E.V. Bolovin, A.S.
Glazyrin.
Department of Electric
Drives and Equipment, National Research Tomsk Polytechnic University, Tomsk,
Russia
Identification of the induction
motor parameters by difference schemes
Abstract
In this paper a method for determining the induction
motor parameters is developed based difference schemes.
Key words: induction motor, identification, difference schemes.
Introduction
The induction motors are widespread in industrial area
due to they advantages such as simple design , reliability , durability , and
low cost. Frequency converters are used in electric drive for increasing motor
productivity and improving the static and dynamic operation. The frequency
converters use the scalar and vector control Both control methods are dependent
on a correct assessment of the induction motor parameters and are very
sensitive to change . So, it’s necessary to continuously monitor changing
parameters of the engine and determine the values of the
parameter estimates with minimum error and quick.
Identification of the
induction motor parameters
The induction motor was considered. Mathematical model of the induction
motor with the well-known assumptions [1], may be written as follows:
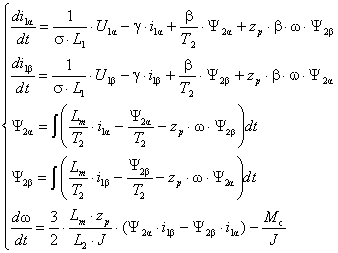
(1)
here ![]()
![]()
![]() T2 – rotor time constant;
T2 – rotor time constant;
R1 - resistance of the stator winding , Ohm;
R'2 - given to the stator rotor resistance , Ohm;
L1=L1σ+Lm - the equivalent inductance of the stator winding , H
;
L2=L′2σ +Lm -
the equivalent inductance of the rotor winding , H ;
L1σ - leakage inductance of the stator winding , H ;
L'2σ - reduced to the stator leakage inductance of the rotor winding , H ;
Lm - resulting inductance due to the magnetic flux in
the air gap of the machine , H ;
![]() - sinusoidal shape
of the stator voltage component α axis orthogonal
coordinate system fixed α, β, V;
- sinusoidal shape
of the stator voltage component α axis orthogonal
coordinate system fixed α, β, V;
![]() -
cosine shape component of the stator voltage axis orthogonal β fixed coordinate system α, β, V;
-
cosine shape component of the stator voltage axis orthogonal β fixed coordinate system α, β, V;
![]() - peak value of the
phase voltage of the stator winding , V;
- peak value of the
phase voltage of the stator winding , V;
U1- phase voltage rms value of the stator winding, V ;
f1 - the frequency of the stator voltage , Hz;
i1α, i1β - components of the stator current ( stator winding phase currents ) in
the coordinate system α, β, A;
Ψ2α, Ψ2β - components of the rotor flux linkage in the system of coordinates α, β, Wb ;
Ìñ - the time of
the static resistance of the motor shaft , including its own engine friction
torque , N·m ;
![]() - scattering
coefficient ;
- scattering
coefficient ;
J - moment of inertia , kg·m2.
After numerous performances and replaced in the system
(1) we obtain the equation (2):
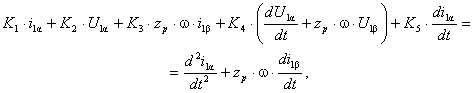 (2)
(2)
here ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Given the interval Δt time sampling measurement system pass from the
differential equation (DE ) to the system of difference equations (SDE ),
written in matrix form with respect to the current and previous tj-x·k=tj-Δt·k moments of time at a constant
guest parameters , where x=0, 1,
2,…5; k - the coefficient of delay
time.
![]() (3)
(3)
where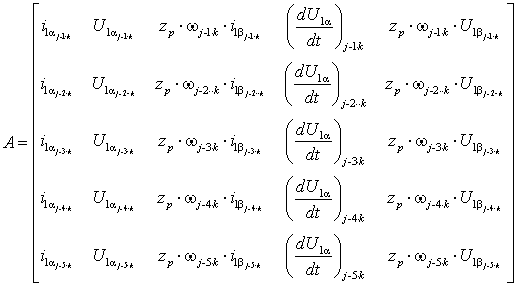
- is the coupling matrix between the unknown parameters and external
forcings,
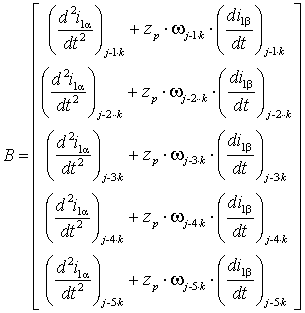
- external influences matrix,
K=[K1, K2, K3, K4,
K5]Ò - the vector of unknown parameters.
In the above matrices ![]() - the components of the stator current (stator
winding phase currents ) in the coordinate system α, β;
- the components of the stator current (stator
winding phase currents ) in the coordinate system α, β; 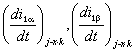 - the first derivatives
of the stator currents (phase stator winding currents ) in the coordinate
system α, β;
- the first derivatives
of the stator currents (phase stator winding currents ) in the coordinate
system α, β; 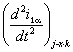 - second derivatives of
the currents along the axis α;
- second derivatives of
the currents along the axis α; ![]() - voltage components a
stator in the coordinate system α, β;
- voltage components a
stator in the coordinate system α, β; ![]() - derivatives stator
voltage in the coordinate system α, β by j, j-1·k, j-2·k,…,
j-5·k steps, respectively.
- derivatives stator
voltage in the coordinate system α, β by j, j-1·k, j-2·k,…,
j-5·k steps, respectively.
We calculate the coefficients ![]() by solving a system of equations (3) by the method of least squares for finding
estimates of the induction motor parameters:
by solving a system of equations (3) by the method of least squares for finding
estimates of the induction motor parameters:
![]()
After finding the coefficients define the parameter
estimates AC-motor as follows:
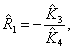
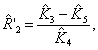

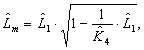

![]()
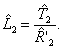
Conclusion
The procedure of compilation the difference equations
for identification the induction motor parameters is presented. This procedure
can be used for adaptive control of electric drive
Bibliography
1. Cincirone, M., M. Pucci, G. Cincirone, and G. A. Capolino. A new
experimental application of least-squares techniques for the estimation of the
parameter of the induction motor // IEEE Trans. on Ind. Applications. Sep.
2003. Vol. 39, No. 5. Ñ. 1247–1255.