Korniyenko B.Y.
National aviation university, Ukraine
Characteristics
of the production of mineral fertilizers in a fluidized bed granulator
Community development in modern
conditions depends on the development and implementation of energy efficient
environmentally friendly technologies. Application of technique of fluidization for
obtaining solid composites with desired properties in the presence of
phase transitions allows to combine a number of technological stages by the
thermal coefficient of more than 60%. The creation of mathematical models for
the purpose of creation modern systems of management processes in disperse
systems is relevant [1].
Granulation processes are different both
in the methods of implementation, and in the hardware design. One of the
promising methods is an obtaining of a granular product in a fluidized bed
apparatus.
The aim of the article is to study the
static and dynamic characteristics of the mathematical model of a fluidized bed
granulator during the intensive heat and mass transfer processes in the
manufacture mineral fertilizers.
Feature of the
process of formation of solid humic-mineral composites is uniform distribution
of mineral and humic substances throughout the volume of grain and in physical and mechanical properties:
spherical shape, diameter 1.5 - 4.5 mm, strength ≥ 10 N/grain. This solution
dispersed in two-phase system: granular material - gas coolant.
Liquid phase by the action of adhesive
and sorption forces sticks to the surface of solid particles in a superfine
film. The porous structure of granules causes partial diffusion of moisture. To
films from hot solid particles and gas coolant supplied heat. This leads to
intense evaporation of the solvent resulting in the surface of solid particles
formed a thin layer of microcrystals mineral substance and deposited between
colloidal particles of humic compounds. Further microcrystals serve as centers
of crystallization of minerals with another liquid film, resulting in
increasing the size of granules.
There are several approaches to the mathematical
modeling of dehydration and granulation in fluidized bed.
Granular material is fluidized chaotic
system. For the mathematical modeling of fluidized bed apparatus is also
chaotic hydrodynamics.
Very effective are attempts to explore
the hydrodynamics of multiphase processes in a fluidized bed apparatus using
mikrobalance models. These mathematical models solved to bind the equation of
conservation of energy considering the interfacial interaction. For
multivariate modeling processes of dehydration and granulation in fluidized bed
using two-phase Euler-Euler model.
Transport equation of temperature
granules taken into account convective heat transfer, solid phase voltage, flow
fluctuation energy scattering energy collisions, the energy exchange between
the phases. It is possible to determine the intensity of the interaction of the
gas (solid) environment and solid particles (dispersed phase) at different
hydrodynamic regimes and the corresponding temperature change granules during
dehydration and granulation [2].
Mathematical model [2] fully takes into
account the process, but a large amount of calculation time complicates its use
in driving the process of dehydration and granulation in fluidized bed in real
conditions.
Therefore, use slightly simplified
mathematical model of its structure corresponds to the model described above,
but significantly improves its adaptation in driving the process of dehydration
and granulation in a fluidized bed.
According to the results of experimental
researches it was found that for the kinetics of the process of obtaining a
stable final product with desired physical and chemical properties in fluidized
bed granulation prerequisite is respect given temperature in the layer.
Therefore, to research the static and dynamic characteristics of selected
mathematical model with lumped parameters - the ultimate coolant temperature
and temperature fluidized bed.
The dynamics of thermal balance coolant-air can
be described by the following equation:
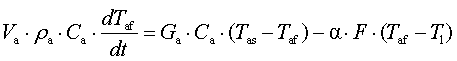 ; (1)
; (1)
where Tas,
Taf– initial and
final air temperature, Ê; Tl – temperature
layer, Ê; F– surface mass transfer, ì2; α– heat transfer coefficient, W/ì2·Ê; Ga– air flow, ì3/ñ ; Ca– heat capacity of air, J/kg·Ê; Va– the air volume, ì3; ρa– air density, kg/ì3.
Dynamics of heat balance particle fluidized bed
is described as follows:
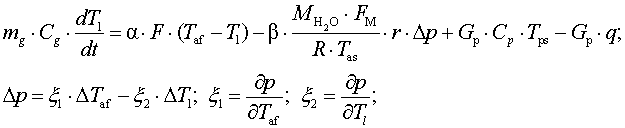 (2)
(2)
where β –
coefficient of mass recoil, ì/s; ÌH2O
– molecular weight of water, kg/mol; F
– mass of transfer surface, ì2; FM –
particle surface, ì2; R – universal
gas constant, J/(mol·Ê); mg– mass of
granule, kg; Ñg - specific heat of
the material granule, J/kg·Ê; Gð –
expenditures of solution, kg/ñ; Δð
– difference of partial pressures, Pà; xp
– moisture content of the material; Òðs
– initial
temperature of the solution, Ê;Ñð -
heat capacity of solution, J/kg·Ê; r– heat of vaporization, J / kg; q - heat
released by crystallization solution, J/kg.
Possible channels
"expenditures coolant-temperature fluidized bed", "cost solution
- temperature fluidized bed."
For static characteristics are equation
based finite temperature and the temperature of the layer changes the air flow
and solution:
![]() ; (3)
; (3)
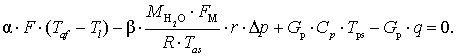 (4)
(4)
From equations (3) - (4)
we obtained an expression for the temperature fluidized bed:
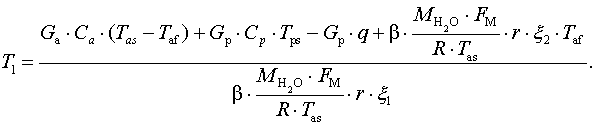 (5)
(5)
Conclusion
This mathematical model describes the
static and dynamic characteristics of the process in a fluidized bed
granulation and shows the change in coolant temperature and fluidized bed
during the heat-mass transfer processes in moving granular material through
appropriate technological zone in the apparatus, which providing granular
product with the desired properties.
The variation of
temperature determines the granulation kinetics and physical and mechanical
properties of the pellets. Therefore, the proposed mathematical model can be
used to create an effective system of control the process of formation of
mineral fertilizers in the fluidized bed with liquid dehydration systems.
Bibliography
1.
Korniyenko B.Y. Features modeling of transport processes in disperse systems / B.Y. Korniyenko // Journal
of the National Technical University of Ukraine "Kyiv Polytechnic
Institute" series "Chemical engineering, ecology and resource
conservation". – 2011, ¹ 2(8). - P. 5-9.
2.
Korniyenko B.Y. The dynamics of the processes of dehydration and
granulation in fluidized bed / B.Y. Korniyenko // Journal of the National Technical
University of Ukraine "Kyiv Polytechnic Institute" series
"Chemical engineering, ecology and resource conservation". – 2012, ¹
1(9). - P. 15-19.