Beata
Nowotarska-Romaniak
Akademia Ekonomiczna
Katowice
Marketing Department
Marketing
Strategies of Polish Insurance Companies
1. Introduction
The dynamics of
current insurance markets in Poland, systematic increases in the velocity of
available products and increasing expectations of customers highlights the
scale of competition in this particular sector[1].
Insurance companies have started to innovate their products in order to achieve
an advantage over their competitors. In these circumstances planning, coordination and commitment to
marketing activities have to be combined into a coherent company strategy. The
importance of well a planned and executed strategy have significant
consequences in building the uniqueness of a company and gives an opportunity
for employees to distinguish their company from others in the market. In order
to achieve this status companies need to base their strategic decisions on the analysis
of the market. The basic questions that need to be addressed are:
·
Are the external conditions suitable to the accomplishment of company
strategic marketing objectives?
·
Are the means of distribution adequate to the situation in the market
and are they efficient? Are the alternative channels required?
·
Are existing selling methods compatible with adopted strategy?
·
Is there a connection between advertisement and other promotional
methods?
2. Creating the marketing strategy
Marketing strategy
enables a company to:
·
Maximize the usage of its best assets to increase its position on the
market
·
Create a distinguishable status on the market, giving it a clear ‘image’[2]
·
Highlights the advantages for potential customers
·
Uses optimum financial, human and investment resources in particular
market conditions
·
Selects the optimum market and marketing segments- mix
The first stage of
creating a marketing strategy is SWOT analysis. SWOT consists of, on the one
hand, specification of assets and liabilities of the company, and on the other,
of specification of advantages and disadvantages from external economic, social
and political situations. SWOT enables the company to eliminate its
liabilities, calculate the risk and take advantage of external conditions.
When analysing the
activity of companies in the Polish insurance market one must take into account
that in a situation of high market dynamics companies need to adapt to the new
key macro factors i.e. economic, political, and cultural trends. As well as the
important micro factors i.e. customer preferences, competition, suppliers, and
distribution channels. A strategic approach to all of those is crucial for
profit stimulation, establishment of company status on the market as well as
specification of direction of development.
The internal
analysis of a insurance company should include the following elements:
·
insurance system (complexity and completeness)
·
branches net (quantity and density)
·
the structure of sales process (organization of professional, efficient
and rewardable sales process)
·
training program (constant qualifications increase)
·
I.T. advancement (net information transfers, computer data bases
including access to sales data capturing individual customers and sales
leaders)
Recognition of
both internal and external conditions is crucial for deciding on goals and
targets. Inability to provide adequate market and company analysis may lead to
setting unrealistic targets and choosing wrong means. Goals usually include
entering and locating a high volume of products in the new markets, increasing
company share on particular markets, increasing profits and establishing
respectable brands.
When establishing
goals companies must consider:
·
Intensity of competition
·
Customer expectations to the service quality
·
Insurance companies capabilities
- Expectations and needs of employees
The
strategic goals of Polish insurance companies are: acquirement of new customers
(selecting new segments through supplying competitive services), increasing its
share on the insurance market, and reinforcement of company reputation among
potential customers. The goals of the insurance company are directly connected
to products and markets as they are the ones driving company profits. Companies with a strong market
position focus mainly on further growth and increasing its share in the
market (through growth strategy) while
companies in a state of crisis focus on securing its position on the market
(stabilisation strategy, through analysis of causes of crisis).
It is
crucial therefore to address the question of what are the current strategic
goals of insurance companies as well as what will they be in the near future.
Market research presented in this article is based on quantitive and
qualitative survey taken form 10/10/2007 to 30/06/2008 among insurance
companies branches within Katowice city and in their head quarters in Warsaw. The
research includes all companies that agreed to participate. That is: Allianz
Życie TU Polska S.A., Allianz TU S.A., Uniqa TU S.A., Signal Iduna Polska
TU S.A., Signal Iduna Życie Polska TU S.A., Gerling Polska TU S.A.,
Gerling Polska TU na Życie S.A., Amplico Life TU S.A., Pramerica
Życie TU i R S.A., Generali Życie TU S.A., Aegon TU na Życie
S.A., Commercial Union Polska S.A., PZU S.A., PZU Życie S.A., Winterthur
Życie TU, Inter Polska TU S.A., Warta S.A., Warta Vita S.A., HDI Asekuracja
TU S.A., HDI Gerling Życie S.A., Compensa S.a., Compensa Życie S.A.,
PTU S.A., Skania Życie TU S.A
The participants
were categorised into following sub-groups:
·
size of the company: big (28%), medium (48%), small (24%)
·
field of activity: non-life (41%), life (59%)
·
power distribution: head quarters (50%), branches (50%)
All companies,
including insurance companies, set different strategic goals depending on their
potential and obstacles they have to face. The most common are growth and
survival on the market. The surveys outcome indicate that vast majority of
companies, regardless of their size adopt growth strategy. Hence, the main
objective is to increase share in the market (fig. 1). Secondly, the filed of
activity also indicates expansionist policy including both life and non-life
activity. 89% of ‘life’ companies and 87% of ‘non-life’ companies embraced
growth strategy while accordingly only 11% and 13% focused on securing its
share or survival on the market (fig. 2). Thirdly, both head quarters and branches
adopt growth strategy which consequently leads to offensive activities in order
to achieve growth and development.
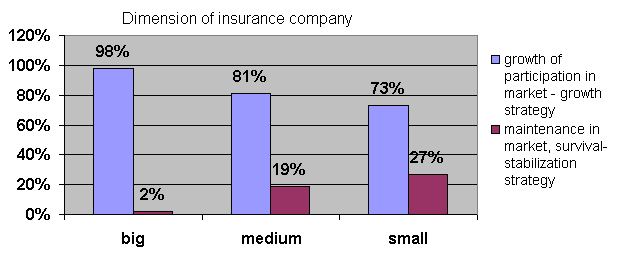
Fig.1 Strategic goal applied
depending on the size of the company.
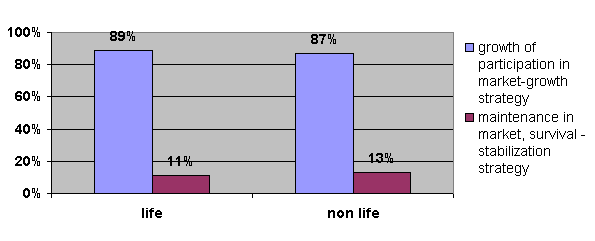
Fig.2 Strategic goal applied
depending on the kind of activity.
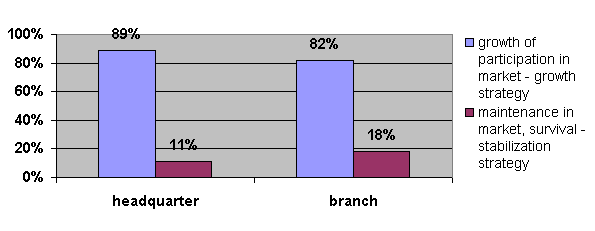
Fig.3 Strategic goal applied depending
on the headquarters or branches.
Another crucial
element of the marketing strategy is market segmentation, that is categorising
customers by established criteria. Selecting customers into consolidated groups
enables company to determine the sphere of activity and sets a departing point
to formulate a program of action. The purpose of the segmentation process is to
address specific insurance products to a particular group of recipients. As all
insurance products are created for a particular group of customers, it is
crucial to specify the segment of customers to establish their wants and
needs.
Marketing-mix is
the following stage of creating marketing strategy. In order to maximize
effectiveness in achieving the set of objectives and satisfaction of each
segment of the market, the right selection of instruments are needed.
Marketing-mix is a tool used to establish the composition of marketing
instruments and activities to achieve those goals.
Marketing-mix
consists of five elements. The first of which is the product. Insurance
products belong to a category of services that is not visible to the client.
Therefore most of customers do not deem the product as necessary. The choice of
the insurance as an ‘invisible’ product largely depends on company brand,
quality and professional customer service. The following element of
mix-marketing is the price of product. The price (insurance premium) depends on
different criteria i.e. probability of emergence of unfavourable circumstances
or damage (from which client wants to be insured), type of insurance and age of
client. Insurance premium is the insurance dues which the insured is obliged to
pay to insurer for the insurance guarantee (protection) over an agreed period
of time.
Distribution plays
an important role in creating an insurance companies marketing strategy. There
are three types of distribution channels on the insurance market. Those that exist
on the Polish insurance market are shown below (fig 4).
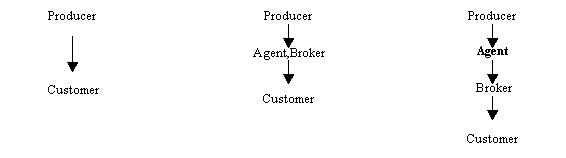 Types of distribution channels figure 4
Types of distribution channels figure 4
The most common
method of product distribution is direct contact or connection i.e. producer of
a product -> consumer (personal sale).
This method of
distribution limits the possibility to access a wider circle of recipients,
however it also has its advantages:
·
Greater ability to control implementation of the product rather than In
the case of insurance brokerage
·
Ability to adjust the product, and its contents to customer needs
through direct contact (information on level and structure of needs, and
eventual changes)
·
Direct feedback from consumers of product and service quality
Therefore,
in the case of insurance products direct distribution gives a possibility
to directly receive the flow of market
information, it enables rapid adjustment to changes in demand and gives direct
control on contracts included.
Other
examples of distribution channels include indirect sale:
·
agents: mostly in travel, hotel and transport insurance
·
brokers: insurance for institutionalised recipients
·
institution agents, independent agents (e.g. in advertisement or capital
trading)
·
agents in trade activity (trade banks products, retail banking)
Insurance companies make use of many channels of
distribution. Insurance polices are available via own branches, agencies, sold
by nets of sales agents, cooperating nets, multi-agents, brokers in cooperating
banks or other financial institutions. Within the direct marketing itself there
are alternative channels of contact i.e. internet and phone.
Another stage of
great importance is promotion. Insurance companies use the promotion of
products to communicate with potential customers, inform about products and
popularise them. The promotional period is used to portray the company in a
positive light, to gain trust of customers and to protect the continuity of its
business. The basic purpose of promotion is:
·
Promoting the company image and gaining customers trust
·
Stimulating turnover of the company and increasing its share on
insurance market
·
Increasing promoted product sale (or group of products)
·
Search and attainment of more customers
·
Providing information on new products
Human resources in
the insurance sector are of great importance. Customers interact with staff in a
variety of ways: personally in the branch, via phone etc. It is staff that have
a big impact on gaining a comparative advantage over the competitors on
insurance market. Commitment and trust in the company can make staff the most
important customers and become a value for company itself. Staff that
recommends their company as best on the market can be more effective than
advertisement in the mass media. Treating staff at all levels as a distinguished
element of mix-marketing can be most rewarding for company.
The last element
of creating marketing strategy is analysis of failed and attained objectives.
Despite introducing this element as the last one, in practice insurance
companies control and assess their objectives regularly in order to correct
their mistakes and wrong decisions.
The results of the
survey clearly show that polish insurance companies focus on engaging in
communication with customers. Companies need to look for new channels of
communication with customers in order to gain advantage on the market. The
dynamics of competition in this matter lies
mostly in the sphere of:
·
Sales net
·
Changes in products construction (in direction of adjusting products to
particular segment of recipient as well as simplification)
·
Changes in company-customer communication (the ideal communication
system in insurance companies is best pictured by 4C model: coherence of
information, consistency, continuity of activity and complementary
communications)
3. Market and product strategies
The dynamics of the
current market situation caused largely by competitors activity, changes in
customers preferences, technological advancement etc. effects in constant
modification of products in order to meet customers increased expectations and
to follow new market trends. As a consequence an insurance companies ability to
forecast and influence the market diminishes. Inability to meet economic
targets forces companies to take a variety of steps that would stimulate the
demand for their products. Conscious and deliberate choice of long run
activities on markets and product planning is the essence of successful
marketing strategy. Strategies, through effective demand stimuli are designed
to guarantee successful accomplishment of given development goals.
The main
objectives of strategy have to focus on:
·
current products and changes in their properties
·
search for adequate market segments
·
adjustment or identification of marketing instruments and activities
·
processes stimulating demand[3]
The basic
variables in the process of shaping the market and product strategy are market
changes and product adjustment activities. The choice or change of direction in
the framework of product and market strategy is a decision of crucial
importance for company. This research presents analysis based on the Ansoff
matrix in relating product – market[4].
The matrix enables four different alternatives of action. Firstly, market
penetration, that is the sale of current products in the present market.
However, it is possible only if a degree of saturation enables attainment of
new customers. Secondly, market development, which means entering the new
market with current products. Often that means entering foreign markets.
Thirdly, product development- supplying new products on current markets and
diversification (which is most risky and consequently results in increased
costs especially if a company introduces a new product on new market).
Figure 5 pictures
proportion of polices undertaken by companies depending on their size.
![]()
![]()
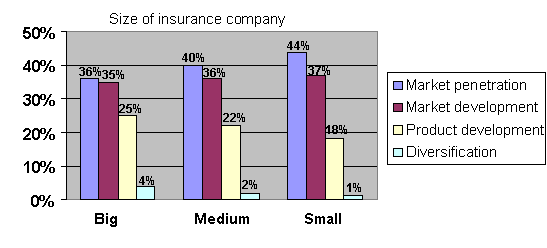

Figure 5. Market
and product strategies depending on company size
The results of the
survey clearly show that large insurance companies focus mostly on market
penetration (36%) and market development (35%). The one quarter of strategies
used by large companies is product development related. Medium and small
companies implement in their strategy market penetration (40%) and market
development (37%) followed by product development strategy (20%).
Insurance
companies depending weather it is head quarter or branch, apply mostly, two
strategies: development strategy (40%) and penetration strategy (39%). One
fifth of marketing strategy consists of development strategy and
diversification is used in a few cases. (Fig. 7).
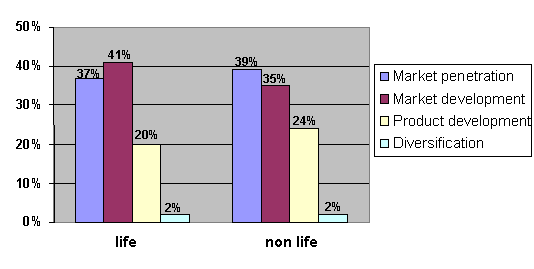

Figure 6. Product
and market strategies depending on field of activity
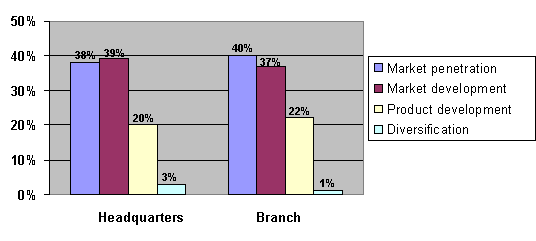

Figure 7. Product
and market strategies in relation to headquarter and branch
The general result
of the survey shows that most insurance companies implement market development
as their main strategy. Development strategy has a large scope of capabilities
from search of new methods of using current insurance products to entering
completely new markets. As a result insurance companies can achieve their goals
through a change in the way of implementing a product as well as the introduction
of product on markets similar to those presently active. Secondly, the most
popular strategy on the Polish market is market penetration. The main objectives that can be realized
though this strategy are sales intensification by increasing interest of
potential customers in the product and increases in sales to existing
customers.
4. Competition Strategy
Competition occurs
when at least two companies operate in the same field on the same market.
Activity of each of the companies is seen as threat to others. Therefore, all
companies regardless of their sphere of activity, competing on the European
Union market have to create a competitive advantage within its sphere in order
to develop. The most fundamental means to create a competitive strategy are all
marketing instruments which influence shaping and changes in the relation of company-competition.
The survey shows
that 40% of participants headquarters cooperate with agents within insurance
sales sector, 28% in using market product gaps and only 4% are applying a strategy
of lower prices. The branches in most cases use product gaps (41%) and market
gaps (24%). (Fig 8).
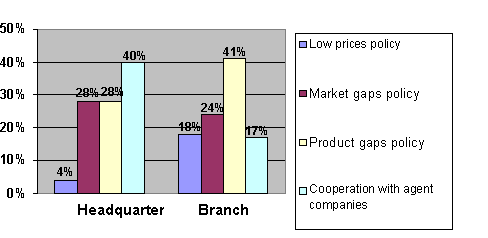
Figure 8.
Competition strategy in relation to headquarter and branch
Large companies activities
rely mostly on exploring products gaps (38%) and cooperation with agents
companies (30%). To a lesser extent, insurance companies exploit market gaps
and practice policy of lowering process. Medium sized companies compete mainly
through exploring product gaps (31%) as well as looking for market gaps (27%).
To a lesser degree they cooperate with agents companies and in very few cases
they compete though policy of lower prices. In the case of small companies, cooperation
with agents companies is of most importance and 41% of them choose it as a
competition strategy. In other cases, increasing competitiveness is pursued by a
search for product gaps and market gaps that take 29% and 25% of their
strategy. Lowering prices finds little practice (fig. 9).
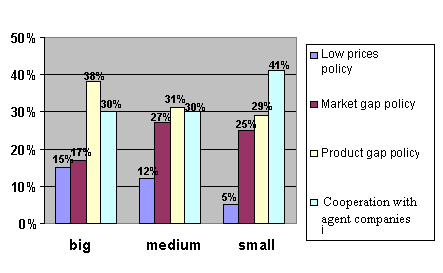

Figure 9.
Competition strategy by company size
Companies
specializing in property insurance in 38% of cases choose to compete through
search for products gaps. 34% of ‘non-life’ companies cooperate with agents and
only 7% lower their prices to become more competitive. Life insurance companies
relay mainly on cooperation with agents companies (45%). 22% of them use
product gaps and 21% rely on policy of lower prices (fig. 10).
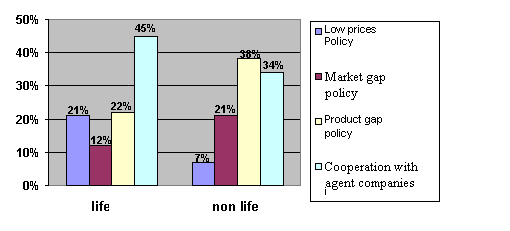

Figure 10.
Competition strategy depending on field of activity
Insurance
companies commitment in marketing strategies prove their importance. When
creating their strategies, companies build their activities on adjusting
products to customers needs and expectations. Therefore, flexibility of price
of purchase and easy access to a
insurance policy become a crucial element of marketing strategy. In the scope
of market and product strategies companies tend not to apply high risk
solutions. In this case, strategies of market penetration and market
development are most common.
Finally,
competition strategy on researched market functions through cooperation with
agents companies, particularly in the field of sales of insurance products and
information collection. Competitiveness is increased as well by looking for
such products gaps that are least provided by other competing companies.