ÓÄÊ
628.218
Yana A. Gusentsova,
Svetlana S. Dulgier, Alim A. Kovalenko
VENTILATION SYSTEMS RELIABILITY WITH THE FLUIDIC
CONTROL DEVICES
Comparison of nonfailure
operation parameters of ventilation systems with different control modes is presented.
It is shown, that using fluidic
components increase the reliability of ventilation systems.
Under tough economic policy
problems of improving all processes associated with energy consumption,
improving working conditions, higher environmental safety are acute.
In such
circumstances efficiency, reliability and durability of the heating and
ventilation systems are actual. Not in the last turn, these parameters are
determined by means of ventilation system productivity regulation. In this
paper comparison of ventilation system reliability executed for three different
control systems – one which is built
with the use of standard apparatus (control device is mechanical with an electro
drive), second – with the use of fluidic (vortex and deflective) control elements,
and third – using theristor device for frequency rotation control of ventilator.
To determine the
reliability of the systems we use the method of flow control structure charts
[1]. For this we represent each system
as series of elements for which the coefficient of reliability is known. At such approach the examined systems are
faultless only in that case, when all elements are faultless. Probability of nonfailure
operation P of successive connection of elements, according to the multiplication
theorem of random values
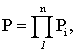
where ![]() is probability of nonfailure
operation of i–element.
is probability of nonfailure
operation of i–element.
During the
operation for the failure rate exponential law of reliability is validate
![]()
In this case for the
n elements serial connection the
equation takes the form
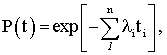
where ![]() is intensity failure rate and time of correct operation of the i- element.
is intensity failure rate and time of correct operation of the i- element.
For highly reliable
components, when the ![]()
![]() .
.
Thus, for
calculating the reliability of arbitrarily complex system enough to know the
composition of elements, their number, the mounting connection and statistical
characteristics of reliability of each item. Data on the composition of
elements are determined by the circuit board, and the statistical reliability
of elements - based on data from the drive, such projected. Below are the failure rate of the system elements
defined within the confidence level α = 0,9, obtained by generalization the data manual fluidic and vortex elements [1,
2, 3]:
Electro mechanic convertors
– 2,5.
Electric motors
- 1,0 . . .4,0.
Pneumatic elements –
1,4.
Deflective elements
- < 0,1.
Vortex elements -
< 0,1.
Mechanical elements
of flow control (shutter) – 2,0.
Theristor convertors
– 5, 7.
Ventilators – 1,0
.. . .4,0.
Calculation of
reliability indices for structural schemes carried out in drive blocks and
units. This allowed us to compare sites in terms of reliability, identify
weaknesses and ways to improve reliability during design and operation.
It should be keeps
in mind that the reliability indices at contradiction with other indicators of the drive quality
(cost, effectiveness, etc.).
With increasing
reliability costs in the design, manufacture and testing of ventilation systems
increases on the one hand, and on the other operating costs by reducing the
number of refusals reduce. These
two opposing trends create the preconditions for the emergence of extremum of
economic efficiency indicators, which corresponds to specific (optimal) value
of the probability of nonfailure operation.
Thus, the problem of
valuation of reliability is converged to the investigation of the total reduced
cost, depending on the probability of nonfailure operation. Functional
relationship normalized cost with the probability of nonfailure operation of
the drive has the form
![]() (1)
(1)
where
![]() is probability of faultless operation;
is probability of faultless operation;
![]() - normalized costs associated with development and production of the
ventilation system with a probability of nonfailure operation
- normalized costs associated with development and production of the
ventilation system with a probability of nonfailure operation ![]() ;
;
![]() - reduced annual normalized costs
of maintenance during operation
- reduced annual normalized costs
of maintenance during operation
The results
obtained calculating the normalized cost for the ventilation system of model
unit with different methjds of productivity changing relative respect to the
throttle, that widely using now
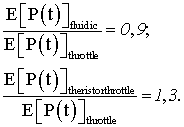 (2)
(2)
Thus it is confirmed
that the using the fluidic and vortex elements to control the productivity of
ventilation system improves its reliability compared to traditional throttling and
theristor control modes.
The calculations
also showed that the ventilation system for power generating unit using fluidic
or vortex devices would increase the probability of nonfailure operation no
less than 9%.
Literature
1.
Ñûðèöûí Ò.À. Íàäåæíîñòü ãèäðî- è ïíåâìîïðèâîäà / Ò.À. Ñûðèöûí. – Ì.: Ìàøèíîñòðîåíèå,
1981, - 216 ñ.
2.
Ãóñåíöîâà ß.À. Âèõðåâûå óñòðîéñòâà â ñèñòåìàõ âåíòèëÿöèè / ß.À. Ãóñåíöîâà, À. À. Êîâàëåíêî, Å. À. Èâàùåíêî è äð. – Ëóãàíñê. - Èçä-âî ÂÍÓ
èì. Â. Äàëÿ, 2006. - 296 ñ.
3.
Ãóñåíöîâà ß.À. Ñòðóéíàÿ òåõíèêà â
ñèñòåìàõ âåíòèëÿöèè / ß. À. Ãóñåíöîâà, Å. À. Èâàùåíêî,
À. À. Êîâàëåíêî è äð. - Ëóãàíñüê. - Âèä. ÑÍÓ ³ì. Â. Äàëÿ – 2007. - 292 ñ.