B.S.Akhmetova,
M.E.Nuralina,
R.M.Shajhymbekova, G.K.Asan
RSE «Central laboratory of biocontrol, certification
and preclinical tests» SK MES RK,
Almaty
THE
METABOLIC EFFECT OF
"RIFAMPICIN-ROMA0T1"
IN COMPARISON WITH
"RIFAMPICIN-NOVARTIS"
Abstract
The
study was undertaken for preclinical test of preparation
"Rifampicin-romat" in comparison with preparation Rifampicin-novartis. Rifampicin-romat offered for
research differs from initial
preparation Rifampicin-novartis by biologically active antioxidative substances
included into the rifampicin structure for lowering it’s collateral toxic
effect.
Experiments have been conducted on 34 unbred rats of both sexes with
body weight 120-180 g, fed with standard vivarium diet. 14 rats daily
received "Rifampicin-romat" per oral in a dose of 10 mg/kg, 10 rats –
“Rifampicin Novartis” (the same dose),
10 rats (control) - 1ml of 0,9% NaCl. Concentration of aspartataminotransferase (GOT),
alaninaminotransferase (GPT), alkaline phosphatase (AP), glucose, cholesterol,
triglycerides and cellular content of blood
have been measured in 14 days of
dosage.
Results of our experiments on
analysis of hepatic markers (GOT,
GPT, glucose, triglycerides, platelet) show statistically significant toxic
effect of "Rifampicin-novartis" and much less
toxic effect of "Rifampicin-romat".
Introduction
Last decades the world has appeared before threat of new epidemic of a
tuberculosis owing to a mutation of causing it micobacteria which become steady
against traditional antitubercular medical products. Kazakhstan is the world
leader in a tuberculosis with
multiresistance per capita.
Pathomorphosis of tuberculosis in a combination with
micobacteria medicinal stability to
widely applied tuberculastatic
preparations leads to use intensive, high dose, aggressive
polychemotherapy [1]. The essential negative effect of such treatment is toksiko-allergic influence on a
macroorganism and development of collateral reactions from many systems of organism. Liver participating in
inactivation of hepato toxic preparations
suffers the most dramatic
functional damage. Therefore the developing and introduction into clinical practice of new domestic effective
antitubercular preparations of
vegetative and synthetic origin possessing an expressed antibacterial effect along with the lowered collateral reactions, is actual and proved. One
of such preparations is "Rifampicin-romat" representing a complex of
Rifampicin with bioactive substances, possessing an antioxidative effect.
The
purpose of current study is preclinical
test of preparation "Rifampicin-romat" in comparison with an initial
preparation Rifampicin-novartis.
Subjects and
methods
Rifampicin (Rifampicinum) - semisynthetic antibiotic, Rifamicin
derivative. Chemical name: 3 (4-Metil-1-3,4-piperazinil-iminometil)-rifamicin
SV2. Rifampicin - a crystal powder of brick or brown-red colour. It is almost
water insoluble and not poor soluble in ethanol. It is sensitive to action of
light, oxygen and air moisture.
Rifampicin-romat offered for research differs from initial preparation by biologically active antioxidative
substances included into the
rifampicin structure for
lowering it’s collateral toxic effect.
Experiments have been conducted on 34 unbred rats of both sexes with
body weight 120-180 g, fed with standard vivarium diet. 14 rats daily received
"Rifampicin-romat" per oral in a dose of 10 mg/kg (group N3), 10 rats
– “Rifampicin Novartis” (the same dose; group N2), 10 rats (control; group
N1) ) - 1ml of 0,9% NaCl. The
blood for biochemical analisys have
been taken from experimental animals under thiopental narcosis in 14 days of
dosage. Concentration of
aspartataminotransferase (GOT), alaninaminotransferase (GPT), alkaline
phosphatase (AP), glucose, cholesterol, triglicerides in blood plasma have been
measured with the use of Biosystems (Spain)
commercial test sets on semi-automatic
biochemical analyzer ScreenMaster (Italy).
Cellular analysis of blood have
been performed on citofluorimeter
Sysmex ÊÕ - 21 (Japan). Obtained data have been processed statistically with the use of
t-test and parameter changes
considered statistically significant
at Ð <0,05.
Results and
discussion
The results of analysis of GPT, GOT and
AP in serum of control rats, rats receiving
"Rifampicin-romat" and rats receiving
"Rifampicin-novartis" are
presented in figure 1. Statistically
significant changes of all studied
indicators between control and "Rifampicin-novartis" rats are found
out: concentration of GOT increased by 40 % (Ð
<0.05), that of GPT - by 47 % (Ð <0.05), and that of AP – by 60 % (Ð
<0.05)in group 2 comparing with group 1 animals. Animals receiving "Rifampicin-romat"
showed the same orientation of shifts
of studied indicators in comparison
with control rats but the size of these
changes has appeared doubtful: concentration of GOT has appeared higher by 10
%, that of GOT - by 12 % and that of AP
- lower by 19 % than that of
corresponding indicators of control rats.
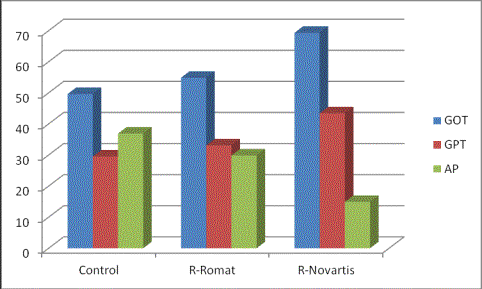
Figure 1. Concentration (U/l)
of GOT, GPT and AP in serum of control rats, rats receiving "Rifampicin-romat" and
rats receiving «Rifampicin-Novartis».
The results of glucose, cholesterol
and triglicerides measurements in blood
plasma of control rats, rats receiving "Rifampicin-romat" and rats
receiving
"Rifampicin-novartis" are presented in figure 2. "Rifampicin-novartis" has caused
an increase by 43 % (Ð <0.05) of glucose
concentration and by 41 % (Ð <0.05) - cholesterol concentration
in blood plasma in comparison with control. In a case with "Rifampicin-romat" the level of
glucose has raised by 9 %, and that of cholesterol - by 26 % (Ð <0.05). Hence "Rifampicin-romat" has shown more sparing
action in comparison with a
"Rifampicin-novartis" concerning glucose and cholesterol
level. The level of triglycerides at action of
"Rifampicin-romat" has fallen
down by 30 %, and at action
of "Rifampicin-novartis" -
has raised by 19 %, as a result the
difference in the triglycerides between groups N2 and N3 has appeared statistically significant (Ð <0.05).
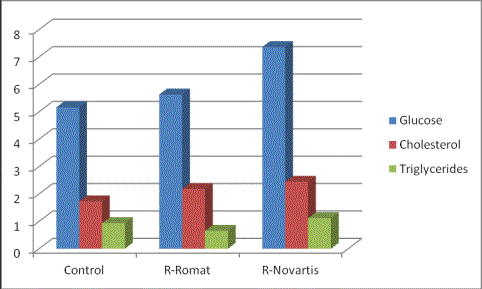
Figure
2. Concentration of glucose, total cholesterol and triglycerides in blood plasma of control rats, rats receiving "Rifampicin-romat" and
rats receiving «Rifampicin-Novartis».
The results of blood
cellular content analysis
of experimental animals are given in a table.
Table. The
cellular content of
blood of control rats, rats receiving "Rifampicin-romat" and rats receiving
«Rifampicin-Novartis».
|
|
Control |
"Rifampicin-romat" |
«Rifampicin-Novartis» |
|
Red blood cells, ×1012/l |
7,42±0,54 |
8,32±0,66 |
6,52±2,0 |
|
Hematocrit, % |
42,26±3,09 |
44,86±6,82 |
34,96±8,51 |
|
Platelets, ×1011/l |
6,36±1,96 |
6,23±3,12 |
3,72±2,04 |
|
Leucocytes, ×109/l |
7,01±2,99 |
5,13±1,94 |
6,60±2,54 |
|
Lymphocytes, % |
56,4±10,8 |
71,9±9,1 |
71,2±9,5 |
The
level of red blood cells in
Rifampicin-romat rats has raised by
12,1 % in comparison with control animals while in Rifampicin-novartis rats it has decreased by 6,9 %.
Hematocrit indicator in
Rifampicin-romat rats has raised by 6,3
% in comparison with control rats, and in
Rifampicin-novartis rats it has decreased by 17,3 %. The platelet amount
has decreased in Rifampicin-novartis rats - by 41,5 % in comparison with
control animals, in Rifampicin-romat rats – by 2,0 % only. The level of
leukocytes in Rifampicin-romat rats has
decreased by 26,8 %, and in Rifampicin-novartis - by 5,8 % in comparison with
control animals. Concentration of lymphocytes has raised in
group 2 and 3 animals by 26,9 %.
As it is known the blood level of GOT,
GPT, platelet are used as biochemical
markers of liver disturbance[2]. GPT
appears in blood after the damage of hepatic cells where the enzyme is present
in norm. GOT is also present not only in hepatic cells but in red blood cells, heart
and skeletal muscle also. At patients with diseases of a liver the
spleen often increases in sizes that leads to a delay of platelet in sinusoids
of a spleen and as a result to decrease
in their level in blood. The level of glucose and triglycerides is an indicator
of liver decease as well.
Our
data are in accordance with
widely known toxic to liver effect of
rifampicin to people [3]. In uncompensated cirrhosis
the toxicity of rifampicin can be developed during the period from 4 till 150 days and
lead to death [4]. Results of our experiments on analysis of
hepatic markers concentration
(GOT, GPT, glucose, triglycerides) show statistically significant toxic
effect of "Rifampicin-novartis" and much less
toxic effect of "Rifampicin-romat". As a whole,
the toxic to liver effect of
"Rifampicin-novartis" has appeared
3 times more expressed, than that of "Rifampicin-novartis".
Considerable decrease in platelet level
under the influence of Rifampicin-novartis also indicates it’s
toxicity to liver whereas in a case with Rifampicin-romat – the stable level of platelets speaks about absence of considerable liver
disturbance. As a whole, by the level
of red blood cells, platelet and hematocrit indicator Rifampicin-romat has shown less
negative effect on cellular content
of blood in comparison with
Rifampicin-novartis.
Thus,
results of our experiments have shown the sparing action of
"Rifampicin-romat" concerning biochemical markers of hepatic disturbance in comparison with expressed toxic to liver effect of "Rifampicin-novartis".
References
1. Pereverzev V. G, Sagindykova B. A,
Syzdykova S.A., Markevich of M. M. Organizational-economic aspects of the
Kazakhstan manufacture of imported medicines.//the Collection of materials of
XIV Russian congress «the Person and a medicine» on April, 16-20th, 2007,
Moscow. - with. 861
2. Tierney L., McPhee S., Papadakis M.
Current Medical Diagnosis and Treatment. - Stanford, CT: Appletion and Lange,
1999. - pp. 638-677
3. Newton R.W., Forrest A.R.W. Rifampicin
overdosage - The red man syndrome//Scot. Med. Journ. - 1975. - V.20. - P.55-56
4. Di Piazza S., Severe rifampicin
associated liver failure in patients with compensated cirrhosis//The Lancet. -
1978. - P.774