Alfreda Zachorowska
The Czestochowa University of Technology
Investment risk management – chosen aspects
Uncertainty and risk are the normal phenomena following economic undertakings, especially investment activity of enterprises functioning in market economy conditions. Risk and responsibility for the present and future results of activities are the basic principle of market economy. Recognizing the idea of investment risk and its mechanisms, are necessary in order to restructuring the enterprises towards active and innovative undertakings.
1. The idea and
kinds of investment risk
Term risk and uncertainty, thought they are often thinking
they are identical, do not determine identical phenomena. These categories concern
chronological and alternative followed phases of the same decision-making
process[1]. The risk changes
together with uncertainty, so that’s why it can be the function of uncertainty.
Especially, this function has the character of simple relationship: the broader
range of uncertainty, the higher risk, and vice-versa. When undetermined and
uncertain factors decrease – the risk is going down.
Investment
risk is the element of economical risk and it is tightly connected with potentially danger during
gathering in future forecasted economic effects[2]. The risk character
is very differential. We can meet with one directional risk (loss), and
multidirectional risk (profit, loss)[3].
The risk is often shown as the essential condition of economic development, and
on the other hand as the source of economic success of the enterprise. Risk can
lead to success by detailed analysis of chances and threats, and that’s why by
using the restructuring of its threats into development chances.
Investment processes are very complex and differential. So we can make
mistakes during these processes. It can be, for example, not proper
localization of object, not proper or irresponsible contractor. The possibility
of mistakes concern both decision-making process and the process of realization
given investment. Every next choice making during the investment process is
determined by investment decision, which was made in the beginning. Future
success depends on its accuracy and it is the critical point for the whole
investment process.
Certainty is the state of being
when the manager have information that are helpful in order to proper
forecasting the effects of his decisions. Risk means, that manager can
determine the range of some consequences of his decisions. Uncertainty is when
we have the situation, that manager can’t determine the possibility of his
decisions.
So, the investment decision-making process is very essential, and the
biggest threat for the investor is risk of unsuccessful effects or even more
the loss of assets. That’s why the uncertainty can lead, in some cases, to
stagnation in new investment or inhibition of investment processes, that were
started.
2. The idea and range of investment risk management
Risk
management is the generally accepted term, used in investment practice. It
means the identification of phenomena, that can be dangerous for the financial
effects (profit) of this activity, or planning precaution that can limit
negative effects of given risk. However, investors practice micromanagement in
relation to individual risks, rarely (because of high costs) they practice
global risk management[4]. The central
decision problem, in risk management, is the appraisal and choice of
alternative methods, strategies, projects and means of reduction the risk.
Every time, the risk should be, as early as possible, identified, analysed and systematic
controlled. Simultaneously the manager should correct methods and instruments
of its reduction, accordingly to changing conditions. It is a process ex ante,
that depends on recognizing and prevention of negative risk factors, or depends
on using factors that have positive impact on investment process[5]. Simultaneously it
is also directed on the absorption of negative effects of deviation and can be ex post activity. In
both variants of risk management (ex ante and ex post) it regards the minimisation of negative
effects.
In case
of investment processes, risk management should exist in every phase of
investment cycle. The implementation of risk management in the early phases of
investment cycle is more effective, though more strategic than operational
character, because of limited range of information. In these phases we can make
some changes, improve technical and economic assumption, and verify solutions,
what can lead to risk reduction[6]. In this aspect,
it is very essential the last phase of preinvestment stage – phase of creating
the technical conception of investment project[7]. It is a phase with determined program, the investor
have additional analysis (simulations, analysis taking into consideration
probability mathematics, etc.), that are in relationship with the most
uncertain areas of given project.
From
the point of view of uncertainty and risk it is necessary in the last phase of
preinvestment process, when making detailed technical project , to make the
plan of risk management. Such plan can show, from the one hand, what kind of
strategy should be undertaken (with suppliers and contractors on the stage of
realization) and on the second hand – it can make easier making choice of most
advantageous contracts[8].
3. Stages of investment risk management
Risk management should have
planned and target character. It means, that these activities should be
systematic and long-term, and the effect is maximal risk reducing and protecting
against its negative impact. Often we can distinguish three stages of this
process[9]:
- risk identification
and quantification,
- risk steering,
- risk controlling, in
order to its maximum.
The first stage, of
informative and forecasting character, is the risk identification, determining its
specific, character and kind. Proper identification and appraisal are depended
on the range, completeness and quality of data. The identification of risk
enhance on gathering proper methods of its measurement (quantification).
After identification of risk sources for given investment, we can analysing risk
of every kind. The appraisal of the influence different kinds of risk on the
realisation process is very essential. Risk quantification is one of the most
difficult stages of risk management. Many techniques have to be used here, and
the selection of these techniques depends on many objective and subjective
factors. Objective factors can be following: type and size of investment, range
and plausibility of gathered data, time-consumption and also costs of risk
analysis and appraisal, and experience
and knowledge of analysts[10].
The group of subjective factors includes among others economic potential
and financial condition of investors. After risk quantification one is possible
to qualify the direction of further activities and go to the second level -
risk controlling. This stage consists of taking decisions which limit risk and
have an active or passive character.
The control of efficiency methods and forms of risk minimizing is the
last management level of this process. It includes a lot of states aiming at
effectiveness evaluation and efficiency of applied methods along with
instruments reducing risk. Generally, one also distinguishes here physical and
financial control of risk. The physical control of risk consists of all actions
and instruments which lead to the total elimination of loss probability (it
means risk avoiding or prevention the losses), or its large limitation (with
the use of frequency measures calculating losses’ size).
The financial control of risk includes all activities and instruments
leading to risk stopping (independent risk management) or to risk transfer. The
control system enables therefore the evaluation of effectiveness of actions
reducing risk.
It should be underlined, that there is no universal procedure of risk
management in all conditions and for each investor. The procedures ought to be
constructed individually, adapted to external and internal conditions of
particular investment activity.
4. Chosen methods
of investment risk minimizing
On the one hand investment risk is the result of uncertainty noticed by
investor, on the other hand - it results from the size of the capital engaged
in investment process. These connections determine the directions of negative
results reduction as far as risk is concerned. The reduction of investment risk
may be done by[11]:
-
reducing the amount of capital involved in risky undertakings,
-
uncertainty minimization,
-
risk burdening over different economic entities.
The minimization of risk in functional aspect consists in undertaking
some activities focused on its negative results’ correcting. Also some actions taken to anticipate the
harmful consequences of risk belong to this group. One should underline, that
the proper risk identification and its evaluation is the information basis
needed to choose methods and forms for risk mitigation. Generally in literature
one distinguishes three ways of evening risk out[12]:
-
risk compensating with the use of location (diversification) of
enterprise capitals in productivity fields and risk fund optimizing,
-
risk division, among others through dispersion of common shares,
-
transfer of risk for insurance institutions.
There can appear four typical reactions of investors corresponding with
reducing methods or the total reduction of this phenomenon in the process of
risk management. These are[13]:
-
risk avoidance,
-
risk stopping,
-
transfer of risk,
-
risk reduction.
In dependence from degree of threat the risk, the investor decides on
use one of methods of reaction on this phenomenon, introduced on drawing 1.
Depending on the
level of risk threat, the investor decides to use one of reaction methods
presented on Figure 1.
![]()
![]()
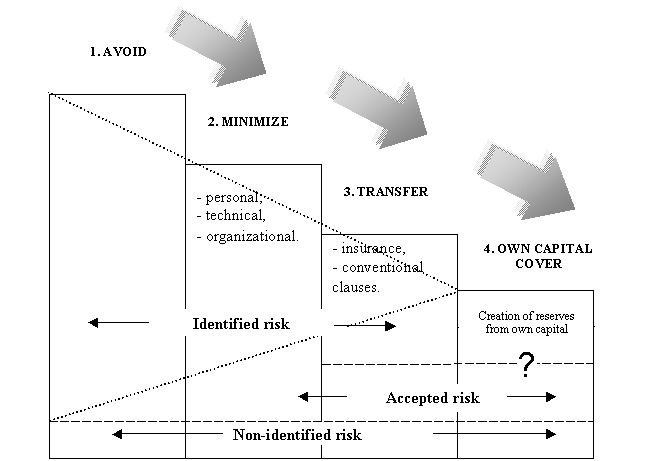
Figure 1. Methods of investment risk reducing
Source: prepared on the basis: K. Homann: Risikomanagement im
Immobilienunternehmen. Berufsakademie Stuttgart, University of Cooperative Education, Akademie der
Immobilienwirtschaft (ADI) GmbH, Stuttgart – Leipzig – Hamburg 2003, p. 27.
Risk avoidance is a situation, where the conscious
refusal of even temporary risk acceptance appears. It is the easies, but the
least effective form of risk management, however the probability of possible
losses is zero in this case. This method belongs to negative techniques of
reactions to risk[14].
Often occurring method of risk reducing is so called retention, which
means risk stopping. It is rather more popular in large and financially strong
corporations than in small enterprises. This method means, that enterprise chose
the variant of possible losses covering with own financial resources. The most
popular form is to create a special purpose fund (reserves) for financing the
costs of probable failures. Its additional function is self-insurance enabling
to cover losses. There is no uniform opinion in literature according to the
range and subject of reserves. They can be created by all participants of
investment process and they can simultaneously concern not only investment
expenditures, but also the costs of exploitation and even the time of
investment realization[15].
Even though there
exists a wide range of factors influencing the size of reserves, the decisive
role is fulfilled by the exactitude of parameters of investment project. These
resources can be the smaller, the better are individual parameters of project
quantified. The uncertainty decreases in the next phases of investment
realization, because the estimates are more exact. One can create smaller
reserves because of that.
The compensating of risk negative results with reserves’ creation
(special purpose fund) in relation to chosen variables of investment project
reflects the possibility of avoidance of additional payments in case of cost
limit crossing incurred by the investor. The aim of applied reserves is therefore
to cover the additional costs being the result of unforeseen events in investment realization. It may concern
both its realization time, as well as the exploitation costs of realized
project. The creation of reserves involves however the maintenance of part of
financial resources. It may contribute to the increase of realization costs and
extension of realization time. Therefore its is essential to create these
reserves on the optimum level, taking into regard both the protection against
risk, as well as the burden of capital
financing investment realization.
Also of
great importance is the awareness of the possibility of unexpected losses and
the necessity to cover them with current resources, usually net profit, or
resources from the sale of assets in order to replace the lost or destroyed
ones. These are the consecutive ways of implementing this method. However it
can not be used for risks with hard to predict effects and potential losses. It
also refers to cases of relatively high potential losses and high probability
of their massive accumulation.
Risk
retention, both complete and partial, can have an active form, as a result of
conscious actions, or passive, usually resulting from the lack of knowledge of
the character and size of this phenomenon. Active method is used mostly towards
risks of high frequency and low sharpness, i.e. when potential losses are low.
Passive risk retention is usually means the investor’s passive attitude towards
risk, that can also be caused by the character of this phenomenon. It usually
applies to risks of low frequency, which are unnoticeable by the person in
risk.
Another
method of limitation of investment risk is transferring it to other business
units, called risk reallocation. Distributing risk across different units is
one of the basic forms of risk management. It means the transfer of total or
part of responsibility for covering possible losses. It can have two forms:
transfer of activity generating possible losses or transfer of responsibility
for covering possible losses. Negative financial effects of risk can be
transferred using e.g. financial derivatives, classic insurance method, or
proper leasing agreement.
Risk
distribution instruments also include agreements with future users, sponsors,
and term purchase agreements. Thanks to those the investor gets the possession
of resources during the investment process, in exchange for the specified part
of outcomes of finished project.
In
investment processes, risk transfer usually takes the form of[16]:
- proper conditions
of contracts between parties of the investment project,
- risk insurance.
That
way the whole or the part of risk is transferred to insurance company,
agreement counterparty, or other unit. This method allows to run the investment
process in full range, with simultaneous transfer of problems of evaluation and
cost of risk to other unit[17].
Proper allocation of risk across parties of investment process can be done with
contracts, although their formulation is not easy. Agreements between investor
and contractor serve i.a. two main purposes[18]:
- they determine the
liabilities of both parties, including mutual obligations,
- they determine the
way the risk related to particular activities will be allocated across the
agreement parties.
Risk
transfer can also take place in form of subcontract – hiring other unit for
particular range of works, generating possible losses. The same effect can be
achieved with proper clauses in contract, regarding works of high risk, leading
to situation, where investor is free of the responsibility for losses included
in the agreement.
Parties
of the investment process have different interests, which leads to difficulties
in constructing contracts. By the same reason, in case of risk occurrence there
are difficulties with its cause determination, and the allocation of its
effects across investment process parties. Risk allocation through contracts
can also be obstructed by the nature of events being the source of risk. Some
events are easy to identify and evaluate. However some risk sources are
difficult to detect, and their negative effects can emerge in later time. In
such cases prior precise determination of nature of events, potentially being
the sources of risk, risk transfer cost and risk managing parties can all be
very helpful[19].
The commonly
used instrument of risk limitation are guarantees, given by government or other
parties with proper financial standing. Those parties through guarantees take a
part of investment risk.
Risk
transfer can also take form of risk insurance. It is the basic and also the
most often used form of risk transfer. The distribution of negative effects of
random events across numerous units leads to their full removal or partial
reduction[20]. Insurer
sells the protection from the negative effects of risk, and the insurance taker
buys the protection. Insurance premiums are the cost of transferring the
negative effects of risk to insurance company. Risk insurance is particularly
important in the case of real investment. Apart from construction project one
can also buy insurance for different parties of investment process and the
loans drawn for this purpose. During the investment process there is a
possibility of occurrence of various unexpected and unfavorable events
negatively affecting the effectiveness of the process. Risk can also refer to
project works. Losses caused by the mistakes in planning can be so significant
and expensive, that their removal can be impossible due to the financial
capability of the contractors. Thus the subject of insurance can be not only
the various construction objects, but also construction in progress and the
parties responsible for the planning. Insurance subjects can also be machinery
and construction equipment, investor property, and construction facilities,
such as administration and social buildings, warehouses, workshops and their
equipment. One can also buy insurance from third-party liability caused by
accidents on construction site. Insurance subjects may also refer to
maintenance, modernization and reconstruction of objects.
Insurance protection includes all stages of investment cycle, and also
the operation stage of the object. During the investment process, the most
popular insurance is all-risk insurance, where insurer does not list threats
that he is responsible for, but list events that are not covered by the
protection. On the other hand, in the operation stage of the object insurance
companies refer to their conditions of property insurance.
Risk
reduction can also be achieved through diversification of investment portfolio.
However in case of real investment there is no possibility to distribute risk
like in financial investment case, that is by creating optimal investment
portfolio. Investor often has to engage the majority of his resources with the
investment process, without the possibility to secure the desirable
profitability. Nevertheless the main element of risk protection strategy is
investing only when expected rate of return is higher than the cost of capital
increased by the risk premium. This idea can be realized only when investor is
able to distribute risk across numerous optimal investment projects. The method
is of limited use though, as it is available only to financially strong
investors (such as concerns or financial institutions). Small investors usually
do not have enough capital in their disposal to invest in many projects.
However simultaneous investing in different assets, and splitting capital into
different projects significantly reduces the risk. There can also be a complete
limitation of risk there, as negative effects on one asset can be balanced by
the same effects positively affecting another asset[21].
Activity diversification enables investor to increase his adaptation
capability, thus to limit the uncertainty and reduce risk.
Conclusions
It has to be noted, that there is no way to eliminate risk completely, only to reduce it significantly. According to the level of risk, investor can use different methods of its limitation. If the possibility of risk is insignificant, investor can accept it and take it by himself. But if the analysis shows that the possibility is high, and risk can bring great losses, investor should adequately earlier avoid it or reduce or transfer[22]. When selecting the risk limitation methods, one should take into consideration the nature of the problem, time needed for its e