Экология/6. Экологический
мониторинг
Sailaukhanuly Ye., Kenessov B.N., Kamysbayev D.H.
Center of Physicochemical Methods of Research and
Analysis,
Al-Farabi Kazakh National University
Determination of DDT in water using solid
phase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography mass spectrometric
detection
Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane
(DDT) is a known insecticide, which was first synthesized in 1874, insecticidal
properties of DDT were found during the Second World War. By the middle of
1980s in the world produced about 3.5 million tons DDT [1].
DDT
has mutagenic and carcinogenic properties, is a poison the central nervous
system. Causes pathological changes in the liver and kidneys of animals. It has
a cumulative effect. Retained in the bodies of up to 20 days [2]. Of particular
concern raised when DDT was detected in breast milk. The ability of DDT to
accumulate in human adipose tissue and produce high residual toxicity was the
cause of termination of production of DDT in the 70-80s by the highly developed
countries [3].
DDT
is very persistent in the environment, the half-life ranges from 2 to 25 years.
In the environment, DDT can break through the biotic and abiotic ways. DDT in
soil can also be deployed. Movement of pesticides in soil can occur by
leaching, runoff and volatilization. Over very long periods of time DDT may be
able to eventually leach into groundwater, especially through soils with little
soil organic matter [4].
The
method of solid phase microextraction is clean and rapid method compare to
other methods using a large quantity of organic solvents [5].
The fiber 100 μm
polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) was selected for determination DDT, as DDT has a
high octanol-water and slightly soluble in water [5]. This PDMS fiber is the
most optimal for the direct extraction of DDT from aqueous samples. DDT was
extracted with direct input fibers in water 60 minutes with constant stirring. GC–MS analyses were carried out using an Agilent
6890/5973 N (Agilent, Santa Clara, USA).
We
obtain the calibration dependence of the peak area of DDT
concentrations in the concentration range of 10-1000 ng/L methods SPME/GC/MS (Figure
1). Dependence described by the following equation:
S = 0.0616 x CDDT
Where,
S - area of the peak of DDT, × 10-3 and CDDT
- the concentration of DDT ng/L.
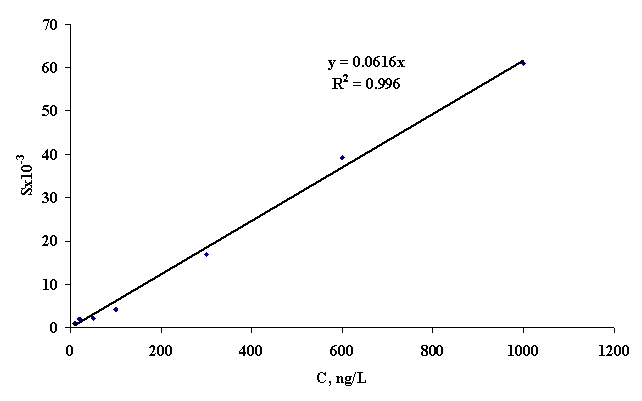
Figure 1 - The calibration dependence of
the peak area of DDT concentrations in water
Approximation
coefficient (R2) was 0.996. So, during experiments, the optimal
parameters determinations of DDT were optimized by SPME/GC/MS. The method has
been successfully tested water samples contaminated with DDT.
References:
1.
V.A.Isidorov. Introduction to chemical ecotoxicology. - St. Petersburg. -
HimIzdat. - 1999. – 140 p.
2.
M.D.Shvaiko. Toxicological Chemistry. - Moscow. - "Medicine". -1975.
376 p.
3.
G.Fellenberg. Pollution of the environment. Introduction to environmental
chemistry. - Moscow. - Mir. - 1997. – 232 p.
4. Sh.U.Kahn, Fundamental Aspects of
Pollution Control and Environmental Science 5. Pesticides in the soil
environment. Elsevier scientific publishing company, New York, 1980, 240 p.
5. J.B.Pawlyszin, S.Magdic, Analysis of
Organochlorine pesticides using solid-phase microextraction. Journal of
chromatography A, 723 (1996), p.111-122.