Ёкономические науки/ 6. ћаркетинг и
менеджмент
Zhumabaev Arman
2nd
Year Master Student,
KBTU,
Almaty
The
role of Innovations in Global society
The main direction
of the current world economic and social development is the activation of
innovation and diffusion of innovative technologies, products and services. One
of the priority tasks of the state is to ensure the dynamic development of the
national economy over the long term. Important tool for accelerating the development
of the domestic economy becomes innovative development. The Strategy of
Industrial and Innovation Development of Kazakhstan tasked with
" economic diversification , promoting sail on
raw materials and prepare the ground for the transition to long-term service
and technology economy. "
In the
twenty-first century success will always remain those who can reform faster and
deeper than others . Attempts to preserve the raw orientation , relying on
natural resources, can not lead to sustainable economic growth and improve the
quality of life of the population . Kazakhstan as a state should be able to
function in the permeability of borders and international interdependence .
State should adapt to the demands of the global economy . Country should provide
the main function develop long-term strategies for the development given the
growing international competition. In the new economic paradigm , which moves
the entire global economy , scientific and technological progress , and
knowledge are the principal growth factors. Republic of Kazakhstan must become
innovative. In 2010, as part of the Strategy "Kazakhstan- 2030"
started " Five-Year Plan for Accelerated Industrial and Innovative
Development ." Among the priorities of industrial-innovative development -
" development of the information sector." In the context of problems
of innovative development of Kazakhstan seems unacceptable currently existing
technological gap enterprise Kazakhstan in the field of IT technologies from
world-class development.1
Need new intensive
technologies , as well as facilities, equipment , providing highly
cost-effective , resource-saving , reliability and environmental safety , based
on recent advances in fundamental and applied sciences. In this regard,
research and application in the modern market environment experience of foreign
IT companies in the organization and conduct of innovation policy in the
creation and implementation of specific innovations and innovative technologies
in various sectors of production , it is necessary and timely .
The concept of
" innovation" and related terms in the system has been actively used
in many different sectors of human activity. In papers on the economy,
depending on the subject and object of research , innovation is considered by
several authors as a process , the result of the system and change. The most
common are two approaches : the first - the innovation appears as a result of
the creative process in the form of new products ( equipment) , technology,
method , etc. , the second - the process of introducing new products ,
components , approaches, principles instead of acting .2 The
approach to understanding the essence of innovation is carried out by the
authors is subjective, based on the object and purpose of the study. In most cases,
the innovation process is described as linear, although the " nonlinear
behavior " of the economy is evident. Currently in the works of foreign
and domestic scientists appeared model in transition, where the innovation
process is represented as a linear sequence of steps. However, it was noted
that it is important to abstract from factors feedback between the various
elements . It is important not to take into account that the innovation process
follows the laws of synergy , as " managing the feedback between its
various elements ," complicates the model and requires the introduction of
a new paradigm , a new terminology. Analysis of scientific papers on topics of
innovation allows us to conclude : the study of innovative development issues
faced with the fact that available terminological stock symbols of the linear
paradigm of economic development gives the number of events , phenomena,
meanings and signs that are necessary to describe nonlinear processes. In our
opinion, in the context of the global financial crisis the world is the most
effective process-based approach to understanding the essence of innovation .
Innovation - is a global socio-cultural phenomenon , reflected in the human
mind as a product and a process which ђ rye receive considerable attention in
the socio-cultural environment and result from a combination of creative and
theoretical material and practical subjects ђ project activities . At the same
time innovation - the process of transition of some self-organizing system (
science, market , society, culture ) from one state to another, this system
works in cycles , according to the laws of synergy ( Figure 1).
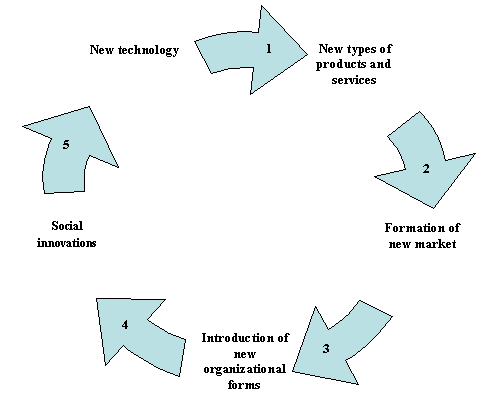

Figure
1 - Innovation as a cyclical process
If the creation of new technology finds its
continuation in the new organizational forms and social innovations , the cycle
has not been completed , and innovation can be regarded as insufficiently
effective , ie not held . Innovation is successful only when the innovation
consistently passed all stages of the cycle , reflected in all fields of human
activity - from basic science to popular culture. Therefore innovation - is a
cyclical process of competitive interaction of several self-organizing systems (science,
market , society , and culture) . This process occurs in the active medium of
information , which in the literature by the term " communicative space
." The assumption of the communicative nature of innovation that
consciously and purposefully manage innovation man can not in principle - as
well as can not control natural phenomena. Successful innovation is a kind of
natural disaster , which resulted in a chain of changes in various
self-organizing systems - informational, economic, social , natural.
Development of innovation as a cyclic process of competitive interaction of
several self-organizing systems is determined by the interaction of the
following mechanisms:
Х limitations defining the limits of development of
the innovation process in the force of impact on the system of physical ,
economic, social , legal and other factors;
Х locking associated with the inability , or
unwillingness inexpedience subjects of innovative activity to further promote
innovation, as well as various risk factors that can lead to complete or
partial blockage of the innovation process ;
Х feedback is the process of transmitting information
from later to earlier stages of the innovation process ( the most important of
"stages of feedback" is a consumer response to the emergence of a new
product on the market) ;
†Х time delays
that occur at all stages of the innovation process and stages of feedback;
Х gain, which appear in the case when in the course of
the innovation process elements of a positive influence on each other , causing
a synergistic effect . Innovative activity has three qualitative differences
from other types of economic activity :
†Х fundamental
difference in the laws of creation, existence and development of the
intellectual and 'material' capital ;
Х other laws of existence and development of human
resource , which is a consequence of the practical impossibility of effective
replacements in real time (as opposed to all kinds of industrial or commercial
activities );
†Х
fundamentally deeper feedback effect in all the processes of innovation
management .
That's why predominating in the world
economic activity algorhythms and control systems, showing results in the
management of industrial and commercial companies , in most cases turn out to
be ineffective in the management of companies with a high coefficient of
importance of intellectual property and human resource ђ as a capital .
Scientific community, on the one hand, is a social environment that breeds
innovation, on the other hand, it prevents the adoption of new scientific
ideas. Business community acts as an organizing element, and a system of values
with respect to an objective definition of innovation to society.
Basis of innovation development is a specific self-organizing system, which can
be described as " state innovation policy + + private venture capital
funds innovative + scientific community ", which in modern conditions
became an independent branch of the economy , this industry innovation3.
For
successful implementation of innovative strategies in Kazakhstan need to see
experience of countries with developed market economies. Which shows that the
implementation of a high-tech way of economic development of the country can be
carried out by two fundamentally different directions. The first is related to
the implementation of the industrial policy, the second - with the
implementation of policies aimed at promoting and enhancing competition.
Implementation
of the first path involves the centralization of decision-making and choice of
priorities for economic development. This path is aimed at supporting domestic
companies through government intervention in the competition through
protectionist instruments and tax policies. The countries in which has been
successfully implemented industrial policy, typically defined as Japan and the
"Asian tigers ."
Competition
policy is based on the principles of low-level constraints for business
development at equal conditions for domestic and foreign companies. The
emphasis is not on the vertical branch development, and to promote
cross-sectoral linkages. A typical example of countries to successfully
implement competition policy , are the United States and Finland .
Kazakhstan's
success in the transition from the inertial to the innovative development
scheme largely depends on the correct choice of strategy. Obviously, such a
strategy should be aimed at restoring the role of the scientific potential of
Kazakhstan as a necessary link in the production process of competitive
domestic products. It is also obvious that it is necessary to solve this
problem is not due to increased government involvement in the funding of
science, and by eliminating the gaps of the innovation cycle.
References:
1. http://www.akorda.kz/ru/category/gos_programmi_razvitiya
2.
‘атхутдинов –.ј.
»нновационных менеджмент = Innovatory management: учебник дл€ студентов
вузов по специальности и направлению УћенеджментФ. Ц ћ.: Ѕизнес-школа Ђ»нтел-—интезї, 1998 г.
3.
Christensen C. M., Roth E. A., Anthony S. D.2004.
Seeing whatТs next: Using Theories of Innovation to Predict Industry Change.
Harvard Business School Press: Boston.