D.e.s.
Dulambaeva R.T., Marat A.A.
Kazakh National University named by
Al-Farabi, Kazakhstan
Budgetary
funding of healthcare system in the Republic of Kazakhstan
In the modern period the economic development of the Republic
of Kazakhstan distinguish with social orientation. In the context of
socially-oriented economy the health sector is one of the priorities of our
country. For the health system of Kazakhstan is the most relevant problems of
increasing the efficiency of the quality of medical services now. Therefore,
fiscal policy in the field of health care financing includes providing
affordable and quality health care to the entire population of the Republic of
Kazakhstan [1].
The last 20 years in Kazakhstan attempts to reform the
national health system, where the main target of innovation is the system of
financing health care. National Healthcare Development Program of the Republic
of Kazakhstan "Salamatty Қazakstan" for 2011-2015 by the Decree
of the President of the Republic of Kazakhstan was developed to improve the
health of citizens. The aim of the Programme is sustainable social economic
development of the country.
The key objectives of the program are:
-
strengthening
intersectoral and interagency cooperation on issues of public health protection
and sanitary and epidemiological welfare;
-
development and
improvement of the Unified National Health System;
-
Improvement of
medical and pharmaceutical education, development of medical science and
pharmaceutical activity [2].
Reform of the budgetary system of the Republic of
Kazakhstan is associated with the transition to methods of Performance-based
budgeting. In the medium term, taking into account new approaches in budget
planning pursue moderate policies of government spending, providing not a
limitation, and growth of budget expenditures has a stimulating effect on the
economy as a whole.
Theory and practice of financial funding the health
care industry are reflected in the works of Kazakh scientists and economists:
Ilyasova K.K., Tuseeva M.H., Iskakova Z.D., Zeynelgabdina A.B., and the
problems of health care financing are investigated in the works : Zhuzzhanova O.T.,
Rahypbekova T.K., Kurakbaeva K., Sharmanova T., Kim S. [3].
Any financial system should answer three questions:
How are financial resources, as allocated and how effectively used. According
to the results of the study of international experience financial resources of
the health system depends on the level of income of the population, policy
priorities and formed by public or private funding sources. For example, in
Germany, where health care is based on compulsory insurance, this ratio is
composed as follows: through paid services Medicine receives about 5%, premiums
for voluntary insurance - 10, the mandatory insurance premiums - 75%, tax - 10%
of all financial resources.
1 – graph. The financing of national health systems in
2013.
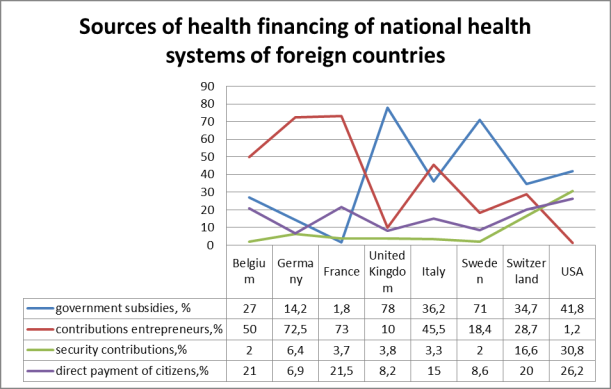
Note - compiled by the author based on the world
statistics [4].
In general, the EU medical expenses left 5.4% of GDP,
peaking in Sweden (7.5%) and the Netherlands (6.3%). In total expenditure on
social protection of population health care costs range from 30 to 46% [4].
As international experience shows, the nature of
reforms with a predominance of state forms of health care financing in many
ways reflect the state of the national economy. Therefore, in the country to
organize an effective system of financial support healthcare, aimed at creating
a healthy competitive nation.
The main elements in the mechanism of allocation of
budgetary resources are the controls that govern regulatory legal acts and
tariff system. As an additional source of funding to engage in certain specific
gravity, it should be recognized medical services on a fee basis. [5]
2 – graph.
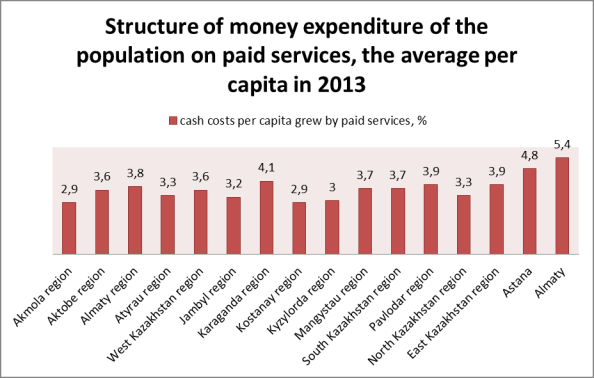
Note - drawn up on the basis of the Committee on
Statistics of the Ministry of National Economy of the Republic of Kazakhstan
[6].
As we can see in the graph, the largest portion of
spending money on paid services in the city of Almaty - 5.4%, while in other
regions of the country even less. This shows that the smallest number of people
use health services on a fee basis.
If we talk about the past performance of 2014, the
volume of services by main activity rendered by health organizations and social
services in the Republic of Kazakhstan amounted to 199414,4 million.tenge, with
79.8% of the executed budget funds, 13.2% - the funds received from the public,
7.0% - at the expense of enterprises. The largest volume of services was formed
due to the activity of hospital organizations, they provided services worth
121772,5 million.tenge (61.1%). Organizations engaged in general practice,
rendered services to the amount of 25383,0 million.tenge (12.7%), an
organization engaged in other activities to protect human health in the amount of 26804,6
million.tenge (13.4%), an organization providing social services with
accommodation in the amount of 9879,3
million.tenge (5.0%) [6].
You can also add that in 2015 Kazakhstan plans to
introduce a compulsory health insurance in the amount of 3% of payroll to
reduce the financial burden on the budget. The introduction of compulsory
insurance a medical suggests that pay for treatment will take on an employer
deducting monthly in specialized medical fund tax. According to the author,
working Kazakhstan scheme compulsory insurance a medical should incorporate the
best practices in the local context. In other words, together with the
Foundation, which implements a cumulative function in the compulsory insurance a
medical should definitely participate insurance companies engaged in a
supervisory role [7].
None sector of a modern market economy, including
health care, can not effectively exist and develop without a well-functioning
financial system and funding sources. Therefore, the construction of an
effective system of health care financing, based on the study of the experience
of developed countries in terms of mechanisms for the allocation of public
expenditure on health care.
References:
1. Increase of financial efficiency in the health system of the Republic
of Kazakhstan. Bulletin of the Kazakh National University. Al-Farabi Kazakh
National University, Almaty, 2005 ¹ 2.-0,2 PL,
2. National Healthcare Development Program of the Republic of Kazakhstan
"Salamatty Kazakhstan" for 2011-2015 approved by the Decree of the
President of the Republic of Kazakhstan ¹ 1113 dated November 29, 2010. http://www.akorda.kz/ru/category/gos_programmi_razvitiya
3. The reforms in the system of health care financing and their
relationship with the public policy of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Proceedings
of the international scientific-practical conference "Actual problems of
economic and customs policy in the context of globalization and
integration", Karaganda, KEUK, 2005-0.2 pp, http://avtoreferats.com/article/view/id/16379
4. The official website for "World Health Statistics - 2013», http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2014/world-health-statistics-2014/en/
5. Role of information for effective functioning of the healthcare
system. International scientific-practical conference "Education and
Science - 2006", Dnepropetrovsk "Science and Education"
(Ukraine) together with "Rusnauchkniga" (Russia), Dnepropetrovsk,
2006-PL 0.21
6. The Ministry of National Economy of the Republic of Kazakhstan, the
Committee on Statistics, express information "Cash expenditure on health -
2013-2014 year», http://taldau.stat.kz/ru/NewIndex/GetIndex/2971915
7. Site of the magazine «Exclusive», Issue 4 February 2014., Http://pravo.zakon.kz/4600786-v-kazakhstane-budet-vvedeno.html