Samarina V.P. PhD
(geography)
Stary Oskol
technological institute «National research technological university MISIS»
Export policy of Russia
as one of the reasons of the economic crisis
The
research is executed at financial support of the Russian humanitarian
scientific fund, the project ¹ 09-02-55205 à/Ö
The influence of global crisis on Russian economy is quite
obvious and natural. For many years Russia pursued a policy of integration into
universal economy and as a result it became the part of global economic and financial
system. Therefore, global crisis processes could not but change institutional conditions
of the development of Russian economy.
There is a fact that does not
give rise to doubt. What is at issue is, one of basic reasons of spreading
of an economic crisis in Russia consists in the heavy dependence on external
demand for basic products of Russian export, such as energy supply, wood and
metal.
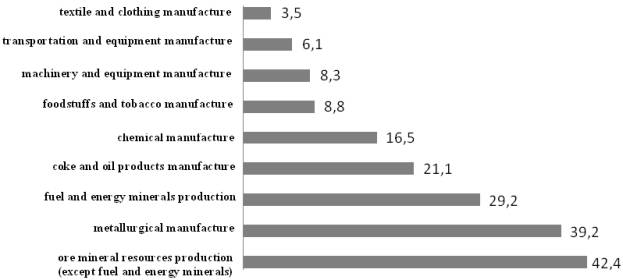
Pic.1. The profitability of
Russian manufacture in 2008, % (provided by the materials of All-Russian public
organization “Business Russia” [1]).
As a result of orientation of economy of Russia to production
and primary processing of minerals, there have taken place the essential break
as regards the profitability between raw
material and not raw material sectors of Russian economy (pic.). Thereby, the profitability of ore mineral resources
production (except fuel and energy minerals) in 2008 was 12,1 times more than
profitability of textile and clothing manufacture and 5,1 times more, than profitability
of machinery and equipment manufacture.
Table. Commodity composition of export and import of the Russian
Federation (%) (provided by the materials of Federal Service of government
statistics [3]).
|
Year Sorts of production |
1995 |
2000 |
2002 |
2003 |
2004 |
2005 |
2006 |
2007 |
|
Provisions and agricultural raw materials |
1,8* |
1,6 |
2,6 |
2,5 |
1,8 |
1,9 |
1,8 |
2,6 |
|
28,1 |
21,8 |
22,5 |
21 |
18,3 |
17,7 |
15,7 |
13,8 |
|
|
Mineral products |
42,5 |
53,8 |
55,2 |
57,3 |
57,8 |
64,8 |
65,9 |
64,7 |
|
6,4 |
6,3 |
3,7 |
3,8 |
4 |
3,1 |
2,4 |
2,3 |
|
|
Chemical production, rubber |
10 |
7,2 |
6,9 |
6,9 |
6,6 |
6 |
5,6 |
5,9 |
|
10,9 |
18 |
16,7 |
16,8 |
15,8 |
16,5 |
15,8 |
13,8 |
|
|
Rawstock
(leather goods), fur (peltry-ware) |
0,4 |
0,3 |
0,3 |
0,2 |
0,2 |
0,1 |
0,1 |
0,1 |
|
0,3 |
0,4 |
0,5 |
0,4 |
0,3 |
0,3 |
0,3 |
0,4 |
|
|
Timber
and pulp-and-paper industries production |
5,6 |
4,3 |
4,6 |
4,2 |
3,9 |
3,4 |
3,2 |
3,5 |
|
2,4 |
3,8 |
4,2 |
4,2 |
3,8 |
3,3 |
2,9 |
2,7 |
|
|
Textile goods and footwear |
1,5 |
0,8 |
0,8 |
0,7 |
0,6 |
0,4 |
0,3 |
0,3 |
|
5,7 |
5,9 |
5,3 |
4,8 |
4,3 |
3,7 |
4 |
4,3 |
|
|
Metals
(hardware), precious stones (jewels) |
26,7 |
21,7 |
18,7 |
17,8 |
20,2 |
16,8 |
16,3 |
16,1 |
|
8,5 |
8,3 |
6,4 |
7,3 |
8 |
7,7 |
7,7 |
8,2 |
|
|
Machinery,
transportation and equipment |
10,2 |
8,8 |
9,5 |
9 |
7,8 |
5,6 |
5,8 |
5,6 |
|
33,6 |
31,4 |
36,3 |
37,4 |
41,2 |
44 |
47,7 |
51 |
|
|
The rest |
1,3 |
1,5 |
1,4 |
1,4 |
1,1 |
1 |
1 |
- |
|
4,1 |
4,1 |
4,4 |
4,3 |
4,3 |
3,7 |
3,5 |
3 |
* numerator - export; denominator -
import
Natural consequence of this situation became the
commodity composition of Russian export
and import (table). From 1995 to
2006 the quota of mineral raw material in total volume of export of the country
was stably increasing and by 2007 had made up 65,9 %. The quota of an end-product,
for example, machinery, transportation and equipment in export was gradually
falling: from 10,2 % in 1995 to 5,6 %
in 2007. At the same time the part of import of the same product was accruing:
from 31,4 % in 2000 to 51 % in 2007.
The quota of import of both provisions and
agricultural raw materials was extremely great. However it is possible
to note some positive tendencies. Though the part of export insignificantly
grew (from 1,8 % in 1995 to 2,6 % in 2007) over the same period of time, the part
of import went down from 28,1 % to 13,8 %. In whole, it should be emphasized,
that direct dependence of economy of Russia on import cannot but cause anxiety.
The existing situation, out of question, undermines foundations of national
safety.
As a result, the country by leaps and bounds was
involved in the economic crisis as soon as demand for Russian export of raw
materials was reduced. The focus of
national economy on raw export led to some unfortunate results: the domestic
demand could not replace the external one that reduced from the end of 2008 to the
beginning of 2009. The decrease in industrial and economic activity of
enterprises had taken place, and hereupon, the crisis of non-payments occurred.
Thereupon, directed at
modernization of economy crisis-proof policy gains special currency. The president
of the Russian Federation D.A.Medvedev, issuing an appeal to Federal Assembly
of Russia in 2009 emphasized, “We have to begin modernization and technological
renewal of all industrial spheres. In my strong opinion, it is a question of a
survival of our country in the modern world” [2]. The realization of this tendency
will allow to create the basis for sustainable development of Russia in long-term
outlook.
References
1. An output from crisis: Refusal of raw model. New
industrialization. The Annual economic
report of the All-Russian public organization “Business Russia” (2009). //
http://www. deloros.ru/ http: // www.regionalistica.ru/projects/geo/
2. Medvedev D. À. The Message to Federal Assembly of the Russian
Federation // http: // www.consultant.ru/online/base/
3. The site of Federal Service
of government statistics // http: // www.gks.ru.