Agriculture/3.Soil control agriochemical
PhD doctorant Akhauova G.K., professor Asanov A.A.
Taraz state
university, Kazakhstan
Structure formation of soil in the
presence of copolymerization products of maleinic acid and acryl amide with
nitrogen containing base
Structure formation
activity of carboxide-, amide containing water soluble polymers (WSP), obtained
under different conditions, have been studied. The dependence of structure
formation properties of WSP upon conformation of macromolecules, that altered
with the quantity of organic base, coordinated to carboxide functional groups
as a counterion or neutral molecule in free state, has been shown.
In most cases the intensive
exploitation of soil by application of agrochemical and reclamation methods in
order to obtain high crop leads to the degradation of natural structure of soil
[1]. The necessity of regeneration of soil structure is actual, because its
fertility depends not only on chemical
composition, but mechanical structure as well [2]. At present time high
molecule WSP, obtained by polymer analogous transformation of natural or
synthetic polymers [3], or by polymerization and copolymerization of monomers
with hydrophilic ionized or not ionized functional groups [4] are recommended
for regulation of soil structure. Structure formation activity of WSP depends
not only on the nature and proportion of functional groups, but mainly on the
nature of counter ions and attendant electrolytes, coordinated to the
functional groups and influencing the conformation state of macromolecules.
In the present paper the structure
formation of soils of the South region of Kazakhstan by the application of
copolymerization product of maleinic acid
(MA) and acryl amide (AA), taken in optimal molar proportion (1.0:4.0
moles), with nitrogen containing base as a counter ion and attendant electrolytes is discussed. The
sample, synthesized by copolymerization of MA and AA in water media with the
initial pH value, was marked as MAAA-3-H. MAAA-3-DMA sample has been obtained
by neutralization of MAAA-3-H to pH value 8.0-8.5 with dimethylamine (DMA), and
MAAA-3-DMA+5%DMA by the addition of 5% excess of DMA. The sample marked as
MAA-3-H, synthesized by copolymerization of MA, neutralized to pH value 8.0-8.5
with DMA, with acryl amide, has been studied as well. For characterization of
these samples the determination of viscosity (η), electrical conductivity
(χ) has been carried out, as well as the calculation of molecule
transformation effect (MTE) and effectiveness of electrical conductivity (EEC)
according to [5]. The structure formation activity has been studied via
alteration of quantity of water stable aggregates (WSA) in unstructured soil in
the presence of WSP, synthesized under different conditions. The results
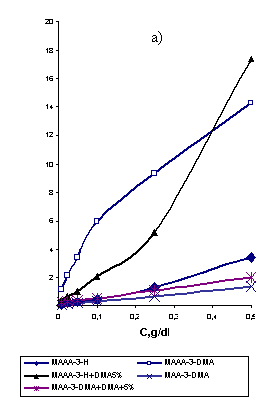
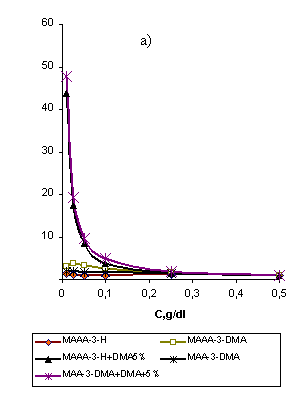
obtained (picture 1a, 1b) demonstrate proportional alteration of WSA quantity,
specific electrical conductivity (χs) and viscosity (ηs)
values when the concentration of WSP solution increases.
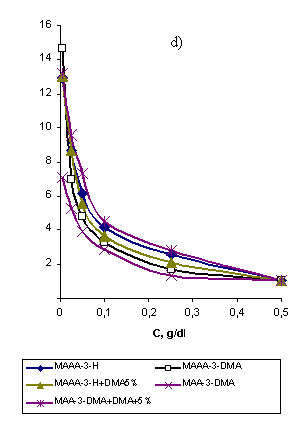
On the
contrary the reduced electrical conductivity (χr) and viscosity
(ηr) values decreased as the concentration of WSP solutions
increased. It is related to the macromolecule transformation effect,
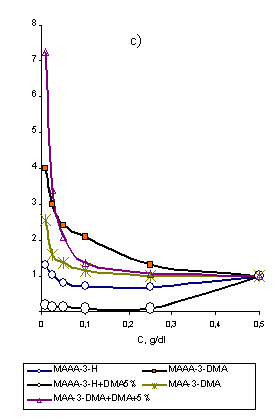
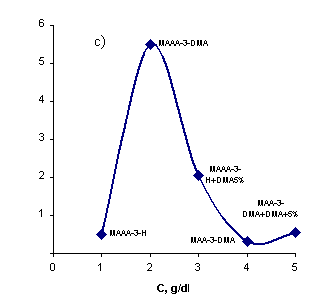
characterizing the conformation state of the macromolecule, which raised due to the alteration of EEC (picture
2a). The objective laws stated helps to understand the reason of alteration of
structure formation effect (SFE) calculated in accordance with the equation
[5], including the concentration values of WSP solutions.
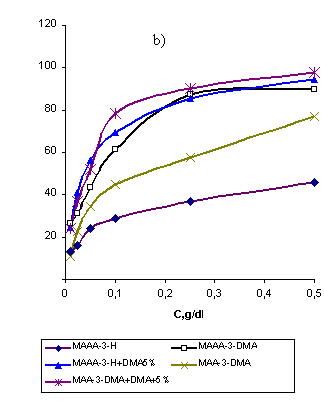
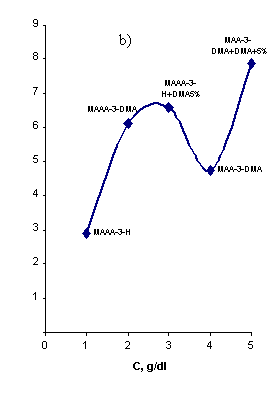
All WSP
samples studied demonstrate the growth of structure activity effect with the decrease of concentration and in the presence of organic bases in free
state (picture 2b). This is related to the enforcement of ionization of
functional groups when solution is diluted and the macromolecule acquires less
folded structure. Incidentally the chain length is growing and the quantity of
free active functional groups as well, that leads to the enforcement of
interaction with the soil surface and formation of strong relations and bridges
between small soil particles.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Picture 1. Alteration of physics-chemical characteristics and structure
formation activity, depending on the
concentration of WSP
|
|
|
|
|
|
Picture
2. Alteration of EES (a), ηr (c) and structure
formation activity (b) of
WSP samples, depending on
the concentration of WSP
The influence of increase of
quantity of active functional groups, macro chain length, presence of organic
bases as counter ions or in free state is perfectly obvious when χs, ηs and
the quantity of WSA of 0.1g/dl solutions are compared (picture 2b). At the same
time the positive influence of free organic bases on the structure formation
activity of WSP is related to the synergetic effect [6], intensifying the
structure formation process.
Based on the comparative analysis of
physics-chemical properties of solutions and structure formation activity of
WSP obtained in different conditions, the dependence of structure formation of
soils in the presence of WSP on the conformation of the macromolecules, which
altered with the quantity of organic
base, coordinated to the functional groups as a counter ion or in free state,
have been stated.
References:
1.
Ãðèøèíà Ë. À., Êîïöèê Ã.
Í., Ìîðãóí Ë. Â. Îðãàíèçàöèÿ è ïðîâåäåíèå ïî÷âåííûõ èññëåäîâàíèé äëÿ
ýêîëîãè÷åñêîãî ìîíèòîðèíãà. – Ì.: Èçä-âî ÌÃÓ, 1991. – 82 ñ.
2.
Ìîòóçîâà Ã. Â. Ïðèíöèïû
è ìåòîäû ïî÷âåííî-õèìè÷åñêîãî ìîíèòîðèíãà. – Ì.: Èçä-âî ÌÃÓ, 1988. – 101 ñ.
3. Àõìåäîâ
Ê.Ñ. è äð. Âîäîðàñòâîðèìûå ïîëèìåðû è èõ âçàèìîäåéñòâèå ñ äèñïåðñíûìè
ñèñòåìàìè.- Òàøêåíò: Èçä. ÔÀÍ.- 1969.-
Ñ. 2,76
4. Àõìåäîâ Ê.Ñ, Àñàíîâ À.À. è äð.
Óñòîé÷èâîñòü è ñòðóêòóðîîáðàçîâàíèå â äèñïåðñíûõ ñèñòåìàõ.- Òàøêåíò: Èçä. ÔÀÍ.-
1976. -108 ñ.
5.Àõìåäîâ Ê.Ñ., Ïîãðåëüñêèé Ê.Â. Ñïîñîá ïîëó÷åíèÿ
âîäîðàñòâîðèìûõ ïîëèìåðîâ À.ñ. ¹ 399511, 1973
6.Âîþöêèè Ñ.Ñ. Êóðñ êîëëîèäíîé õèìèè. –Ì.: Èçä-âî
Õèìèÿ,1964.
-Ñ.221-222.