Jean-Pierre Ngoma, Cand. Sc. (Eng);
Duala University, Republic of Cameroon
Adolphe Imano Moukengue,
Cand. Sc. (Eng);
Duala University, Republic of Cameroon
Burykin O.B., Cand. Sc.
(Eng);
Vinnytsia National Technical University,
Ukraine
Sikorska O.V., Postgraduate
student
Vinnytsia National Technical University,
Ukraine
Power LOSSES SENSITIVITY To ELECTRical POWER SYSTEMS TRANSITS CHANGES
The method of an estimation
of electrical power system (EPS) mode parameters sensitivity to changes in the
nodes load is developed. Possibility of sensitivity to changes in the nodes
load of other systems estimation allows to estimate sensitivity of losses from
transit overflows in separate EPS elements. The method is based on use of
calculation and estimation algorithms and programs of electric networks with
transformer communications interference.
Keywords: electrical power system, power transit, the sensitivity analysis, power losses distribution.
Introduction
Taking into consideration that
fact, that the electrical power system (EPS) is opened for all energy market
participants, a research problem of transit power flows (TPF) contribution to
the electrical power additional losses and their reduction in networks EPS is
appears. Now days there are variety of transits power loss (TPL) definition
methods is created [1-4]. They are intended for definition of losses of the
electric power for the certain period of time. For the various reasons of value
of transit overflows throughout this time can essentially change considering
ways of course of transit and a place of an adjunction with other systems (fig.
1) that influences accuracy of definition TPL. Absence of methods of operative
calculation TPL does not allow to correct in due time parameters of the
regulating devices intended for optimization of transit overflows.
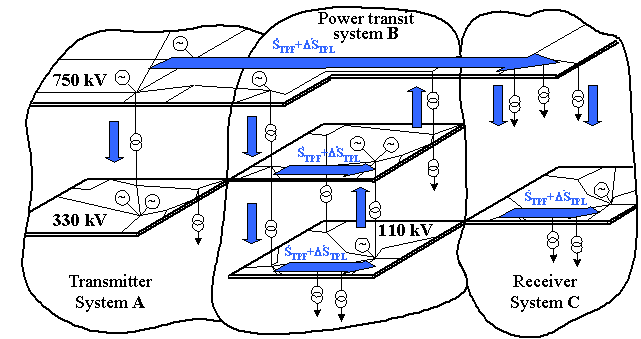
Fig. 1. An example of possible ways of course of transit of the electric power
Corresponding methods are
necessary for operative monitoring TPL and optimum control of transit overflows.
One of problems of these methods is definition of elements EPS the most
sensitive to transit overflows and in which TPL more all changes during
indignations, both external, and internal. The account of sensitivity of
optimum decisions to change of value of transit overflows will resolve, having
revealed in EPS the most sensitive elements to carry out actions for reduction
of losses of active capacity by more effective and economically expedient ways.
Besides, change of parameters of these elements will give the chance to reduce
heterogeneity of system in the greatest measure and, thus, to approach it to a
homogeneous condition reducing additional losses of capacity.
Given article is devoted
working out of a method of an estimation of sensitivity of parameters of mode
EPS to change of loading in nodes of scheme EPS, including in nodes of an
adjunction with other systems (the last allows to estimate sensitivity TPL in
separate elements EPS). The method is based on use of algorithms and programs
of calculation and an estimation of interference of electric networks EPS with
transformer communications [6].
Definition of a matrix of factors of sensitivity of losses of capacity
In [6]
it is shown, that capacity losses in branches of scheme EPS taking into account
transformation factors are implicitly defined thus:
![]() , (1)
, (1)
where – ![]() a matrix of factors of distribution of losses of capacity in
branches of electric networks depending on capacities in nodes taking into
account factors of transformation of transformers of communication;
a matrix of factors of distribution of losses of capacity in
branches of electric networks depending on capacities in nodes taking into
account factors of transformation of transformers of communication; ![]() – a vector of loadings in scheme nodes.
– a vector of loadings in scheme nodes.
Accordingly (1) losses of
capacity in i-é branches EPS pay off under the formula:
![]() ,
,
where
![]() , (2)
, (2)
Line of a matrix which ![]() answers i-é to a branch;
answers i-é to a branch; ![]() – the transposed vector of pressure in nodes including and
balancing; ÌΣi – i-ÿ a line of a matrix of
connections of branches in nodes including and balancing; –
– the transposed vector of pressure in nodes including and
balancing; ÌΣi – i-ÿ a line of a matrix of
connections of branches in nodes including and balancing; – ![]() i-ÿ a vector-line of a matrix of distribution of currents in
nodes on scheme branches;
i-ÿ a vector-line of a matrix of distribution of currents in
nodes on scheme branches; ![]() – a diagonal matrix of pressure in nodes including and
balancing.
– a diagonal matrix of pressure in nodes including and
balancing.
Let's assume that factors of
distribution of losses of capacity in ![]() branches do not depend on capacity of transit
overflows and are constants. Then, during change of loading in nodes, capacity
losses in i-é the branches which value pay off according to expression will
change:
branches do not depend on capacity of transit
overflows and are constants. Then, during change of loading in nodes, capacity
losses in i-é the branches which value pay off according to expression will
change:
![]() , (3)
, (3)
Where – ![]() change of capacity of loading of nodes EPS during transition
from k th to k + 1st mode.
change of capacity of loading of nodes EPS during transition
from k th to k + 1st mode.
If change of capacity of
loading occurs only in j th knot the gain of losses of capacity in i-é branches
from change of capacity of loading of j th knot will be defined as follows:
![]() . (4)
. (4)
From expression (4) follows,
that
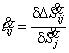 . (5)
. (5)
The factor meets the requirements,![]() resulted in [7], and is factor of sensitivity of losses of
capacity in i-é branches to change of capacity of loading of j the knot. Thus,
the matrix establishes
resulted in [7], and is factor of sensitivity of losses of
capacity in i-é branches to change of capacity of loading of j the knot. Thus,
the matrix establishes ![]() connection between increases capacity losses in branches EPS
and changes of capacity of loading in nodes and is the sensitivity matrix which
each factor consists of kind elements
connection between increases capacity losses in branches EPS
and changes of capacity of loading in nodes and is the sensitivity matrix which
each factor consists of kind elements![]() .
.
In practice in EPS there are
problems when in nodes active or jet capacities change only. If in a transit
overflow active capacity (![]() ) from (5) follows, that changes only
) from (5) follows, that changes only![]()
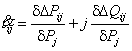 . (6)
. (6)
In other case, during
indemnification of a jet overflow in knot jet capacity (the source of jet
capacity joins or switched off,![]() ) then according to expression (5) we will receive, those
changes only
) then according to expression (5) we will receive, those
changes only![]()
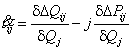 . (7)
. (7)
As criterion of an optimality
of normal mode EPS in the given work are losses of active capacity special
interest is represented by the first component of expression (6) and the second
component of expression (7). According to the specified factors matrixes of
sensitivity TiP and TiQ
losses of active capacity in branches to change of active and jet capacities of
loading in nodes accordingly are formed. Then losses of active capacity in i-é
branches at change of capacity of loading in nodes are defined on expression:
![]() ,
, ![]() , (8)
, (8)
Where and ![]() –
– ![]() change of active and jet capacities of loading in nodes EPS,
accordingly.
change of active and jet capacities of loading in nodes EPS,
accordingly.
Factors of sensitivity of losses of capacity in branches to pressure in
nodes
Apparently from (2), values of
factors of a matrix of sensitivity generally ![]() depend on pressure in nodes which,
depend on pressure in nodes which,![]() in turn, also depends on capacities of loading and
generating in nodes. In this case during change of capacity in nodes, loss in
i-é branches will change and, unlike (3), will be equal:
in turn, also depends on capacities of loading and
generating in nodes. In this case during change of capacity in nodes, loss in
i-é branches will change and, unlike (3), will be equal:
![]() .
.
Taking into account that,![]() and,
and,![]() last expression will be copied:
last expression will be copied:
![]() =
=
![]() ,
,
Or
![]() . (9)
. (9)
If changes have occurred only
in one knot – j the according to (9), the gain of losses of capacity in i-é
branches from change of capacity in j the knot is
defined ![]() as follows:
as follows:
![]() . (10)
. (10)
From last expression the
factor of sensitivity of losses of capacity in i-é branches to change of
capacity in j the knot at transition from k the to k + 1st mode taking into
account change of pressure in nodes, is defined thus:
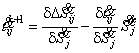 . (11)
. (11)
From comparison (5) and (11)
it is visible, that generally, sensitivity of losses of capacity in i-é
branches to change of capacity of j the knot is caused also by factor of
sensitivity and ![]() values of capacities of loadings of nodes in an initial mode
values of capacities of loadings of nodes in an initial mode![]() .
.
Expression for definition of
factors of sensitivity is defined,![]() how a difference of factors of a matrix for
how a difference of factors of a matrix for ![]() k the and k+1 the mode, each of which is defined from (2):
k the and k+1 the mode, each of which is defined from (2):
![]() =
= ![]() –
–![]() =
=
=![]() ,
,
Where – ![]() the diagonal matrix, which each element is defined from the
relation
the diagonal matrix, which each element is defined from the
relation
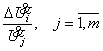 ,
,
Where – ![]() pressure recession in i-é scheme branches.
pressure recession in i-é scheme branches.
Value of factors of a matrix gives the chance ![]() to define what branches in the greatest image react to
pressure change in nodes which, in turn, also depends on capacities of loading
and generating in nodes.
to define what branches in the greatest image react to
pressure change in nodes which, in turn, also depends on capacities of loading
and generating in nodes.
Conclusions
1. For operative monitoring of
losses from transit overflows and their optimization factors of sensitivity of
losses of capacity to indignations in system, in particular to change of
loading or generating in nodes can be used. The matrix of factors of
sensitivity is formed by results of calculation of the characteristic
established mode and if necessary specified by the account of change of
pressure in nodes of scheme EPS.
2. The developed method of an
estimation of sensitivity of parameters of mode EPS to change of loading in
scheme nodes, allows to estimate sensitivity of losses of capacity in its
separate elements during external and internal
indignations, such as change of loading or generating of separate
nodes of the scheme. Application of a method
concerning nodes of an adjunction with other systems allows to estimate
sensitivity of losses in separate elements EPS to
transit overflows.
References
1. Talasov A.G. Losses on the transit of electricity and the
distribution of energy among the participants // Elektricheskie stantsii. –
2002. – ¹ 1. – P. 20 – 25. (Rus.)
2. Stogniy B.S., Pawlowski V.V. Determination of power losses in
transit fragmented electric networks of regional utility companies // Energeticheskaya
politika Uknainyi. – 2004. – ¹ 5. – P.
26 – 31. (Rus.)
3. Potrebich A.A. The definition of standard electricity losses regional
power companies, taking into account the transit flows // Energetika i elektrifikatsiya. – 2000. –
¹ 10. – P. 20 – 23. (Rus.)
4. Lezhniuk P.D., Kulyk V.V., Buryk³n O.B. Losses of power in
electric power systems from transit flows // Energetika ta elektrifikatsiya. –
2006. – ¹ 3. – P. 26 – 33. (Ukr.)
5. J. Conejo, J. M. Arroyo, N. Alguacil, and A.L. Guijarro, //
Transmission loss allocation: a comparison of different practical algorithms // Power Systems, IEEE, - vol. 17,
pp. 571 - 576, Aug. 2002.
6. Lezhniuk P.D., Kulyk V.V., Buryk³n O.B. Evaluation of electric
networks of power transformer connections // Tekhnichna elektrodynamika.
Tematychnyy vypusk: problemy suchasnoyi elektrotekhniky. ch. 7. – 2006. – P. 27
– 30. (Ukr.)
7. Rosenwasser E.N., Yusupov R.M. The sensitivity of the control
systems. – Moskva: Nauka, 1981. – 464 p. (Rus.)