Prof.,
DScTech Sarguzhin M.Kh., prof., DScTech Dzhienkulov S.A., prof., DScTech
Sazambaeva B.T., postgraduate Imangaliyeva A.E.
Institute
of Industrial Engineering named after A. Burkitbaev
Kazakh National Technical
University named after K.I. Satpaev
Almaty, Kazakhstan
IMPROVEMENT
OF CONVEYER INSTALLATIONS FOR LUMPY CARGO
Abstract: In this arider considered the ways of
improving belt conveyors and loading device for lumpy cargo.
Nowadays, in the open
pits of the country about 10 billion tons of rock mass is produced annualy. A
large number of mining equipment were employed in the process of developing
half-rock and rock species. The most widely used as a means of mass transport
are conveyors. High performance, low power consumption, the ability to fully
automate the transport processes and environmental cleanliness make this kind
of transport more effective for companies with a large goods turnover [1-11].
In belt conveyors the
traction element is an endless transport belt.
Belt conveyor consists
of a frame with two terminal drums: driving and tightening, turned with endless
belt, the upper arm of which moves the material. Carrying rollers support the
upper arm of the belt (the carrier), and the carrying rollers support the lower
arm (idle). Deflecting drum increases the angle of wrap of driving drum with belt.
(Fig.1).
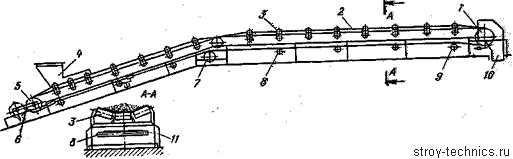
Figure 1 - The belt conveyor.
Advantages of belt conveyor:
• great length of
transportation;
• long lifetime
(10-15years) by reducing the load on it;
• low coefficient of
resistance movement (0,015-0,02);
• compared to belt
conveyors the specific energy consumption (30% -40%) and metal consumption line
part is less(2-3 times).
Disadvantages:
• Limited lumpiness of the rock mass;
• relatively short lifetime of ropes (up to 7-8
thousand per hour).
Conveyors in the usual
performance are not adapted to move the mountain cargo with pieces having
dimensions over 300mm. This is due to the fact that in the process of rolling
the belt with cargo on roller carriages, dynamic shock is transmitted, causing
its destruction. Using absorbing roller carriages, flexible rope; reduction of
step arrangement of carrying rollers, increase the belt tension - all these
known means of reduction of dynamic loads are not effective enough, though it
can increase the permissible size of the pieces to 400 -500mm.
Improvement of belt
conveyors with fixed carrying rollers towards their fitness for transport of
rocks and ores is carried out in recent years in two directions: on the one
hand, to increase the strength and durability of carrying roller and conveyor
belts, on the other hand, the use of hanging rollers of daisy type (with swivel
fixtures of roller axes) and flexible rope for the purpose of depreciation
dynamic loads in the process of rolling loaded belt on roller carriages.
One of the special
conveyors capable to carry rock mass with dimensions up to 1000mm
directly from the face after blasting work is a belt conveyor on running
supports, the design of which was proposed by prof. A.V.Spivakovskii. [12].
High load capacity and
the ability to move lumpy rock mass with conveyors of this type are achieved
through the fact that, unlike traditional schemes of belt conveyors, where the
upper arm of the cargo (1) rolls along a stationary support rollers, at belt
conveyor with running supports it lies on the arc-shaped crossbars - traverses
(2) with running rollers - wheels (3) at the ends resting on the guide rails
(4) (Fig. 2).
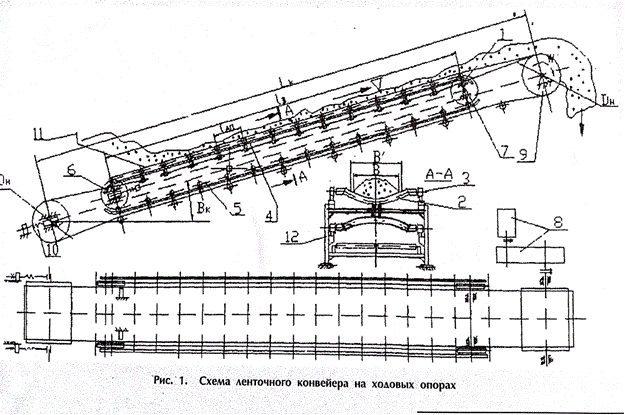
Figure 2- Scheme of belt conveyor with running
supports
Design features of the
conveyer consist in lining the surface traverse, on which cargo branch of belt
is leaned by rubber to improve the grip, and using of two closed chain rounds
connecting traverses and placed inside the round of driving belt. [12].
One of the major
disadvantages of belt conveyors with running supports (conveyor of
A.O.Spivakovskii) is a low efficiency and reliability of the design due to the
support skewness relatively to the horizontal axis, which affects on the
stability and the level of congestion of support elements and descent of
support from guides that does not exclude the possibility of an accident
situation. In addition it should be noted that the connection of arcuate
traverse with flexible body in the form of a chain, limits the speed of
movement of horizontal axis carrying
surface (of belt) and supporting
surface (arcuate traverse’s round).
These design flaws were
fixed in a special conveyor design KazNTU – by belt trolley [13] , with the use
of additional guiding located between the main lateral guidings, and traverses
were made with mounted in the center of the rollers for more
interaction with the guide, wherein each running
support has two rollers installed in series, and
connecting arcuate traverse with flexible element is made of rope, which allows
to increase movement speed of CS with
cargo, hence, productivity of conveyor generally, belt carriage conveyor as a
belt wheel conveyor allows transportation of cargo with maximum size of pieces
up to 1000mm and a capacity of up to 6500 tones per hour at a speed of moving cargo V=2,5 meters per second (due to the application as a flexible part
of ropes instead of chains in belt wheel conveyor ) and width of CS B = 1200mm
(Figure 3).
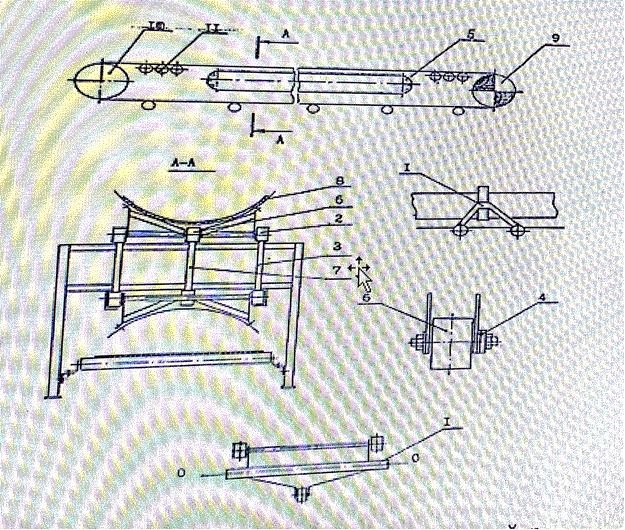
Figure 3- Scheme of rope-belt conveyor
But a carriage belt
conveyor has drawbacks: the limited length and angles, determining factor of
which is the ability to pull the belt.
In KazNTU named after
K.I.Satpayev to increase traction ability, length and angles of a carriage belt
conveyor was offered prospective design
of conveyor installations with a trailer towing carrier belt and draft rope
[14].
Construction of
rope-belt conveyor with an infinite load-carrying belt, freely lying on
supporting arcuate cross arms; upper and lower branches of closed traction
rope; traverse axis made composite with swivel arms and having a
spacer clips for interaction with the driving traction ropes on both sides,
allows to increase adhesion forces between the ropes and the frictional
engagement elements of traverse in both cargo and conveyor idler branches (
Figure 4).
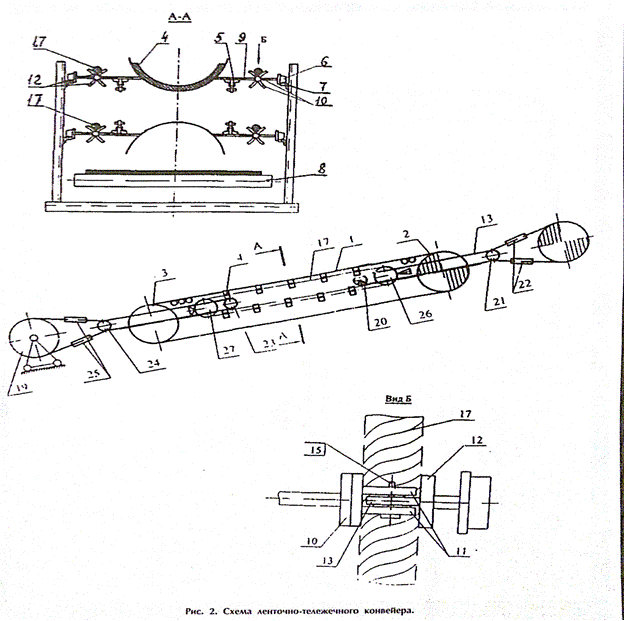
Figure 4. Belt carrying conveyor
Unlike the other
conveyor constructions and a belt carriage conveyor ( KazNTU named after
K.I.Satpayev) this construction of the belt carriage conveyor for the lumpy
cargo can improve efficiency of use of the traction rope by the ability of both
linear along the length of the conveyor, and in drive, while avoiding slip
phenomenon, which in turn provides an increase in the length of conveying of
1.5 ... 2.0 times the tilt angle up to 250 ... 300. Therefore, increasing the
flight length of this belt conveyor carriage to one gear in transporting over
long distances reduces the amount of transfer points from one conveyor to
another. [1,2].
Existing boot devices
have drawbacks that reduce the effectiveness of conveyors: works unsatisfactory
in the presence of moist and sticky goods, does not provide the exit speed of
the transported material from the tray when the physical and mechanical
properties of the cargo is changed; others have a greater height of the load on
the belt[2].
Effective use of
conveyors for lumpy cargo demands perfection of loading device (LD).
The new design of LD
created in KazNTU eliminates the noted deficiencies, provides traffic load on
the described above conveyors for lumpy cargo[15].
A distinctive feature of
the new design of LD for bulk cargoes, transported by conveyors compared with
known designs of tray LD is that tray of curvilinear profile consists of two
interconnected spring-loaded and swinging on parts axes. The upper one of them
is installed on fixed frame with rollers (trolley) connected to flexible link
with the upper swaying part.
Overloading mechanism
consists of three connected with each other moving parts: the upper swivel
tray, inextensible flexible connection between the tray and the trolley, and
set on it the swaying tray.
This design provides
damping of shock pulses from loaded material pieces falling on the upper part
of the tray, which, when it falls it twists the upper part. It will shake it in
its turn, hitting the bottom, thereby eliminating sticking fines of loaded
material.
Improving the efficiency
of LD is achieved by providing a centering and speed regulation of freight
transport of bulk cargo on the output from tray with change in shape of the
trough of the lower tray and additional installation guiding of curved profile
along the longitudinal axis of the tray. The design schemes for new LD were
proposed and obtained according to assess the driving force and displacement of
mechanisms of LD used in the computation of static and kinematic parameters,
there was developed a mathematical model to study the dynamics of LD
mechanisms, the methods of calculating the dynamic of LD of belt conveyors.
Research results of
conveyors for lumpy cargo and loading device can be used by researchers and
designers in the calculation and projection of installations.
The given conveyors are
able to move practically all rock mass, prepared by drilling and blasting way,
and do not require the use of expensive crushing units and additional means of
cyclic transport.
List of used materials:
1. Mulukhov K.K. – “Osnovy
dinamiki i razrabotka konstruktsii i metodov rascheta lentochno-kolesnyh
konveyerov dlya krupnokuskovyh gruzov” – Vladikavkaz, 2000.
2. Sarguzhin M.Kh. –
“Perspektivnye konstruktii konveyerov i oborudovaniya dlya krupnokuskovyh
gruzov”.- Gornyi zhurnal Kazakhstan, 2006.
3. Havelka Z. Moglichkeiten
der Staggering der Betriebszuverlassigkeit und der Arbeitsproduktivitat von
Grobandlagen // Bergbautechnik. – 1987. – Vol. 17, ¹ 12. – Ð. 630-635.
4. Âãàdå Ê., Ìånning G.
Rationalisierung an Grobbandanbagen duzch zmeekmassige Guãtspannungsregelung //
Âergbautechik. -1969. – Vol. 35, ¹ 10.- Ð. 413-419.
5. Lae Ba Toon.
Ustanovleniye tipa I osnovnyh parametrov lentochnyh konveyerov dlya
krupnokuskovyh gruzov: synopsis. Candidate of technical sciences:
05.05.06. – M.:MGI, 1970. -16 p.
6. Vierling P. Messung von
Horizontalkraft und Durchgang in einer Bandanlage mit vergrobertem
Tragrollenabstand // Fordertechnik. - 1969. – Vol. 11, -82 p.
7. Bahr J. Neuts Erkentnisse
beim Antrieb von Forderbanueen // Freiuerger Forschungsheite. –1959. – Vol.
120, ¹ 3. –Ð. 88-101.
8. Hudson W.G. Conveyors and
Related Equipment. New York, USA, 1964.
9. Immer J.R. Materials
Handling, London, 1963.
10. Mining Engineering Handbook, vol.
II, SME, 1973, USA.
11. Multipurpose Transportation System.
“ Mechanical Engineering”, June, 1970,
p. 47-50.
12. Spivakovskii A.O. – “Lentochnyi
konveyer. Avtorskoe svidetelstvo SSSR ¹166272”. – biulleten izobretenii, 1964,
¹21.
13. Dzhienkulov S.A., Sarguzhin M.Kh.,
Bitimbayev M.Zh., M. – “Lentochnyi konveyer dlya krupnokuskovyh gruzov”.- A.S.
RK. ¹5792. Published in 12.05.93.
14. Omarov K.A., Sarguzhin M.Kh. and others
–“Lentochno-kanatnyi konveyer dlya krupnokuskovyh gruzov”- R.K. Conclusion to
the application for a provisional patent 2004/1224.1, ¹16290/02 from 26.09.05.
15. Dzhienkulov S.A., Sarguzhin M.Kh.,
Tuleugaliyeva G.B. Zagruzochnye ustroystva dlya lentochnyh konveyerov.-Almaty:
Prioritetnaya spravka ¹2007/05,07,1 from 13.04.2007. RKKP NIIS RK to the
application for a provisional patent of RK for the invention.