Åêîíîì³÷í³ íàóêè
Graduate student Salamatska O.
Alfred Nobel University, Ukraine
Structure of the building branch of Ukraine
The building industry is included into the basic,
fundamental and fund-creating branches indicated the rate of Ukrainian economy development.
The history of the establishing of the building branch of Ukraine is divided by
R. Guiccu into four stages:
1 pre-perestroika stage (1988 – 1990);
2 transitional, hybrid and unstable stage (1990 –
1994);
3 uncivilized and marketable stage (1994 – 1998);
4 civilized and marketable stage (1998 – 2008)
[1].
As Isaenko D.V. pointed out, at the period of the
financial crisis 2008 – 2010 “the new stage – catastrophic - was appeared (2008 – 2010). Lack of current
assets made building owners to scale down the volume of works, discontinue
building activities including those with a high level of construction
preparedness. As a consequence, the intake of constructional materials and
products was decreased. This fact deteriorated financial situation of enterprises
of the building industry and construction materials producing industry that led
to reducing of production in all relating branches, job cuts, reducing of the
budget revenue etc.” [2, p. 206-207].
The period of re-constructing (the first stage) was
connected with the beginning of the building branch downswing in Ukraine.
Reducing of demand for products in more than three times and inflation which took
current assets, effectless amortization policy specified the state of productive facilities of the branch,
employment level and direction of economic entries’ activity in this sphere. In
the meantime in very this period the market of non-state property began to
form.
After the secession of Ukraine from the USSR in
1991 there was the breakdown of the building branch which has been continuing
till now. So, for example, from the middle of 1980s the USSR began the programme of reconstruction, modernization and
technical re-equipment of the active industrial enterprises. In 1991 realization
of this programme was winded down. Only housing constructing and building of
non-productive assets such as hotels, trade enterprises, warehouses, sport
facilities, office buildings and roads were popular at the building market.
In 1994 – 1998 the building complex was recovered
a little from the transitional stage and began to enhance production volumes.
But the hyperinflation and the crisis of 1998 – 1999 had totally destroyed the
rest of one of the largest building complexes of the former USSR.
The resumption of the building and construction
materials producing industry began approximately in 2000. The economic
situation of the country became more or less stable. The investor came and the
new bank crediting system of the building branch began to develop. The fourth
stage was described in terms of reliability of the fulfillment of treaty obligations, the character and the level of
price competitiveness formed at the market, the similar standards of duration
of different objects building and civility of the level of profitability.
And again the building branch got hurt form the
crisis 2008 – 2009. The building activity was stopped, banks refused to credit,
building owners became bankrupts and investors outlaid fair financial assets
and lost confidence to the Ukrainian building branch and the state taken in its
entirety.
Such a situation made the government of the
country to pay attention to reanimation of the branch. The set of legislative
initiatives was adopted: the Law of Ukraine “On prevention of influence of the
world financial crisis on development of the building branch and housing
constructing”, the Law of Ukraine “On regulation of town-planning activity”,
the legislative initiatives of The President of Ukraine “Affordable housing”
etc.
Doroguntsov S.I. put into the building complex
the following productive industries: the building industry, construction
materials producing industry, production of building constructions and details.
Meanwhile the author notices that in the set of scientific researches the
structure of the building complex is understood in a more comprehensive sense:
it includes building and road engineering, special infrastructure (research-and-development
organizations, research and engineering organizations, higher and specialized
secondary educational establishments, technical vocational schools, training
courses for construction staff; banking establishments financed building
activity; organizations of material support of enterprises included into the
complex; specialized transport) [3].
Ovsiannikova T.Yu. included regulatory agencies
and architectural and construction supervision, research-and-development
organizations, architectural and design organizations, design and research
organizations, constructional materials enterprises, enterprises of operations
and maintenance of construction machines and equipment, construction and
erection organizations into the building complex [4, p.21].
Buzyrev V.V. and other authors mark out five
structural groups of the building complex in their textbooks:
1.
permanent construction
organization (contracting agencies), enterprises of the building industry;
2.
enterprises and organizations
which provide work objects for building activity (enterprises of construction
materials and constructions producing industry, enterprises of mechanic
engineering, wood and timber industry etc);
3.
enterprises and organizations
which provide work equipment (building and road engineering, production of
equipment for construction materials producing industry);
4.
enterprises of infrastructures. The
infrastructure means the whole set of branches serving the production and
providing the conditions of society’s activity;
5.
organizations realizing
management of the building activity – ministries, departments, communities,
associations etc [5, p.11].
In accordance with the status
reports of the State Statistics Committee of Ukraine the native building branch
directly includes building activity inclusive of housing constructing and
construction materials producing industry.
In our opinion the building
branch consists of building activity, constructive materials producing
industry, enterprises and organizations of infrastructure (architect bureau,
scientific and research institutes, enterprises of operations and maintenance
of construction machines and equipment) and managed government institutions
(Figure 1).
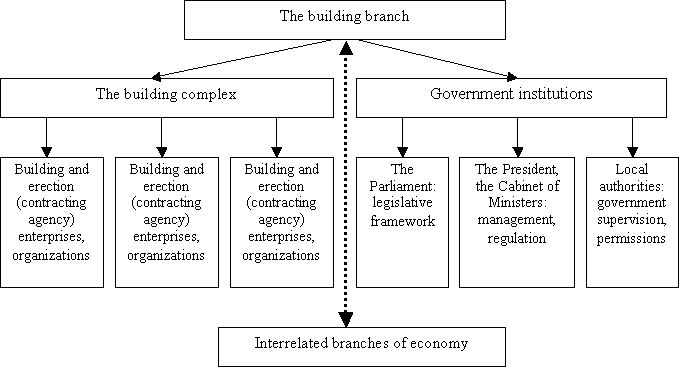
Made by the author
Figure 1. Structure of the building branch of Ukraine
Literature:
1.
Guicci R. Housing constructing in
Ukraine: reasons of the current crisis and conclusions for the economic policy/
R.Guicci, R. Kirchner, R. Vozniak. – The institute for economic research and
policy consulting, Berlin/Kiev. – 2008. – 16 p.
2.
Isaenko D.V. The building complex
of Ukraine: transformation in conditions of transit to market economies./D.V.
Isaenko//The state and society, ¹ 2, 2011.
3.
Ovsiannikova T.Yu. Economy of the
building complex; Economic grounding and realization of investment projects:
Textbook – Tomsk: Publisher of Tomsk State University of Architecture and
Building, 2003. – 239 p.
4.
Economics of location and
regional economics: textbook/ S.I. Doroguntsov, T.A. Zaiats, Yu.I. Pitiurenko
etc.; Under the general editorship of S.I. Doroguntsov. – K.: Kyiv National
Economic University, 2005. – 988 p.
5.
Buzyrev V.V., Ivashentseva T.A.,
Kuzminskiy A.G., Scherbakov A.I. Economy of a construction company: textbook. –
Novosibirsk: The Novosibirsk State University of Architecture and Civil
Engineering, 1998. – 175 p.