Stochastic features of
formation of a temperature field of preparation when grinding
Dyakonov A. A.,
Ermilov S.A.
South-Ural State
University, Russia, Chelyabinsk
Occasional
approach to thermal-physic task decision of grinding theory and numeral
analysis based on imitation model realization by means of computer for the
first time allow discovering the number of physical particular qualities of
temperature field blank formation in this process.
The
fig. 1 illustrates, there is the contact length at the axis of absciss and
there is the grinding width at the axis of ordinates. It allows to monitor the
nature of temperature field formation in the contact zone both in the cutting
moment by grains (maximal temperature tops) and in the «rest» time until the
next grain enters when the material is getting cold. At the graphs you can see
the critical fluctuation points of temperature field – maximal and minimal
temperature. Furthermore, the temperature field has the not stational and
irregular character both at the contact length and the contact width, in other
words the temperature fluctuations move to the area of higher temperature at
time.
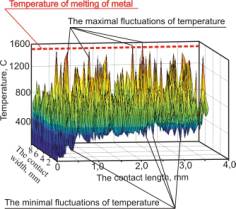
Fig. 1. The temperature field blank kind by grinding
For the all materials the maximal temperatures could reach and even
exceed melting-point and independently on processing kind. It is the
demonstration of one assumption influence using in thermal-physics model,
namely metal – isotope and while
calculating its phase transformations during heat spread process (latent warmth
melting) are not taken into account. It allows avoiding nonlinear thermal
conductivity differential equation. It is very important to solve this problem
for investigations those concerned with determination of structural changes in
the surface layers. This problem is not discussed in the present report.
Moreover, A.A. Koshin [1] represents that material melting temperature is
available only on the surface, and in the significant volumes of surface layers
determining the quality of processing this effect is not monitored.
Thus, the maximal temperature that appears in the thin surface layers,
could reach physically the melting-point and since this time the getting cold
happens whish is describing in the designed thermal-physics model.
The particular cases are recognized after analyzing the great number of
temperature field diagrams. So, for the all examined material marks
independently on the grinding kind, the sudden increases and drops interchange
in the temperature of getting cold is monitored in the high temperature zone.
It is concerned with nonlinear changes of dependence “Solidity-Temperature” for
that diapason in which the meanings of material solid characteristics (σi) and intensity heat sources
(q) are not taking into account.
Comparing
the given temperature fields for different kinds of grindings it could be
established that while the contact length increases the temperature gradient
increases too. So, during the round outside grinding of carbon steels the
average temperature gradient is 380 °C, during the flat grinding – 650 °C and
during the internal grinding – 310 °C.
On the
other hand, the temperature increase is not proportionate to contact length
increase as correlation of the contact length at flat and outside round
grinding at average technological conditions is 3,8 : 1, and correlation of
temperature is 1,7 : 1. This event could be explained by availability of acceleration
and stabilization zone (fig. 2) at temperature field. The drastic temperature
increase that practically equals the maximal temperature happens on the contact
length that is 1 mm not dependently on grinding kind, and the future
development of temperature field happens at stabilization dependence relatively
to abscissa axis. However the part of acceleration zone of the contact length
for every kind is not similar, for example, for the round outside grinding it
is 100%, for the internal grinding – 62%, for the flat grinding – 25%.
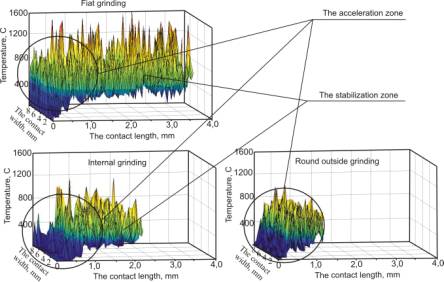
Fig. 2. Characteristic sites of temperature field blank formation
Consequently
the temperature field blank by grinding possesses of two criteria zones: the
zone of drastic temperature increase (the acceleration zone) and the
stabilization zone.
Modification
of the given diagrams into the line level diagrams (fig.3) allows to monitor
distribution and heterogeneity of temperature field blank in the contact zone.
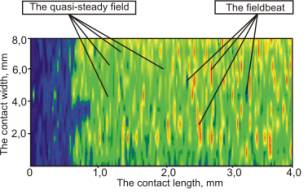
Fig. 3. The line
level heterogeneity diagram of temperature field blank
in the contact zone by grinding
Fig. 2
illustrates quasi-stationary temperature field is created in the results of the
frequent influence of abrasive grains on the stabilization zone that is 800
ºÑ, due to occasional grinding
process temperature pulsation happens in the interval of 200–1400 ºÑ.
The
main particular quality of temperature field, which was idealized vastly by
investigators [2], is occasional character of its formation. Starting from this,
to evaluate temperature field in the contact zone the application of
mathematical statistics is required as the average of temperature in this case,
obviously disfigures the real situation.
Two
central moments of mathematical statistics are implemented for evaluation:
M (U) –
mathematical temperature waiting in the considered interval at the contact
length;
R(U) –
swing of temperature relatively to mathematical waiting in the considered interval at the contact
length.
Two-parameter
evaluation system was realized by computer statistics prognostication STATISTICA
6.0. To determine mathematical waiting
M (U) and swing R (U) in every interval at the contact length the meanings of
temperature at the contact width included in this interval are considered.
The
example of trusting temperature field evaluation at flat grinding of AISI304 is illustrated on the fig. 4. The results confirm the
necessity of two-parameter evaluation system as the swing in the dependence on
the considered contact length could obtain 220–980ºÑ. The analyzing of the graphs allows concluding that
temperature field blank possesses additional particular qualities besides indicated
earlier.
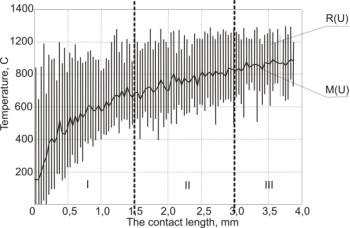
Fig. 4. The
temperature swing interval statistics
The
temperature swing obtains the different meanings on the individual contact
length in which connection its meaning decreases while the contact length
increases.
The temperature swing interval statistics
|
The grinding kind |
Number of the site |
||
|
I |
II |
III |
|
|
R (U), 0Ñ |
|||
|
Round outside |
530 |
500 |
421 |
|
Internal |
550 |
390 |
– |
|
Flat |
560 |
421 |
320 |
Conclusion
Occasional
approach to thermal-physic task decision of grinding theory and numeral
analysis based on imitation model realization by means of computer for the
first time allow discovering the number of physical particular qualities of
temperature field blank formation in this process.
It was
established that temperature field has quasi-stationary occasional character.
It was
discovered that availability of two criteria zones – the acceleration zone was
defined by drastic temperature increase
and the stabilization zone was conformed by constant level of temperature field
formation – is typical for temperature field in the contact zone by grinding.
The
statistic characteristics – two central moments of mathematical statistics: the
mathematical waiting M(U) and the swing R(U) are offered for numeral evaluation
of temperature field blank in the grinding zone.
References
1.
Koshin A.A. Research of physical
communications at grinding // The Processing
of metals. Novosibirsk, 1997. ¹1. P. 22–25.
2.
Korchak S.N. Productivity of process of
grinding of steel details. M.: Mechanical
engineering, 1974. 280 p.