Technical sciences/1. Metallurgy
|
Dr.Tech.Sci. |
A.V. Satonin |
, Ph. D. M.G. Korenko, A.S. Churukanov,
A.A.
Satonin
Donbass State Engineering Academy, Ukraine
Kryvyi Rih Metallurgical Institute of the State Higher Education
Institution "National University of Kryvyi Rih", Ukraine
PJSC "Novokramatorskyi Machine-Building Plant", Ukraine
Development
of numerical one-dimensional mathematical models of stress-strain state of
metal at relatively cold rolling of
narrow strips and sheets
One of the
technological features of the cold rolling production process of relatively
narrow strips and sheets is the increased degree of influence of the edge effect,
which determines the levels of broadening and power parameters of the process
[1]. Thus the specificity of the mechanism of
formation of the boundary conditions causes a substantial modification
of the scheme of stress-strain state of metal exactly on the edges of the
rolled strips and sheets, which makes it necessary to account for this effect
both in terms of power parameters and in terms of quantifying the degree of ductility
capacity [2; 3].
Partition of the entire length of the plastic forming section
to the n number of the i elementary volumes (Fig. 1) to
determine the current values of normal contact stresses ![]() for each of them will produce
further partitioning of the
cross-section to the half of the width
of the rolled strip or sheet to the
final t set of j elementary volumes, performed by
analogy with the methods indicated in [4].
for each of them will produce
further partitioning of the
cross-section to the half of the width
of the rolled strip or sheet to the
final t set of j elementary volumes, performed by
analogy with the methods indicated in [4].
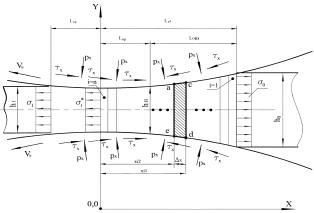
a) b)
Fig. 1. Analytical models of integral deformation zone
(a) and the selected i elementary
volume of plastic forming section (b) in relation to one-dimensional numerical
mathematical modeling of stress-strain state of metal for cold rolling of relatively
thin strips and sheets
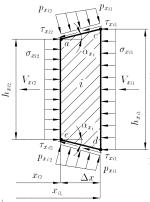
Consider the
condition of static equilibrium for each of them within the design of all
forces on the z-axis (Fig. 2) :
![]() , (1)
, (1)
where ![]() ,
, ![]() are normal axial stresses acting in the
initial (the final numerical index 1) and in the final (the last numerical
index 2) sections, the positive values of which correspond to compressive stresses;
are normal axial stresses acting in the
initial (the final numerical index 1) and in the final (the last numerical
index 2) sections, the positive values of which correspond to compressive stresses; ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() are the current values of tangential contact stresses applied to the
rolled billet considering its cross section by the lower (the first numerical index
1) and upper (the first numerical index 2) roll dies;
are the current values of tangential contact stresses applied to the
rolled billet considering its cross section by the lower (the first numerical index
1) and upper (the first numerical index 2) roll dies; ![]() is the thickness of the rolled billet in the final boundary section
of i elementary volume obtained by
dividing the deformation zone along the x-axis
is the thickness of the rolled billet in the final boundary section
of i elementary volume obtained by
dividing the deformation zone along the x-axis
![]() , (2)
, (2)
![]() ; (3)
; (3)
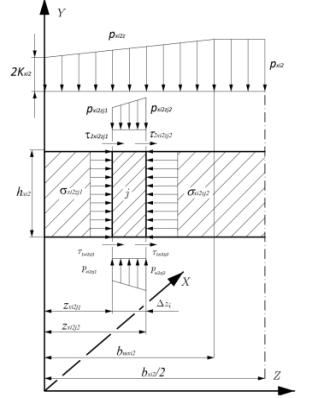
Fig. 2. Analytical model of deformation zone for
numerical mathematical modeling of stress-strain state of metal on the edges for cold rolling of relatively thin strips and sheets
![]() , (4)
, (4)
where ![]() is the step of
partitioning width of rolled billet for j elementary volumes defined by their total number
is the step of
partitioning width of rolled billet for j elementary volumes defined by their total number ![]() .
.
Based
on the analytical description of the tangential contact stresses ![]() , provided that
, provided that ![]() ,
, ![]() at
at ![]() when plasticity condition is
when plasticity condition is ![]() or
or ![]() equation (1) can be transformed as follows:
equation (1) can be transformed as follows:
![]() (5)
(5)
wherefrom, in relation to the desired values of normal contact ![]() and normal axial stresses
and normal axial stresses ![]() , in its final form represent:
, in its final form represent:
 ; (6)
; (6)
![]() , (7)
, (7)
where the quantitative
assessment of stresses ![]() and
and ![]() is known, according to the applied recurrent solution pattern, based
on the results of the previous calculation of elementary cross-section
is known, according to the applied recurrent solution pattern, based
on the results of the previous calculation of elementary cross-section ![]() ;
; ![]() is the current doubled value of the shear resistance along the
length of the deformation zone;
is the current doubled value of the shear resistance along the
length of the deformation zone; ![]() are the current values of the coefficients of external friction, which, according to Amontons-Coulomb law
are the current values of the coefficients of external friction, which, according to Amontons-Coulomb law ![]() [5], characterize the value of tangential contact stresses in the
deformation zone.
[5], characterize the value of tangential contact stresses in the
deformation zone.
As
a direction of the recurrent solution we used the direction
from the edges of the rolled tape to its middle, i.e.
the direction corresponding to the z-axis, which originates on the edge
and which is perpendicular to the rolling axis (see Fig. 2). With this in mind,
the initial conditions and the connection conditions of the
applied recurrent pattern comply with:
![]()
![]()
![]() (8)
(8)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() . (9)
. (9)
Direct numerical recurrence
solution, taking into account the symmetry of cross-sections
of the deformation zone, is produced only for
one of the edges (see Fig. 2), completing it as equality of normal
contact stresses, obtained by calculating the length ![]() and breadth
and breadth ![]() of the rolling axis, i.e. as a fulfillment of
the condition
of the rolling axis, i.e. as a fulfillment of
the condition ![]() .
.
Thus, the
geometric coordinate ![]() , corresponding to the beginning of
the present condition, is taken for the length of the zone of high broadening
, corresponding to the beginning of
the present condition, is taken for the length of the zone of high broadening ![]() for each of the edges.
for each of the edges.
With a regard to the
quantitative assessment of the sequence number of j elementary section ![]() , the average integral value of
normal contact stresses for i
cross-section of the entire deformation zone is also determined:
, the average integral value of
normal contact stresses for i
cross-section of the entire deformation zone is also determined:
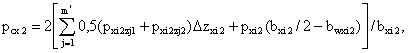 (10)
(10)
It is the knowledge,
which is necessary for the subsequent numerical integration by the i recurrent solution procedure and determination of integral value of rolling force
in the zone of plastic forming of metal taking into account the presence of the edge effect:
![]() (11)
(11)
In
general, the presented dependences (6)–(11) contributed to the mathematical
software subprogram specifying numerical mathematical models of the processes
of symmetric and asymmetric rolling of relatively narrow strips and sheets. As
an example of the results of numerical realization of the obtained software
figure 3 shows calculated normal distribution of contact stresses within the cross-section
width of the deformation zone.
Analysis
of the obtained results have proved that the edge effect, taken into account, leads
to the decrease of average integral value of normal contact stresses ![]() ,
and, consequently, to the reduction of the integral value of the rolling force.
The degree of refinement on the calculation of the rolling force is in the
range 5...15 %, the larger values of which correspond to the rolling of more narrow
strips and sheets.
,
and, consequently, to the reduction of the integral value of the rolling force.
The degree of refinement on the calculation of the rolling force is in the
range 5...15 %, the larger values of which correspond to the rolling of more narrow
strips and sheets.
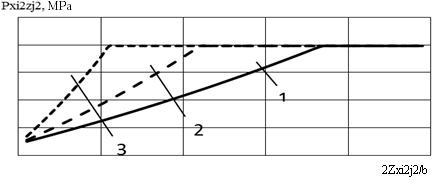
b = 30 мм; 2 – b = 50 мм; 3 – b = 100 мм
Fig. 3. Estimated normal distribution of contact
stresses within the width of the zone of deformation at cold rolling of brass CW508L; (DIN:
2.0321) by reversing mill 250
The
obtained theoretical solutions (6), (7) are used as the initial data for
calculation of the employment degree of rolled metal plasticity capacity,
implemented on the basis of V.A. Ogorodnikov’s methodology [3; 4], and,
consequently, with the regard to the improvement of technological modes of
intermediate annealing and subsequent cold rolling of relatively thin strips
and sheets.
On
the basis of the numerical approach, which intends splitting the deformation zone
along its length and width, followed by recurrent solution of the conditions of
static equilibrium of allocated elementary volumes, numerical mathematical
models of rolling processes of relatively thin and narrow tapes and sheets have
been specified, which provide for the accounting of the edge effect. Thus the
degree of qualifying the rolling force, as demonstrated by the quantitative
evaluation of the obtained results, is in the range 5...15 %, and the degree of
qualifying the employment of plasticity capacity of rolled metals or alloys
corresponds to 10...20 %.
References:
1.
Сатонин А. В. Расчет напряжений и деформаций по кромкам прокатываемых лент
и полос / А. В. Сатонин, М. Г. Коренко, И. С. Сухоруков //
Восточно-европейский журнал передовых
технологий. – 2011. – Вып. 5/7. – С. 63–66.
2. Колмогоров В. Л.
Напряжение. Деформация. Разрушение / В. Л. Колмогоров. – М. :
Металлургия, 1970. – 229 с.
3. Огородников В. А.
Оценка деформируемости металла при обработке давлением /
В. А. Огородников. – К. :Вищашк., 1983. – 175 с.
4. Федоринов
В. А. Математическое моделирование напряжений, деформаций и основных
показателей качества при прокатке относительно широких листов и полос :
монография / В. А. Федоринов, А. В. Сатонин,
Э. П. Грибков. – Краматорск : ДГМА, 2010. – 156 с.
5. Целиков А. И.
Теория продольной прокатки / А. И. Целиков, Г. С. Никитин,
С. Е. Рокотян. – М. : Металлургия, 1980. – 320 с.