Bakhtiyar
Balzhan Torepashkyzy
Candidate
of Technical Sciences, senior teacher of AUES
Thermodynamic bases of regenerative heating of feed water on thermal
power plant
The thermodynamic essence of a
regenerative cycle can be understood by consideration of change of a condition
of steam in ideal steam-power installation. Thus it is supposed that heaters
have no resistance of transition of heat through a wall.
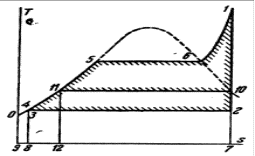
Fig. 1 Ts-diagramma of a
cycle of Renkin and regenerative cycle.
The amount of heat turned into
mechanical energy is measured by the area of the closed cycle 3-5-6-1-2-3 curve.
The ideal regenerative cycle can be imagined as follows. Let's say that all
steam which came to the turbine repeatedly to be taken away from it heaters of
feed water and comes back to the turbine. When passing via the turbine of
couples extends adiabatically. When passing through heaters of couples it is
partially condensed, heating water in a heater to temperature of saturation of
the heating steam. Such cycle is represented in Ts coordinates in fig. 2
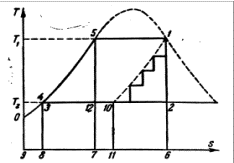
Fig. 2 Ts-diagramma of a
limit regenerative cycle.
At infinitely large number of
removals of steam process of alternate expansion of steam in the turbine and
partial condensation in heaters to be represented by the line 1-10. Such cycle
is called as a limit regenerative cycle. The amount of heat transferred to feed
water is represented of 1-2-6-11-10-1, and it is supposed that water heats up
to boiling temperature in a copper.
Heat turned into work is represented
of 3-5-1-10-3 and will be less, than in Renkin's cycle. The amount of heat
brought in a cycle to working substance is represented of the 8-3-5-1-10-11-8.
This area is much less, than Renkin's cycle, due to heat of feed water. The
efficiency of a limit regenerative cycle makes:
Also equals to thermodynamic
efficiency of a cycle of Carnot.
In the valid regenerative cycle to
be taken away from an intermediate step of the turbine only some part of steam
which is completely condensed in feed water heaters. Change of a condition of
this part of steam is shown in Ts coordinates in fig. 1 and coincides with
process of a cycle of Renkin for purely condensation installation, except for
condensation process which proceeds with more high pressure and according to
more high temperature. Process of condensation of the selected steam is
represented direct 10-11. The area of the closed curve 10-11-5-6-1-10
corresponds to amount of heat turned into mechanical energy.
Warmly selected steam it is used at
first in the turbine where it makes work, and then it is transferred to water
with which comes back to the steam generator. Thus, warmly fulfilled steam of
regenerative selections of the turbine it isn't lost in the turbine condenser
with the cooling water, and remains at power plant; being transferred to
condensate or feed water, it is as if restored, regenerated.
Thermal profitability and power
efficiency of regenerative heating of water is defined, therefore, by reduction
of loss of heat in the turbine condenser (in comparison with the elementary
condensation power plant without regenerative heating of water) owing to
selection of part of steam for the specified heating. Therefore, the efficiency
of steam-turbine power plant thanks to regeneration increases. Thus production of electric energy as a result of work
of steam of regenerative selections in the turbine is essential. The
regenerative heating of the main condensate and feed water is one of the most
important methods of increase of profitability of modern thermal power plants.
Thus the main condensate is understood as a stream of condensate of working
steam from the condenser to the deaerator, and as feed water - a stream from
the deaerator to a copper (steam generator).The regenerative heating is carried
out by the steam which fulfilled in the turbine. The heating steam, having made
work in the turbine, then it is condensed in heaters. The warmth of phase
transition which is marked out with this steam comes back to a copper.
Depending on initial parameters of steam and number of selections of steam on
regeneration relative increase of efficiency of the turbine plant due to
regeneration makes from 7 to 15% that is comparable to the effect gained from
increase of initial parameters of steam in front of the turbine.
Regeneration can be considered as
process of the combined development of energy with internal consumption of
warmth of steam which is selected from the turbine. The regenerative heating of
water reduces loss of warmth with the fulfilled steam in the turbine condenser.
Abstracts of thermal power plant.
LIST OF REFERENCES
1.The review of the market of thermal
pumps in Sweden, Finland.//AVATARS, 2002, No. 1, page 40-41.
2. Antonio Bridanti. Thermal pumps in
premises.//AVATARS, 2001, No. 5, page 24-32
3. Petin Yu.M. Experience of decade of
production of thermal pumps in JSC Energiya.//Power policy, 2001, Vyp.3, page
28-33.