Технические
науки \ 8. Обработка материалов в машиностроении
Goncharenko V.V., Mikulenok I.O., Goncharenko M.V., Gerasimov G.V., Martynenko N.M., Shvachko D.G.
The National Technical University of Ukraine
“KPI”
Temperature tailored sensor-actuator
on a basis of the shape memory metal reinforced polymer matrix composites
The study
of the shape memory materials is the “hottest area” in current research [1].
One of the uses of these tailored materials is in fire-fighting systems [2].
Such materials may be of different types, depending on the use to which they
are put. If the metal reinforced polymer matrix composite materials can be
tapped, there would be a promising source for the fire-fighting systems [3].
Matrix
compound of such composites can be prepared from the linear polyethylene which
has a high fluidity limit of melt. Lowering of the temperature threshold sensibility
is achieved by an increase of paraffin concentration in matrix compound. Such
tailored composite materials for predetermined temperature threshold sensibility
hold the greatest promise for increased fire safety. The integration sensor’s
and actuator’s properties has made it possible to refuse from electric reverse
communication. The abandonment from the electric reverse communications has
made it possible to arrive at the higher degree of reliability of the
fire-fighting systems.
The
straightened metal springs are used as the reinforced element. If temperature
of these tailored sensor-actuators arrives at the temperature threshold sensibility,
the straightened metal springs due to shape memory effect make a demonstration
of partial shrinkage. Such primary thermal shrinkage initiates sharp collapse
of stress in the reinforced springs close to level of the high fluidity limit
of the polymer compound melt. Lowering of the fluidity limit of the polymer
matrix compound melt stimulates more complete thermal shrinkage of the
reinforcing metal springs in a moment of achievement of the temperature
threshold of sensibility.
The goal
of our study is receiving of more complete thermal shrinkage of the metal
reinforced polymer matrix composite materials in a moment of achievement of the
tailored temperature threshold of sensibility.
Utilization
of polyethylene designed for rotation molding LLDPE M3804 RWP (produced by
SCG-Chemical in Thailand) permits to the most lowering of the fluidity limit of
the polymer matrix compound melt. For reference, two thermo mechanical curves
of different polyethylene are (of great importance for) plotted in the same
figure 1. As will be seen from the diagrams, the polyethylene LLDPE M3804 RWP
is characterized by a sharp lowering of a stress resistance. This is in general
agreement with the very little fluidity limit of the polymer melt.
Any melt
temperature of this polymer matrix compound is function of a paraffin
concentration. Such melt temperature ![]() depends on paraffin
concentration
depends on paraffin
concentration ![]() in following manner:
in following manner:
![]() ,
,
where ![]() is melt temperature of the polyethylene LLDPE
M3804 RWP:
is melt temperature of the polyethylene LLDPE
M3804 RWP: ![]() K;
K; ![]() is material constant:
is material constant: ![]()
Concentration
within this matrix compound can be raised to get to 0,175 of the paraffin. The
melt temperature of the polymer compound in this situation must be equal 680C.
The complete thermal shrinkage of such metal reinforced polymer matrix
composite material at 680C is quite important for the purposes of
the fire-fighting.
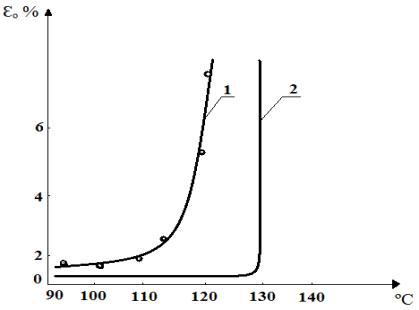
Fig.1.
Thermo mechanical curves: 1 – low density polyethylene 15803-020 (Novo-Pollock,
Belarus); 2 – polyethylene LLDPE M3804 (produced by SCG-Chemical, Thailand); ![]() is
relative deformation, %;
is
relative deformation, %; ![]() is temperature, 0C.
is temperature, 0C.
References:
1. Shahinpoor,
M., Shneider, H.-I. Intelligent Materials // Tomas Graham House, Science Park.
Royal Society of Chemistry. Cambridge, UK. 2008.
2. Chu, Y.Y.,
Zhao, L.C. Shape Memory Materials and its Application // Preceding of the International
Conference on Superelastic Technologies and Shape Memory Materials // USA.
2001.
3. Goncharenko,
V.V., Loboda, P.I., Goncharenko, M.V., Yakovlev, M.A. Application of the metal
reinforced polymer matrix composite in the sprinkler fire-fighting systems // Science
bulletin of the National Polytechnic University of Ukraine. Series “Chemical
engineering, ecology and care of resource”. No.1. 2010. Pp. 42-43 (In Russian).