Ýêîíîìè÷åñêèå íàóêè /5.
Óïðàâëåíèå òðóäîâûìè ðåñóðñàìè
Master’s degree student Sultanovà A.A.
Karaganda Economic University Kazpotrebsoyuz
THE TENDENCY OF HUMAN RESOURCES’ DEVELOPMENT IN SOCIAL ORGANIZATIONS
"An
important aspect of modernization - the creation in Kazakhstan effective public
management of social processes, constructed” vertical "and"
horizontal", a professional body of experts and managers at all levels of
government." [1]
N.
Nazarbayev instructs to develop and submit comprehensive proposals to improve
the efficiency of public management of social processes, including planning,
coordination, analytical support, partnerships with non-governmental sector,
etc. In his address to the people of Kazakhstan from January 29, 2010 Head of
State talking about the components of the Strategic plan for the Development of
Kazakhstan till 2020, said: “We have to invest heavily in the future for
improving the competitiveness of human capital."[2]
Social
services in the market today offer a variety of services such as education,
medical services, utilities, etc. On the market today is quite a wide selection
of services, then there is a high level of competition, where the main
objective of any organization providing services is a broad the task of
attracting customers by providing quality services. Quality of service mainly
depends on the qualification of the personnel and the organization plays an
important role here effectiveness of human resource management. Consequently,
the effective management of human resources is one of the most important
functions of an organization of social spheres.
The question of human resource management is sick for any organization. There
are many organizations where staff numbers "do not pull" the quality
of work and without some of the staff could do with proper load distribution,
given the potential of each employee. It is thus possible to increase the productivity
and quality of work, reducing the cost of "unnecessary" footage, and
savings, for example, to pay to other employees in the form of differentiated
pay, which would serve as motivation to work.
In our
country's economy is dominated by the service sector, rather than production.
If most of the income it brings services, it is necessary to improve the
industry by improving the quality of service, and what can be achieved through
effective management of human resources, as it provides alignment of staff
capabilities and objectives, strategies, conditions for the development of the
organization.[3]
Modern personnel policies should be consistent development strategy of the
organization and lead human resources in line with its strategy. The personnel
policy currently make integration of personnel management with the business
strategy, the increasing role of the individual worker, knowledge and
motivation of group setting workers and their ability to be formed in
accordance with the development strategy of the organization. Human
capabilities are crucial in achieving these goals.
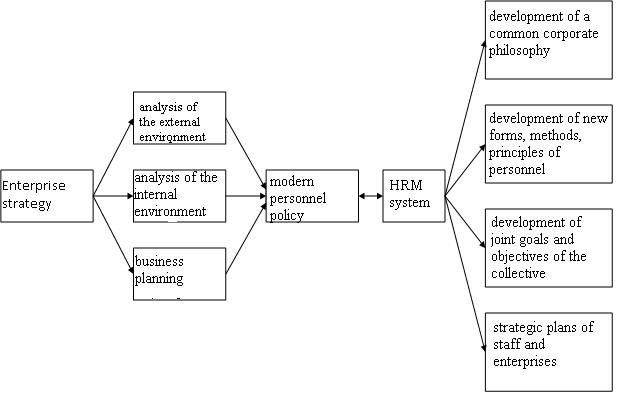 Not e - Compiled by Utarbaeva G.K. [4]
Not e - Compiled by Utarbaeva G.K. [4]
Figure
1 – Strategy and system of human resources in the enterprise
Human
resources management system, composed by Utarbaeva G.K. [4], shall consist of
the items presented in Figure 2. Such a control system, according to the
author, is the most viable in any organization.
Very
important element of human resource management system - is the management of
investments in human capital. It includes the training of personnel in
educational institutions, training of management personnel abroad,
communication with schools on a "Fair specialists", providing places
to practice in organizations with further employment. This element in modern
organizations has received little attention, and he was not assessed by the
management organization properly.
Development
of market relations in Kazakhstan has put forward to the economy of our country
a number of fundamentally new issues related to new approaches to the use of
human resources.
The modern concept of the development of
production is that the maximum productivity, quality and competitiveness can
only be achieved with the participation of each employee to improve the
production process initially in the workplace, and in the future in the
organization as a whole. Employee involvement in the process of improving
production and creates a creative environment is a powerful motivator for staff
to work that allows each employee to maximize their experience and creativity.
With the development of market relations
and increasing forms of management there is an urgent need for the development
of an appropriate organizational structure, a clear division of functions,
powers and responsibilities between the government on its levels, as well as
the development and breeding of a new formula for success of a new model of
human resource management in the social sector.
During the years
of independence, Kazakhstan has established a strong foundation of the welfare
state. The country has come close to the quality level of social development of
Central European countries. [1] The new stage of development of the country,
mainly consists of a number of new challenges to strengthen the economy and
improve the welfare of the people, on which a decision should be oriented all
state agencies. [2]
Kazakhstan aims
to become one of the fifty most competitive countries in the world that
requires a deep scientific study of human development issues, in particular
relating to the prospective development of labor relations and employment. It
is necessary to promote attraction of investments into innovative sector of
economy, increase in employment and improvement of competitiveness of small and
medium business. [18] Government regulation and self-regulation of labor
relations and employment based on the principles of new major economic activity
of the population, corresponding to changes in the forms of ownership. The main
purpose of market production is to maximize profits. The state is largely gone
from the regulation of social and labor relations outside the public sector.
This retreat of the state was motivated by the perception that the market
performs self. However, experience in market development shows that the market
is unable to provide social orientation and often works against the interests
of employees. [11] That is why Kazakhstan is vital to find a balance between
economic success and providing public goods. This is a key task of
socio-economic modernization.
System of labor
relations in Kazakhstan at the stage of market economy, especially in times of
crisis is approaching its characteristics to a model of labor relations in the
United States. Workers in enterprises can be dismissed if necessary reduction
in the labor employed or curtailment of production, low covered by collective
agreements, insufficient attention is paid to training in-house. Such a policy
of firms leads to a high mobility of workers.
For today's
socio-economic conditions in Kazakhstan characterized by high cost of housing,
lack of a developed housing market prevailing mentality of the population and
an underdeveloped market of educational services available is difficult to
expect that in the medium term, a significant majority of the population will
be highly mobile. In this situation, Kazakhstan is more acceptable European
experience and system of labor relations characterized by lower mobility of the
population, but the higher the regulatory role of the state. An important
component of the European system is the active development of the education
system and lifelong learning based on the principle of social partnership - chetyrehpartism where the educational system has become a full
partner and joins the traditional system of tripartism. The current practice of
career opportunities in European countries is based mainly on the growth line
training of employees. Modern regulation of labor relations involves the
following tasks: to promote the flexibility of labor relations and employment
and to ensure the accumulation of human capital, adequate protection of
employees from risks in the labor market. [12]
Kazakhstan
promising in this regard is the use of "European Concept of flexibility
and security in the labor market", which envisages the creation of a basic
social protection systems capable of doing more flexible both companies and
workers who do not fall back into poverty, being unemployed or being employed
part-time (as they receive some support). This concept is realized through the
active use of the mechanisms of social partnership and social dialogue on the
European model.
Principle of
social partnership aims to harmonize the different social group interests and
regulation of conflicts between them in a civilized manner through enhanced
activity of institutions of social partnership, the development of the practice
of social dialogue and the development of mechanisms and procedures for
approval and regulation of interest acceptable to the social partners.
Policy of the
institute of social partnership is not oriented to ensure that any means to
move away from labor conflict, and then to guide these conflicts in a
constructive direction. This requires advanced development institutions to
resolve collective labor disputes.
Area of legal
regulation of labor relations includes the following main areas: state
regulation of wages and labor regime, setting standards for working conditions
and responsibility for their violation. In today's labor laws are an important
part as government guarantees for the reproduction of the essential components
of the employee and the conditions of its life support [13].
In Kazakhstan,
the legislative provision of the development and reform of labor relations has
received considerable attention. Since the beginning of
democratic reforms and the transition to a market economy, which resulted in
conflict situations, especially at work, December 19, 1994 President of
Kazakhstan Nursultan Nazarbayev, the Resolution "On social partnership in
the field of socio- economic and labor relations." A tripartite commission
established at the national, sectoral and regional level.
For consideration
and approval of the draft general and tariff agreements between the Government
of the Republic of Kazakhstan, trade unions and employers' associations and
entrepreneurs Government Order dated 24 August 1992, a special working
committee, and then Republican conciliation commission for the settlement of
collective labor disputes (conflicts). In July 1993, the three main parties
signed a joint cooperation declaration on the basis of cooperation. Given the
importance of social dialogue, the President of the Republic of Kazakhstan
signed a decree on 14 December 1994 "On social partnership in the field of
socio - economic and labor relations", which was provided for continuous
dialogue between the parties. From that moment began the development of social
partnership with the new socio-economic situation in Kazakhstan. Decree was determined
by the need to conclude, sectoral and regional agreements. Since that time the
Republic was concluded and implemented eight general agreements. One of the
legislation on this subject was the Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan "On
Social Partnership in the Republic of Kazakhstan ", adopted in December
2000. In 2007 he was drafted and adopted a new Labor Code, which meets modern
requirements of regulation of labor and employment. Since the introduction of
the Labour Code was declared invalid number of legislative acts:
• Law of RK
"On Collective Contracts";
• Law of RK
"On collective labor disputes and strikes";
• Law "On
labor in the Republic of Kazakhstan";
• Law "On Social
Partnership in Kazakhstan."
In the period
from 2009 to 2011 it made a number of additions and corrections.
With the adoption of regulatory legal act of social dialogue partners acquired
the status of an institutional mechanism. Labor Code enacted mechanisms to
ensure the equal dialogue between the parties, as well as the procedure for
forming tripartite bodies at the national, sectoral and regional levels and
their basic functions [4].
In addition, the
legal framework of the Republic establishes liability for failure to comply
with conditions of social partnership, decorated collective agreement or
agreements, as well as the responsibility of employers who evade social
dialogue with their employees.
Speaking on the
institutional maintenance of social and labor relations, it should be noted
long-term cooperation of the Republic of Kazakhstan and the International Labor
Organization (ILO).
The most complete
idea of social partnership have been developed and implemented in the
theoretical and practical work of the International Labor Organization (ILO).
This is the oldest international organization established in 1919, over the
decades of its existence has not only created an expanded concept of social
partnership, but in essence was the highest link regulation of labor relations
in the global labor market. Since then, the term "social partnership"
received formal citizenship and introduced into a scientific revolution.
The most
important achievement of the ILO lies in the fact that it carried out its
activities and exercises based on tripartism, i.e. equal participation in all
discussions and the adoption of conventions and recommendations of the representatives
of the "three-piece": government, employers and workers. Tripartism
in ILO activities and provide a basis to formulate the principles of social
partnership.[8]
Kazakhstan joined
the ILO in 1993; in 1995 the ILO works Representation in the Republic of
Kazakhstan. The ILO promotes the ratification and enforcement of international
labor standards through the development of policies and technical assistance
through the provision of advice, recommendations, and other orientation and
training programs. [7]
Kazakhstan has
ratified all the ILO Conventions on basic human rights, which include the
Convention concerning freedom of association and collective bargaining (Convention
number 87 and number 98 ), forced labor (Convention number 29 and number 105),
equality of opportunity and treatment (number Convention number 100 and 111),
child Labor ( number 138).
Currently, the
Ministry is working on the ratification of ILO Convention 1952 on maternity
protection.
Given the
priorities of the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan in May 2000 signed
the first program of cooperation between Kazakhstan and the ILO for 2000-2001.
In Geneva,
representatives of the three parties of social partnership of Kazakhstan signed
a program on decent work with the International Labor Organization for 2010 -
2012 years. This program was a continuation of previous programs of cooperation
in the field of social and labor relations in view of the global financial and
economic crisis, which is guided by the Millennium Development Goals and the UN
Development Assistance Framework for the provision of development assistance
(UNDAF).
The program is
based on the national priorities identified in the Strategy of Development of
Kazakhstan till 2030, medium-and long-term strategies of the government, such
as the Concept of Transition of Kazakhstan to sustainable development in 2024
and the Strategic Plan of the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the
Republic of Kazakhstan for 2010-2014. The Programme clearly defined key
performance indicators and strategies needed to achieve the goals and outcomes
in three areas:
- Regulation of
labor relations in accordance with international standards;
- To facilitate
effective employment and social protection for men and women;
- Further
development of trilateral cooperation and social dialogue. [16]
Today, improving
the system of social partnership and social dialogue is extremely important to
improve the efficiency of social policy.
Proof of this was
the Declaration adopted in 2009 in Almaty, the Ministers of the states of
Eastern Europe, Central Asia and Turkey establishing targets to address the
social consequences of the economic crisis.
Constructive
cooperation of the ILO and the tripartite partners of the Republic of
Kazakhstan on the implementation of the program will provide results and
positive changes in the field of social and labor relations.
Therefore, we can
state that was created in Kazakhstan, operating and developing the regulatory -
legal framework for the social partnership.
However, the
situation in the economy and the labor market due to the crisis require further
revision of certain provisions of the labor legislation. In this regard, a
proposal for the reform of the labor legislation, which is a mechanism of
regulation of labor relations, is proposed to introduce the draft documents
relating to the development of human capital.
Further reform of
the labor legislation aimed at promoting:
• increase the
flexibility of labor relations, their adaptability to changes in economic
conditions;
• improve the
territorial, sectoral and occupational mobility of labor;
• gradual
replacement of the informal labor relations and expand the scope of registered
employment ;
• reduce
long-term, long-term unemployment;
• increase the
level of remuneration and its share in the national income, the gradual
approximation of the level of wages of public sector employees to the level of
labor remuneration budget sphere;
• reduction of
occupational accidents and diseases;
• strengthen the
real protection of fundamental labor and social rights of the employee;
• improve
productivity;
• an overall
reduction of social tensions , translation of labor conflicts in the legal
framework of collective labor disputes. [12]
Labor legislation
is necessary to put more emphasis on promoting sectoral and territorial labor
mobility, improving their quality and creating new jobs, taking into account
their cost-effectiveness.
An important
condition for the further reform of labor legislation is to use the
recommendations and decisions, as well as draft documents developed and
reviewed by the social partners.
Given the above,
it should be recognized that the system of labor relations in Kazakhstan mainly
built, but it is far from perfect and needs to be reformed. Labor relations in
Kazakhstan stage of market economy and, especially at the stage of the financial
crisis and coming out of it, characterized by inadequate regulation. The
private sector added almost complete absence of institutions that protect the
rights of hired workers if the public sector is due to a greater extent
macroeconomic problem (bankruptcy and late payments). In this regard, the
principle of social orientation in state regulation of labor relations and
employment , being developed and enshrined in legislation and regulations can
be applied at all levels of regulation (corporation, region, sector, etc.),
providing social protection for workers and their well-being.
References:
1. Nazarbayev N.A.
"Social modernization of Kazakhstan: Twenty Steps to a society of
universal labor"
2. Message from
the President of the Republic of Kazakhstan - Socio-economic modernization -
main direction of development of Kazakhstan, January, 2012
3. S. Beres
Theoretical aspects of the regulation of labor relations in the market system.
/ Work in Kazakhstan. - ¹ 12. -2009. - With. 2-6.
4. Autoabstract Utarbaeva G.K. -
Improving human resource management
in the enterprise - Almaty, 2008/
5. Labor Code of
the Republic of Kazakhstan. - Almaty LLP "Publisher" Norma -K",
2011. - 128 p.
6. Modern Labor
Economics: Monograph/ lead author of the V.V. Kulikov. Institute of the RF
Ministry of Labor (Labor Research Institute ) . Moscow: ZAO" Finstatinform",
2001. - 660.
7.Odegov J.G., P.V.
Zhuravlev Personnel Management: Textbook for universities. - M.: Finstatinform,
1997. - 878 p.
8. Labor
Economics: Labor Relations. / Ed. N.A. Vogina, J.G. Odegova. - M.:"
TEST", 2002. -736 With.
9. V.A. Vaysburd Labor
Economics: Textbook / V.A. Vaysburd - M.: Publishing house
"Omega-L", 2011. - 376 p.
10. Genkin B.M.
Economics and Sociology of Labour: A Textbook for high schools. - 5th edition,
ext. - Moscow: Norma, 2003. - 416.
11. Ostapenko Y.M.
Labor Economics: Textbook. Allowance. - 2nd ed., - M: INFRA-M, 2007. - 272.
12. D. Shajkin.
Features of formation and development of labor relations in the framework of
social partnership in the Republic of Kazakhstan. / Work in Kazakhstan. - ¹ 3,
2009. - With. 2-5.
13. V. Mozharova.
Basic principles of the modernization of labor relations and employment in
Kazakhstan. / Work in Kazakhstan. - ¹ 6, 2010. - With. 2-8.
14. Labor Code of
the Republic of Kazakhstan. Itemized practical comment. - Almaty LLP "
MCFER Kazakhstan", 2007. - 816.
15. Ministry of Labor
and Social Welfare. Mode of access: http://www.enbek.gov.kz.
16. Kiselev I.J.
Comparative and international labor law. Textbook for high schools . - Moscow:
Delo, 1999. - 728 p.
17. Program on
decent work in the Republic of Kazakhstan for 2010-2012. Ministry of Labor and
Social Welfare. Electronic resource. Mode of access: http://www.enbek.gov.kz
18. Ñèõèìáàåâà
Ä.Ð. Ïðèîðèòåòû èíâåñòèðîâàíèÿ íåôòåãàçîâîé ðåíòû // «International journal of
experimental education», ¹10, 2013. Ñ. 145.