J.O. Klymenko, S.N. Baluta, L.O. Kopulova
National University of Food Technologies
Neural networks for the mathematical models for the automatic regulation
system of the metal rolling thickness
The hot rolling
process is accompanied by oscillations in the thickness of rolled. It is a
result of the heterogeneity of physical and mechanical metal properties in
different sections along the length of strip, cooling a part of the strip, that
coming to the finishing of stands, oscillations of tensioning strip during
rolling, different rolled thicknesses, change of expansion between the working
rolls of rolling stand. Тhe automatic regulation system оf thickness (SART) is
based on semiempirical mathematical models, so it can not take into account the
impact of all factors that affecting the process of rolling. Improving the
quality of regulation SART and respectively the quality of metal rolling could
be achieved through the use of intellectual control systems [1].
The
setting of problems and explorations. Development
of effective algorithm of the metal rolling control thickness under incomplete
information about the control object and considering its parametric uncertainty
with methods of artificial neural accuracy of networks.
The materials of explorations. The main criterion of the working of SART is the regulation that
provides control algorithms and high-speed positioning actuators of expansion
changing between the working rolls of rolling stand. The dependence of
Govovin-Sims is realized in SART of broadband hot rolling band ![]() , where
, where ![]() - the thickness of rolled metal,
- the thickness of rolled metal, ![]() - expansion of unloaded rollers,
- expansion of unloaded rollers, ![]() - effort of rolling;
- effort of rolling; ![]() - transfer mobility of rolling stand in the rolling
direction. We must control expansion between the working rolls for the value of
- transfer mobility of rolling stand in the rolling
direction. We must control expansion between the working rolls for the value of![]() depending on the change effort of rolling
depending on the change effort of rolling ![]() , in order to ensure full compensation of longitudinal
different thickness of strip (maintain constant
, in order to ensure full compensation of longitudinal
different thickness of strip (maintain constant ![]() ). For the determination of
). For the determination of ![]() is used analytical models, such as Cook und
McCrum, which include rolled properties that depend on the physical and
mechanical characteristics, temperature and rolled thickness, rolling speed,
features of rolling stand, etc. The accuracy of calculation effort of rolling
once again depends on the initial position of the work rolls and the material
properties (thickness, width, temperature and physical characteristics). The
task of adaptive control is to identify and reduce errors of individual models,
build on existing physical and mathematical models of rolling, through data
analysis and optimization of adaptation mechanisms by applying appropriate techniques.
The artificial neural network as a multilayer perceptron (MLP) are used for the
adaptation of the mathematical model to the conditions of rolling. (draw. 1)
is used analytical models, such as Cook und
McCrum, which include rolled properties that depend on the physical and
mechanical characteristics, temperature and rolled thickness, rolling speed,
features of rolling stand, etc. The accuracy of calculation effort of rolling
once again depends on the initial position of the work rolls and the material
properties (thickness, width, temperature and physical characteristics). The
task of adaptive control is to identify and reduce errors of individual models,
build on existing physical and mathematical models of rolling, through data
analysis and optimization of adaptation mechanisms by applying appropriate techniques.
The artificial neural network as a multilayer perceptron (MLP) are used for the
adaptation of the mathematical model to the conditions of rolling. (draw. 1)
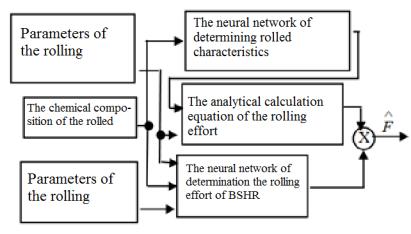
Drawing 1. The
functional scheme of prediction rolling effort using neural networks
The static data
process that characterize the process of rolling is conducted for training the
neural network. The indicated data are divided as follows: the measured values
(temperature of the strip for each stand, rolling effort and
bending effort in each stand, strip’s speed of movement behind each stand,
strip thickness at the inlet and outlet of each of stand), the chemical
composition of rolled (C, Cu, Mn, P, S, Al, Cr, Cu, Mo, Ti, Ni, V, Nb, N, B,
Sn); deformation parameters ( the relative compression in each stand);
parameters of rolling stand (the radius of work rolls of latest stand ).
Statistical research showed that the lapse of thickness rolled strip depends on
the material of strip very much.
Based on the analysis of correlation dependencies established, there are
different clusters that located in different parts of the data plane. Based on
the analysis of correlation dependencies established that there are different
clusters are located in different parts of the data plane. The specified
clusters are determined in order to avoid numerical problems when ANN is
working. As a result of researches, it was found that parameters of the rolls (
such as external diameter or internal
diameter of work and backup rolls, modulus of strip and stand
elasticity, specific heat capacity of the rolls) has impact for the lapse of
controller thickness setpoint.
The rejected values are reflected incorrectly and distorting results
because all incoming values are normalizing. Therefore, it makes
sense to divide the range of products,
rolled by broadband strip of hot rolling (BSHR), into three classes:
traditional steel, stainless steel, rolled of special quality. The approximate
distribution into classes can be done using correlation dependence (draw. 2)
based on the alloying components Cr and Ni.
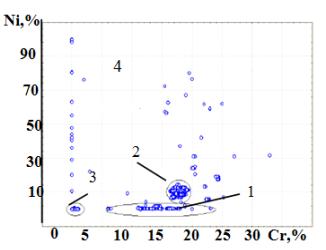
Drawing 2. Separation of steel grades into four groups
1 - a ferrite ; 2 – an austenite; 3 - normal steel; 4 - special types of steel
It is necessary
disregard input variables that are highly correlated with other input variables
or that are very noisy for reliable operation of ANN. It is established, that
there is a high correlation between the final thickness of rolled and rolling
speed in the last stand as well as between the content of alloying elements and
the deviation of thickness strip (draw. 3).
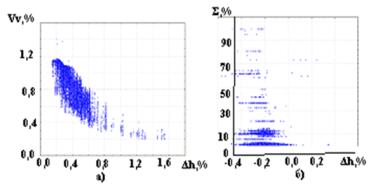
Drawing 3. Correlation
dependence: a) between strip speed in the last stand and thickness deviation,
b) between the content of alloying elements and the deviation of thickness strip
There was investigated MLP for the following target variables, in order
to improve the mathematical models : setpoint thickness, lapse of thickness
setpoint; effort of rolling, lapse of
rolling effort. All the experiments were conducted for the latest stand
of finishing group of BSHR that using ADALINE network [2].
This linear network is not critical to runtime, memory requirements, and can
operate with the 25 input variables in the whole.
The Network lapses of controller thickness setpoint. It is addition in the form of ANN to the usual
analytical models, that allows to estimate impact of input parameters for the
lapse of thickness setpoint (draw. 4). Calculations and researches showed, that
through the use of MLP with 60 neurons in the hidden layer it is possible to
reduce average lapses of setpoint from -0.004924 mm to 0.000684 mm, and improve
lapses in thickness by approximately 10%.
Drawing 4. Functional
scheme of the setpoint correction system of thickness using a network lapses of
controller thickness setpoint (НСООТА)
ANN of the rolling effort is determine the rolling effort used in
calculating the controller thickness setpoint. The research showed, that the
network of the rolling effort is not allowed to achieve the quality of used
analytical models still now. In particular, very simple networks provide
optimization of average lapse and thus pointing the lapse of model, but,
eventually, they do not minimize
standard deviation of lapses rolling efforts.
Lapse ANN of rolling effort is modeling lapse of mathematical models of effort
rolling (rolling network of effort), that in combination with a mathematical
model gives a hybrid model for effort of rolling. Research shows, that ANN of
lapse reduces the average lapse of rolling effort as well as reduces the
standard deviation of lapse effort rolled around 8%.
Conclusion:
The complement of analytical mathematical models that determine the
effort of the rolling ANN of lapse rolling effort on the active BSHR will
significantly improve the quality of thickness regulation and to issue high
quality production of rolling metal.
References:
[1] Богаенко И.Н. и
др. Нейронные сети в системах автоматизации / И.Н. Богаенко− К: Техніка,-1998.- 437 с.
[2] Беркинблей М.Б. Нейронные сети / М.Б. Беркинблей;
Москва Мирос. – М.: Мирос,1993.-464с.