UIC 669.017
STUDYING of ACTION of NOISE
ON the EAR
Batesova F.K. - сand. tecn.
sci., ass. Professor, Kazakh National Technical University after
K.I.Satpaev
Satybaldieva N.K. -
сand.
tecn. sci., ass. Professor, Kazakh National Technical University after
K.I.Satpaev
Akhmetov A. - the
magister of Kazakh National Technical University after K.I.Satpaev
Abstract: the conclusion about
pathognomonic downturn on С4096 for professional
dull of hearing and for a sharp acoustic trauma from here arises. Results of
short-term influence producing noise which have been received on some
manufactures are of interest. After 15-minute stay in a boiler during it
riveting or stampings three persons
with normal hearing reacted downturn of perception of some sounds with significant
individual differences: at once the greatest downturn on С128, at another - on С4096, at the third -
only on С128 is noted.
Keywords:
acoustic, noise, acoustic trauma, vibrating trauma, sensoring corresponding
tones.
The acoustic trauma is the
reason of defeat of acoustical function at enough significant number of
persons, lading with deafness which arises at action on an ear of sounds (noise)
of excessive force and duration. Force of noise 70-80 db is border above which
there is a danger of defeat of an acoustic analyzer, in particular if in noise
prevail high tone (1000-6000 Hz). Low sounds are the least harmful as
sensitivity them is very small.
Harmful action of noise on an
ear is in details studied in experiment on animals and proved, that under
influence of long influence of strong sounds in a snail advance there are
changes on duration all nevron: spiral organ, nervous cells of spiral ganglion
and nervous fibres of an acoustical nerve. At especially long influence there
is an atrophy of all spiral organ besides under influence long noise impact quite often there are changes
in the central nervous system (neurosises, the feeling of weariness, downturn attention,
etc.).
The noise trauma is observed
at persons, is long working in conditions of strong noise. Sometimes the
acoustic trauma arises by accident, sharply, even at short-term influence of
sharp high sounds (for example, a locomotive whistle) or very strong sounds
(for example, noise of the jet engine). It is accompanied by a pain in ears. At
shots harm of influence on an ear develops of an acoustic and air trauma.
Strong explosions cause changes from an internal ear. The vibrating trauma is
closely connected with acoustic. It arises from concussions (vibrations) which
represent infrasound. Concussions arise at work of machines with the big speed,
and also on transport (the car, the railway). The vibrations tested for a long
time, have harmful an effect on all organisms, including on an ear, through
fabrics of a body, especially bone system. In experiment on animals degenerate
changes are found in the internal ear, localized in cells spiral ганглия, mainly in the top curl of a snail, and also in
kernels of the acoustical and vestibular analyzer. However these changes are
expressed much more poorly, than the changes caused by influence of noise.
The air trauma (barotraumas)
is caused by increase or downturn of atmospheric pressure and its especially
fast differences, i.e. fast fluctuations of pressure. The most sensitive to an
air trauma are the drum-type cavity and an internal ear. At explosions, shots
the air trauma is combined with sound. At a blast wave with additional pressure
⅓-½ of atmosphere here is a break of an eardrum.
Researches
of a frequency spectrum of noise and on separate manufactures show audiogram of
workers and their comparison, that prevalence in noise of those or other sounds
does not influence on character relative deafness. So, the frequency spectrum
of noise in boiler shop, on G.L.Navyazhskomu, gives for sound C512 and С1024 maximum loudness
(90 dB), and for С2048 and С4096 - only 30 dB. On a
weaving mill the maximal loudness in 80 dB give just С2048 and С4096; meanwhile
audiogram on the character at weavers and boliermakers it is identical.
Proceeding from a frequency spectrum and the account of loudness of noise of
boiler shop, it would be possible to expect first of all downturn of perception
on С512 and С1024 -Meanwhile downturn of perception of these
sounds, as a rule, comes much later, than perception of higher sounds; the
degree of downturn on these tones also is less. The Same position is established
at pilots. According to Armstrong, in a spectrum of noise of the piston plane
(bomber) prevails a low-frequency component. On the intensity it surpasses
sounds in 1200-2400 vibrations in a second more than on 20 db, sounds above
2400 fluctuations in a second absolutely are absent. Meanwhile defeat of hearing
at pilots begins with 4096 fluctuations in second and perception most of all
suffers on this sound. When occurs actions of pure tones of a sound,
localization of defeat in a snail does not depend, as it is shown in a number
of experiments, from height of applied tone. Н.Ф. Priests has found out pathologic changes in the basic curl of a
snail at impact on an ear of the white mouse a low sound (100 fluctuations in a
second). Marx at influence by pure
tones has found out in a snail of change not only in a zone, sensoring corresponding
tones, but also on both parties from it, and the degree and distribution of
these changes were in a direct communication with force of a used sound and continuance
experience. Experience of Vitmack with using
powerful pure tone in 2048 fluctuations in a second as a result of which there
was a full destruction spiral organ, ganglionic cells and nervous fibres, i.e.
the changes similar to what were observed at an experimental sudden air push stapedius
in an internal ear, shows, that at a powerful sound the mechanism of influence
on an internal ear has a little the general with physiological conditions. It
is revealed in an internal ear of animals after influence of ultrasounds
significant histologic changes in the form of haemorrhages, damaging of spiral
organ, tearing off otolithic membranes and following degenerations of the
damaged cells (R.A.Zasosova and V.F.Unndritsa's research) [1].
Results of works of
L.E.Komendatova are interesting. In pathogenesis traumas it attributes a main role to trophic central influences, originate
in reply to sound irritation. These influences realize on the trophic nervous
fibres going to spiral organ. These return fibres, in its opinion, adjust a
condition not only irritated by a sound of region of spiral organ, but also
wider. Dependence of downturn of hearing on frequency, intensity of tone and
duration of its influence is represented enough complex. Restoration of hearing
usually begins quickly and then all accrues more slowly. Full recovering
hearing at its loss on 60 db demands 4-5 days. The most the hearing for
frequencies about 4000 fluctuations [3] is slowly restored.
In connection with late
researches have begun express opinions on special acoustic properties of noise
as it gives the picture of defeat considerably differing a picture of defeat at
influence by pure tones. That difference consists that at noisy relative
deafness there is a failure on С4096 or its isolated
downturn perception. For an explanation of this failure the hypothesis about
the special pressure tested by a site basic membrana, perceiving С4096 is offered at
irritation with noise. In opinion of Fouler, on this site there is a joint of
turbulences of perilymph, occuring as has shown Bekeshy on models, at influence
of intensive sounds. That circumstance is interesting, that it’s limited defeat
С5 is observed not at
influence of pure tones, namely noise. The conclusion about pathognomonic downturn
on С4096 for professional dull
of hearing and for a sharp acoustic trauma from here arises. Results of
short-term influence producing noise which have been received on some
manufactures are of interest. After 15-minute stay in a boiler during it riveting
or stampings three persons with normal
hearing reacted downturn of perception of some sounds with significant
individual differences: at once the greatest downturn on С128, at another - on С4096, at the third -
only on С128 is noted. Reaction
of an ear of working these noises trades differed greater various. First of
all, at a part of workers after the 8-hour working day of any changes in a
condition of hearing not came, and at the some people the perception of
separate tones, mainly low, even improved. Alongside with it watching and
peracute downturn, mainly at persons with the small experience of work.
Downturn of hearing within day (the hearing was measured some times: In 30
minutes of work, after 2 and 4 hours) gave rather greater fluctuations on
separate tuning forks or on everything, reaching up to 40-50 % to continuance
their sounding. It is impossible to note prior downturn on С4096. Between fatigue
of an ear and its defeat after long influence of noise, it’s impossible to draw
analogies as concerning the mechanism of development and character underlying
downturn of acoustical function of processes, and concerning their
localization. Certainly, elements of fatigues and defeats can be and
simultaneously; however after short rest the first can disappear completely,
the second - remains proof. The rations between expressiveness of each of these
elements can be various. At of some the workers having the big experience work
in noisy shop, it is not visible an appreciable difference between sensory
acuity before long rest and after it. The phenomenon of fatigue is shown mainly
at young workers. As a result of the researches it is established, that the
sharpest deterioration is available for workers with almost normal hearing; at
the big downturn of hearing deterioration is rather insignificant, absolutely
is absent or even small improvement is marked.
These conclusions prove to be
true, data of Ruade and Furer,
established audiometry [1]. Audiograms
were removed first time on Friday in the evening after a week of the work,
second time on Monday in the morning after 1; 60-hour rest and third time -
this very day in the evening after 8 business hours. The appreciable difference
between the audiograms which have been removed before work, is available only
for the young worker (the experience 2 years); at two other workers with the
experience of 10 and 16 years of work which have an expressed degree of
professional relative deafness, small fluctuations of hearing to be in
physiological limits (figures 1-3).
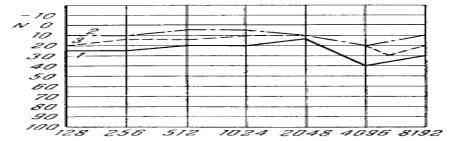
Research of hearing: 1 - on
Friday in the evening; 2 - on Monday in the morning;
3 - on Monday in
the evening
Figure 1 - the Worker of 17 years, the experience of work 2 year
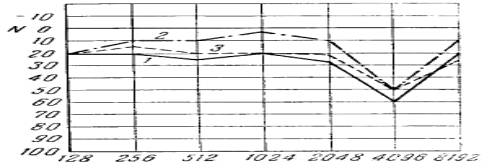
Research of
hearing: 1 - on Friday in the evening; 2 - on Monday in the morning;
3 - on Monday in
the evening
Figure 2 - the
Worker of 28 years; the experience of work of 10 years
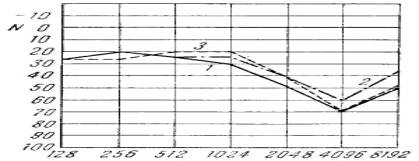
Research of
hearing: 1 - on Friday in the evening; 2 - on Monday in the morning;
3 - on Monday in
the evening
Figure 3 - the
Worker of 32 years; the experience of work of 16 years
The literature
1 Темкин Я.С. Глухота и тугоухость. – М.:
Государственное издательство медицинской литературы «Медгиз», 1957. – 426
с.
2 Сулеев Д.К., Утепов Е.Б., Акубаева Др.М. и др. Проблемы снижения
шума в городах. Материалы пятой Международной научно-практической конференции
молодых ученых. Алматы: КазНТУ, 2002. Ч. 2.–728 с.