OF KAZAKHSTAN’S ECONOMY AND FOREIGN EXPERIENCE IN INNOVATIONS
DEVELOPMENT
Today Kazakhstan stands
on the threshold of a new stage of social and economic modernization and
political democratization.
Only if there are modern
competitiveness and open market economy, not confined by the primary
commodities sector, based on respect and protection of private property and
contractual relations, initiative and enterprise of all members of society, it
is possible to improve the country’s economy to the world standard level.
To achieve the goals set
before the government and people it is essential to give consideration to
innovation development of regional economy and Kazakhstan as a whole.
In the world of economic
literature, the term “innovation” is interpreted as the transformation of the
potential of scientific and technical progress in real progress embodied in new
products and technologies. Innovation is a public economic process which,
through the practical use of ideas and inventions, leads to creation of the
best products and technologies with opportunity to get profit and additional
income. The nature of notion “innovation” is that it is something better than
existed before, something more effective which has only positive result.
However innovation is also understood as a result of creative activity aimed at
designing, creation and distribution of new kinds of products, technologies,
organizational forms and etc.
In accordance with
international standards innovation is defined as the eventual result of
innovation activities embodied in the form of a new or improved product adopted
in the market, new or improved technological process used in practice.
The State Statistics Committee
(SSC) labels as innovation products those which are:
- produced serially for the first
time in the country;
- subjected to quality
improvement;
- based on domestic patents and
inventions;
Strategy of Industrial
and Innovation Development of Kazakhstan for 2003-2015 also considers
innovative development. Strategy of Industrial and Innovation Development of
Kazakhstan aims to conduct research and innovation policy to foster entrepreneurship
in the organization of competitive and exported industries that provides
renewal of technics, technologies, designing and commissioning of technics
which is able to increase productivity of labor, quality of products, automate
the production process as well as create new high-tech branches of industry.
The main prerequisites for
strategy realization are:
- Firstly, ensure favorable
institutional conditions;
- Secondly, identify and shape
businesses’ innovative potential [1].
At present the government
creates all the necessary conditions as the special structures like Kazakhstan
Investment Fund, the Export Credit Insurance Corporation and National
Innovation Fund were established. Institutional tools, to encourage investment
activities in manufacturing and agriculture, were introduced.
Any state, pursuing the
goal of foundation of modern society’s material basis faces problem of foreign
technology’s use.
Therefore, there are
countries–recipients in the world, which are divided into three groups:
- Unable to master and
effectively use modern technology;
- Able to accept modern imported
technology, properly use it to reach the world quality of products without
further development;
- Able not only use advanced
technology, but also to refine it so that their product surpasses primary
source for quality, price and productivity.
The experience of
successful countries in the innovative development sphere - Finland, Israel,
South Korea - proves that the government should implement the function of the
main ideologist of its manpower’s personnel training.
In developed countries
the dynamic development of innovation - one of the main conditions of the
innovation economy. According to the UN, the top ten innovative developed
countries includes Japan, South Korea, Spain, UK, U.S., Sweden, the
Netherlands, Canada, Australia, Singapore. It is innovation in the modern
economy that provides efficiency and brings big profits in return. This is
evidenced by the levels of development of countries such as the US., Japan and
Western Europe. These countries have, in the words of Daniel Bell, occupied the
top level of “technology ladder” [2].
In Kazakhstan the
innovation economy is in the phase of formation. From 2003 National Statistics
has been monitoring a more detailed analysis of this process.
In Kazakhstan quite a
number of products, which were produced in the country for the first time, are
massive, serial and so innovative.
In the period from 2003
to 2010 volume of innovative products of industry enterprises increased to
142.2 billion tenge. The maximum performance was achieved in 2006. In 2008-2009
owing to the impact of the global crisis innovation activity has decreased. The
country managed to increase significantly the volume of production of the
products in 2010. The largest volumes of innovative products workload were
achieved in the manufacturing industry, mainly in the metallurgy, as well as in
food processing, chemical industry, non-metal products, metal ore mining,
production of electrical equipment, drinks. In industry, this performance is
twice exceeds the nationwide level.
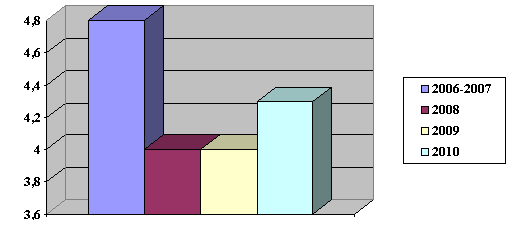
Bar chart-1. Level of innovative
activity of the Kazakhstan enterprises,%
For
comparison: the share of innovative companies in the United States is about
50%, Turkey - 33, Hungary - 47, Estonia - 36 and -9.1% in Russia [4].
In general, the
innovative development of Kazakhstan is underdeveloped and has low activity.
There are many factors constraining the dynamics of the innovation process.
Factors that hinder
active innovative development of the country include: lack of business
incubators, technology transfer centers, science parks, i.e. this arises the
need of shaping and development of innovation infrastructure. The innovation
infrastructure is in constant evolution, from simple forms of innovation units
to more complicated ways of restructuring. Competitive environment in the
global market, low level of branch management, as well as the limited time
frame of commercialization and unequal volumes and conditions of realization
have led to situation when the country’s venture capital funds cannot invest
innovative technology. In addition to the above the organizational system ought
to work clearly. The organizational methods of innovation policy should include
the establishment of an accurate organizational innovation-driven system, in
which each element will be endowed with specific functions, internal and
external connections, and will carry out its activities in accordance with
common goals and objective of the whole system.
Comprehensive scientific
organizations, including economic, marketing, information, commercial units,
must be founded. At the same time thoroughness of the innovation process organization
is very essential: from planning fundamental and applied research and
development of the most priority areas for innovation sphere (with regard of
demand for scientific production) to the final phase of innovation development
and its adoption in the production process.
Another factor which is
hampering the modernization of the national economy and the dynamics of the
innovation process is the low level of funding in research and development,
science and technology.
At the conference “Build
strong Kazakhstan together” on July 4, 2011 President N. Nazarbayev noted that
the state budget increased investment in research and development. By 2015
expenditure will account for 1% of GDP. This will be more than 2 billion U.S.
dollars. And 60 % of these funds will be directed to research and development
work what has never been done before [5].
World experience shows
that without the help of the state, the development of innovations is a complex
process. Implementation of the U.S. scientific and technological policy bases
on the well-developed institutional structure. Special feature of American
structure of science and technology management is the close interaction between
the state and private business. Proportion of the mixed organizations that are
financed by the state and private sources is very significant.
Among them - the Council
of Scientific and Industrial Research, the National Academy of Sciences and the
American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Fundamentals of the
modern concept of science and technology development in Japan were established
by the Japanese government in the early postwar years. Exactly in this period
the long-term forecasts of the national economy’s development were made and
priority sectors and R&D spheres were determined.
At the top of the
hierarchical system of public administration of scientific and technical
progress in Japan is the Science Council, headed by the Prime Minister. Its
members are ministries and representatives of the largest private industrial
corporations. The Science Council formulates strategic line of scientific and
technical development of the country and determines size of R&D
expenditures from the state budget.
In leading European
countries (Germany, UK, France) national public authorities play an important
role in shaping national scientific and technical potential, supporting
corporations which are able to raise the competitiveness of their products and
national economy. Despite the variety of administrative structures, the
differences in principles of macroeconomic politics, tactical goals and so on,
the Western European countries have much in common. State Scientific concept of
these countries is based on encouraging “national champions” - few large
corporations that can compete with the leading firms of the USA and Japan. They
get the vast majority of public funds for industrial research and development.
Sweden and Finland spent
on science 4th % of GDP. Germany and France raise research spending to 3.5. %
In 2010, world business leaders have invested in research and development more
than 500 billion dollars.
World renowned economists
predicted that XXI century will be the century of nano- and biotechnology,
microelectronics, semiconductor and energy technologies. Who will be able to
master these products will be competitive in the next decade.
Head of State N.A.
Nazarbayev has defined innovation as further priority for the country’s
development. In a new message to the people of Kazakhstan “Strategy
“Kazakhstan-2050”: a new policy of the established state”, he defined the goal
for 2050, to create a welfare society based on a strong state, economic
development and opportunities of universal labor. A strong state is
particularly important to ensure the conditions for accelerated economic growth
[6].
It is very significant
for Kazakhstan to develop in the short term competitive innovation environment,
which on the one hand generates innovative solutions, on the other - instantly
finds their application in practice thereby making a profit.
References
1. Strategy
of Industrial and Innovation Development of Kazakhstan for 2003-2015
2. D. Bell The future
post-industrial society. Experience in social forecasting. — Ì.: Academia, 1999.
3. R.Alshanov Kazakhstan's
economy in 20 years: innovation and diversification // Kazakhstan Pravda, 18
november 2011
4. Òîlegen Å.Ò. Study of Innovation Development of Kazakhstan. Àstana - 2011
//www.economy.kz/
5. «Build strong Kazakhstan together», President's speech N.A.Nazarbayev at the Forum July 4th,
2011 http://www.zakon.kz/top_law_news/vystuplenie-prezidenta-respubliki.
6. Message from the President
of the Republic of Kazakhstan to the people of Kazakhstan «Strategy "Kazakhstan-2050": a new policy
established state» // http://www.akorda.kz/ru/