Õèìèÿ è õèìè÷åñêèå òåõíîëîãèè / 4.
Õèìèêî-ôàðìàöåâòè÷åñêîå ïðîèçâîäñòâî
Candidate of
Pharmaceutical Sciences, associate professor Î. À. Rukhmakova, Doctor of
Pharmaceutical Sciences, professor Ò. G. Yarnykh
National University
of Pharmacy, Kharkov, Ukraine
Rationale for an
introduction of sorbitol in the dental gel under conditional name
“Dentavir-phyto”
One of the important medical
and biological requirements for modern dental gels is that they have the
penetrating action. It is known that when the gel is applied to the oral mucosa
appears certain osmotic pressure that causes dehydration of damaged tissues and
the penetration in them hydrophilic solvents with active substances [2, p. 211;
4, p. 71-74].
To ensure the penetrating
action in the composition of developed dental gel under conditional name
“Dentavir-phyto” was introduced sorbitol which has a sufficiently high affinity
for the mucous membrane of the mouth and does not cause its dehydration.
Furthermore, the use of sorbitol sweetening the medicine and provides a slow
sustained release of active ingredients [3, p. 87].
To determine the efficient
concentration of sorbitol in the composition of dental gel we have studied the
osmotic activity of the model samples of gel systems, in which the
concentration of sorbitol was – 5 %, 10 %, 15 % and 20 %.
Osmotic activity was studied
by dialysis through a semi permeable membrane, which was used as a cellophane
tape marks Cuprophan. Approximately 10.0 g of the test sample was applied
evenly to the surface of the cellophane tape, after which an inner cylinder was
placed in the chamber of the dialyzer with the contents of the calculated
amount of purified water. The resulting setup was placed in a thermostat at a
temperature of (37.0 ± 1.0) °C (the temperature of the oral mucosa). The
cylinder with the test sample and the membrane was weighed before the
experiment and then after each hour and one day after start of the experiment.
The amount of absorbed water
was expressed in percentage relative to the initial weight of the sample [5, p.
1307-1311].
 The results of
these studies indicate the presence of an osmotic action of all gel systems
(Fig.). It was established
experimentally that the gel base, wherein the dispersion medium is purified
water, exhibits a sufficiently low osmotic activity, absorbs a slight amount of
water, and its dehydrating ability lasts no more than 5 hours.
The results of
these studies indicate the presence of an osmotic action of all gel systems
(Fig.). It was established
experimentally that the gel base, wherein the dispersion medium is purified
water, exhibits a sufficiently low osmotic activity, absorbs a slight amount of
water, and its dehydrating ability lasts no more than 5 hours.
24 25
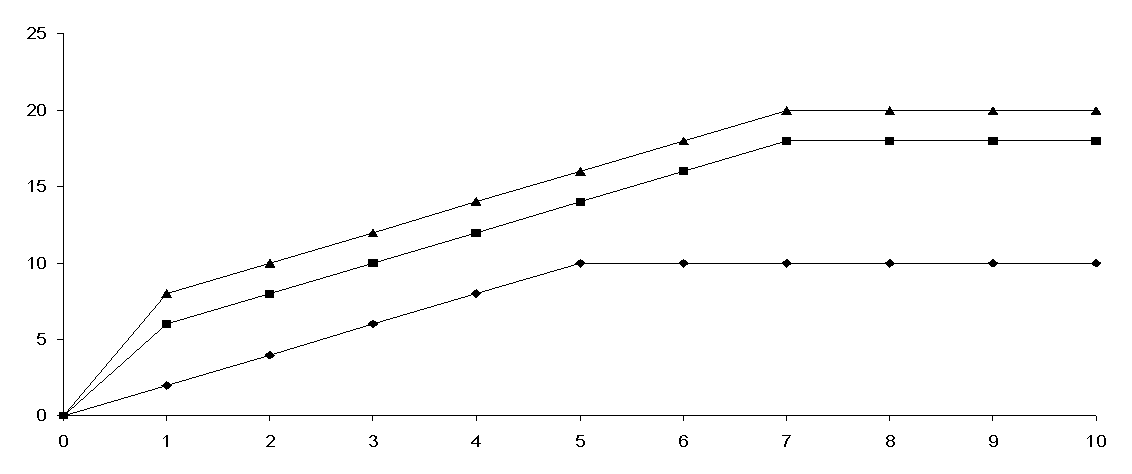
Fig. Osmotic activity of gel
base – 1, dental gels “Dentavir-phyto” – 2 and “Metrogil Denta” – 3
The sample of dental gel
“Dentavir-phyto” with the content of sorbitol 10 % shows great dehydrating
ability compared to a gel base. At the same time, the medicine has a moderate
osmotic effect, which provides a soft dehydrating ability, which will be effect
the decreasing of edema and acceleration of metabolic processes in the tissues.
The samples of gel systems
containing more than 10 % of sorbitol were tacky to the touch and create an
unpleasant sensation when applied to the oral mucosa; the samples with a lower
concentration of sorbitol did not possess sufficient moisturizing action.
When comparing the osmotic
effect of developed medicine and gel
“Metrogil Denta” has been found that osmotic activity of reference medicine is
somewhat above that can be attributed to the presence in its composition as
osmotic active component of propylene glycol having a more pronounced osmotic
properties [1, ñ. 210].
Thus,
the most efficient concentration of sorbitol in the composition of studied
dental gel “Dentavir-phyto” concentration of 10 % was defined.
Literature
1. Additives in drugs technology: impact on technology, consumer, economic
characteristics and therapeutic effectiveness : textbook for
students of higher pharmaceutical educational institutions / ². Ì. Pertsev, D.
². Dmitrievskiy, V. D. Rybachuk et al. ; ed. by ². Ì. Pertsev. – Kh. : Golden
pages, 2010. – 600 p.
2. Davtyan
L. L. Scientific and practical substantiation of soft dosage forms technology
for dentistry: dis. … doctor of pharm. sci. : 15.00.01 / L. L. Davtyan. – Ê.,
2006. – 304 p.
3. Merkulova
E. V. Technology and standardization of dental films with bischofite and gel
with sodium fluoride : dis. … cand. of pharm. sci. : 15.00.01 / E. V.
Merkulova. – Pyatigorsk, 2007. – 162 p.
4. Recurrent aphthous
stomatitis - etiology, pathogenesis / E. L. Panfilova, I. M. Rabinovich, O. F.
Rabinovich et al. // Dentistry. – 2010. – ¹ 1. – P. 71-74.
5. Vorobiova V. M. Technology and quality standards of
experimental dental gel “Estofit Denta” / V. M. Vorobiova, E. V. Alkhimova // Fundamental
research. – 2013. – ¹ 10. – P. 1307-1311.