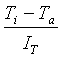G.Bergezhanova, B.Bakhtiyar, A.Tanirbergenov
Almaty,
Kazakhstan
IDENTIFY HEAT WORK UNITS, WHICH
FALLS FROM THE BOARD TO CLEAN COVER
The
energy of sun light falling on the surface of the drive
does not change completely to heat
energy. It comes from the loss of half
of the heat storage. Heat consumption carried
out in different ways. Radiation rays outside
air to a transparent substrate and on the
upper surface. Reasonable costs of
heat through the
bottom and edges of the drive.
To
find the job des creation requires two drive indicator - the amount of energy
absorption and heat consumption in the social en ironmen. Pro fib table energy
is determined by the differ en cebetween the energy absorption between the floe
woof heat to the environment.
Display
useful energy storage :
![]() (1)
(1)
These
parts: G - a liquid storage a real by
1 square meter; Cp-heat capacity;T0 - the temperature of the fluid coming out
of the drive.
We
can determine the profitability drives the outcome of the Testing:
![]() (2)
(2)
When There mo fluidic udder in the drive bet wean the
drive and the thermal resistanceandKSM-4it self
is written to the device. To measure the activity of
radiation on the territory of the drive M-
80pyro meter as tables heed, its CSR performance-output to 4 devices.
To measure the amount of water entering the system drives tables hid a flow meter. Heat trans for fluid in the accumulator it turns out with
such a loop "drive-cubic-drive". In 1986, on September 11
in Almaty results of conducting these trial sure shown in Table 6.5..
The
results of testing of solar installations having three experienced drives:
Profitability
driveturnsusing the map. Flow Rate
of0.0222L\seconds,
storage area 2.4squaremeter.
Provided U
= const driver of it ability![]() dependence of the
lined,
dependence of the
lined,
strengthening
of the right angles
equal to FR UL, and the intersection of the axis of ordinate coordinate point is equal
to ![]() Agra wing of the
results and to FR UL and
Agra wing of the
results and to FR UL and
![]() 8.16Vt\m2and
0.7
8.16Vt\m2and
0.7 ![]() corresponds to
the product of the incident rays
and the smooth surface of the ratio of
observation. The reforest must bees wallow wing ability to
calculate the average monthly
corresponds to
the product of the incident rays
and the smooth surface of the ratio of
observation. The reforest must bees wallow wing ability to
calculate the average monthly![]() . One glass of the collectors
. One glass of the collectors ![]() 0.96 , angle
drive
0.96 , angle
drive ![]() and the
orientation of the south150C.
and the
orientation of the south150C.
change thee
question:
![]() (3)
(3)
You
can measure the activity of radiation rays of the sun, the pressure drop in the daytime,
the temperature and
the instantaneous heat knowing the workings of the fluid temperature, the average monthly benefitrateaction.
Actives
oral radiation IT:
![]() (4)
(4)
![]() - the duration of the day time;
- the duration of the day time;
Giv en
the duration of the day closed the
horizon, in January, March, November
and December, the a verageduration of the day hour, March2, h hours, April and September,2:00,
October 2.5 hours, while in other months1.5 hours.
Conclusion
With this article can
be use full to determine the coefficient of heat and attempts
to work with the help of solar radiation intensity and determine the humidity in
the day time as well as the temperature of the liquid. Therefore,
to assume a lot of times hold be the
ability topic-up the average month lyswallo![]() wing. In this drive system to measure the size of incoming water meter
installation has been installed. The heat transfer fluid to install
rotated "pick -flip-
up" according to the scheme, water rates, the results were taken in the
1sttable shows an example.
wing. In this drive system to measure the size of incoming water meter
installation has been installed. The heat transfer fluid to install
rotated "pick -flip-
up" according to the scheme, water rates, the results were taken in the
1sttable shows an example.
|
Time |
0Ñ |
0Ñ |
0Ñ |
Vt/ì2 |
0Ñ |
|
Vt/ì2 0Ñ |
|
Ti |
Òî |
Òà |
IT |
|
|
|
|
|
1400 |
31,5 |
44,3 |
30 |
845 |
13 |
0,600 |
0,0018 |
|
1415 |
33,0 |
46,5 |
30 |
817 |
13,5 |
0,644 |
0,037 |
|
1430 |
34,5 |
48,0 |
30,5 |
807 |
13,5 |
0,654 |
0,050 |
|
1445 |
36,5 |
49,2 |
30,5 |
799 |
12,7 |
0,620 |
0,0075 |
|
1500 |
36,8 |
49,5 |
30,5 |
775 |
12,7 |
0,639 |
0,0081 |
|
1515 |
37,5 |
50,4 |
30,7 |
738 |
12,9 |
0,682 |
0,0092 |
|
1530 |
39,3 |
51,0 |
31,5 |
702 |
11,7 |
0,650 |
0,0110 |
|
1545 |
40,5 |
51,8 |
31,5 |
644 |
11,3 |
0,684 |
0,014 |
|
1600 |
42,0 |
52,5 |
32,0 |
628 |
10,5 |
0,652 |
0,016 |
|
1615 |
44,3 |
52,5 |
31,5 |
598 |
8,2 |
0,535 |
0,021 |
|
1630 |
44,3 |
53,7 |
31,5 |
573 |
9,4 |
0,640 |
0,022 |
|
1645 |
45,8 |
54,0 |
31,5 |
488 |
8,2 |
0,655 |
0,027 |
Literatures
1.
Lipov
U.M., Samoilov U.F., Vilenskii T.V. The line-upand thethermal design ofthe
steam boiler. – M.:Energoatomizdat. 1988
2.
Esterkin
R.I. Industrialboilers. – L.Energoatomizdat. 1985, Rivkin S.L., Aleksandrova
A.A. Thermodynamic Properties ofWater and Steam.
3. Reference book.- M.:Energoatomizdat. 1984
4.
Kharchenko
N.V.In divi dual solar installation. M.:Energoatomizdat. 1991,210s