Ìåäèöèíà
/ 6. Ýêñïåðèìåíòàëüíàÿ è êëèíè÷åñêàÿ ôàðìàêîëîãèÿ
Galkin O.Yu., Dugan O.M.
National Technical University of Ukraine
“Kyiv Polytechnic Institute”
Peremogy Avenue 37, Kyiv, 03057, Ukraine
Biological
activity of phytopreparation THAT is designed for alopecia treatment
At
earlier stages of research we have conducted pharmacological and phytochemical
design of herbal preparation for the treatment and prevention of alopecia.
Phytopreparation is complex tincture of collection of medicinal plant material,
consisting Arctii Radices, Sophora Japonica fruits, Acorus Clamaus rhizome,
Folia Urticae Dioicae and Humulus Lupulus. Biologically active substances of
medicinal plants have analgetic, antiitch, epithelium creating, and antiseptic
properties. They restore the structure and functions of the skin, improve blood
circulation in the capillary system of the skin, it stimulates metabolism and
trophic processes, improve supply scalp.
It
should be noted that the main criteria for successful implementation of
medicines in clinical practice is its safety and its specific activity. Thus,
the study has been determined to the study of biological and pharmacological
activity of herbal preparation.
Study
antiextravasate activity of phytopreparation have been performed on the “rigid”
model of inflammation, which is swelling of the limbs caused subplantaric
injection of 2% formalin solution. Rating of antiextravasate activity also have
been obtained on the model of adrenalin pulmonary edema. Study of
phytopreparation influence on the proliferate component of inflamed reaction
have been evaluated on the model of “cotton granuloma”. The analysis revealed
anti-inflammatory activity of phytopreparation by antiextravasate and antiroliferate
effects, due to the presence of flavonoids and tannins.
It has
been found that mouse tissue macrophages derived from peritoneal exudate,
become activated when they are cultivated in vitro in the presence of
phytopreparation.
Activation
of macrophages showed by changes in their size and shape, as well as their
metabolic and enzymatic activities. It has been established that
phytopreparation increases the ability of macrophages production of oxidation
metabolites at a meeting with the components of microorganisms. Incubation of
peritoneal macrophages in the presence of phytopreparation for 24 h has not
affected the level of spontaneous chemiluminescence, but has increased markedly
(26%) the ability of cells to oxidative metabolites production in response to
zymozan (fig. 1). This increase in chemiluminescence activity occurs gradually
in the range of concentrations of phytopreparation from 50 to 200 mg/ml and
maximal effect has achieved at concentrations of 300 mg/ml.
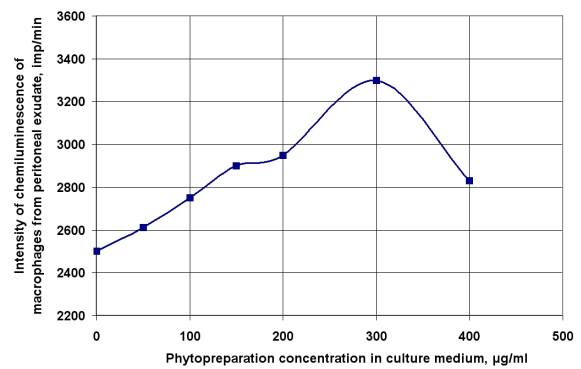
Fig. 1. The intensity of chemiluminescence
of peritoneal exudate cells in response to zymozan after preliminary
cultivation of cells in the presence phytopreparation
These
data agrees well with the concentration of phytopreparation that leads to maximal
activation of macrophages, judging from their morphological characteristics. In
the study of secretion of monocytic cytokines during their cultivation in
phytopreparation containing medium has been installed pronounced effect on
production of IFN-γ and
IL-2 (fig. 2). There has no marked effect on the secretion of interferon
IFN-α, tumor necrosis factor-α, IL-1 and IL-8.
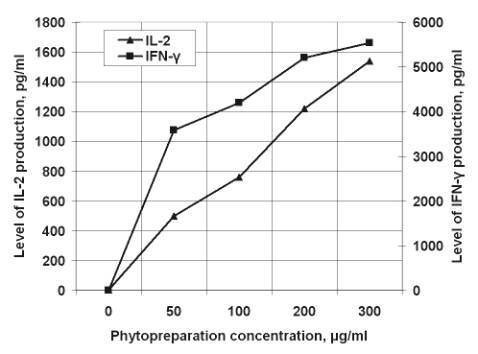
Fig. 2. The contents of cytokines in
culture medium of peripheral blood cells after 12 hours (IL-2) and 48 hours
(IFN-γ) of incubation with medications
Conclusions.
1. The
investigations of acute toxicity of phytopreparation identified its LD50
intraperitoneal (142.0 ml/kg). In examining the impact phytopreparation the
skin and mucous membranes was not detected abnormalities. Phytomedication was
assigned to the small hazardous class substances. It has been found
anti-inflammatory activity by phytopreparation antiexudative and
antiproliferative effects, due to the presence of flavonoids and tannins.
2. It
has been found moderate immunostimulating activity of phytopreparation (in
conditions in vitro).