A. L’vov,
M. Svetlov and Yu. Ulyanina
Saratov State Technical
University named after J.A.Gagarin
Analysis of
pseudo-random sequences
in the non-binary
communication channels
Abstract
An urgent problem in design and operation of
communication as well as control systems is to apply the optimal methods of
information transfer. Two main approaches are often used for solution of this
problem: the synthesis of the optimal signal structure, determined by the type
of code used, and realization of optimal digital signal processing at the
receiver. The analysis of problem showed that the use of pseudorandom signals
(PRS) is the most preferable due to their undoubted advantages. First of all,
PRS provide the greatest immunity to the stationary white noise.
This paper presents an analysis of metric
characteristics of the PRS-code, the synthesis of algorithms for the
calculation of the correlation and spectral estimates of these signals based on
the introduced metric.
Keywords: pseudo-random sequence, communication channel,
correlation, spectrum.
1. INTRODUCTION
Modern digital information systems are characterized by a large amount
of data to be processed, and require high levels of information reliability
which is defined by signals’ noise immunity in communication channels. However,
the most widely used mathematical models and methods of the PRS processing does
not allow one to realize in full the potential of noise immunity of nonbinary
code working sets of PRS (K-ary, K≥3), and get the relationships
between the noise immunity of these signals and their statistical properties.
The performed analysis of mathematical models of communication channels reveals
the necessity of consideration of code pseudorandom sequences’ metrics, in
order to evaluate the information reliability in various channel alphabets.
The works of V. Kotelnikov [1] and K. Shennon [2] established the basis
of the communication systems theory with PRS-codes. Mathematical methods of
signal processing in the PRS form are based on mathematical statistics. It is
known that correlation and spectral characteristics of PRS define their
properties and capacities. In the articles [3, 4], the formulas for calculation
of the normalized values of the coefficients of the
autocorrelation function (ACF) for any binary sequences, including those for
the PSP with the various laws of distribution for arbitrary values
of the probabilities of binary digits in the PRS are given. In
the works [5, 6] the question of the binary signal’s energy spectra obtaining
by its ACF is examined. In [6] the particular interest presents the proposed
estimation of the amplitude spectrum of the signal. However, it should be noted
that the formulas given in these articles, are not applicable for PRS-codes
with heightened channel’s base alphabet. Furthermore, they are very unsuitable
for the use in the machine calculations. However, the main disadvantage of the
proposed approach is using the Hamming metric as the base one. The analysis of PRS-codes application in most modern digital
information systems with non-binary channels, illustrates that the traditional
Hamming metric does not give acceptable results. In [7] a variant of the
ternary code metric is proposed which is fundamentally different from the
Hamming metric. Analysis of K-ary
codes has shown that this approach is effective for the synthesis of K-channels. In this sense, both from a
theoretical and practical point of view the problem of obtaining the formulas
for calculating the statistical characteristics of the K-ary PRS codes based on the proposed geometric models that are
significantly different from those of the classical coding theory present the
definite interest.
2. EVALUATION OF CORRELATION CHARACTERISTICS OF THE NONBINARY CODES
REPRESENTED BY THE PR-SEQUENCES
It is known that the codes with increased base have higher noise
immunity, so they are more preferable. As shown in authors’ previous paper [1],
from the analysis of mathematical models of communication channels that use
non-binary alphabets, it results that for certain values of the
channel statistics Pij and
Pji of transformation probability of non-zero (current) characters
i and j into each other (i,j=1,2,...,K-1,
where K – the base of the channel
alphabet) can be expressed in terms of the values P0i,
P0j, Pi0, Pj0
which are the probabilities of transformation of characters with the null
character:
Pij = Pi0 P0j; Pji
= Pj0 P0i. (1)
In accordance with (1) the probability of transformation of channel
alphabet non-zero symbols with each other is of the second order magnitude
compared with the probabilities of transformation of character with a null
character. This suggests that in the metric of the code space nonzero
alphabetic characters are further apart than the zero symbols.
Figure 1 illustrates the geometric model of the trinity-single-digit
code.
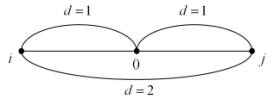
Figure 1.
Geometrical model of the trinity-single-digit code.
Analysis of mathematical models of communication channels suggests the
need to consider the fundamental metrics of code memory bandwidth for
non-binary signal correlation estimates for the construction of optimal
algorithms of encoding, decoding, modulation, demodulation and adapting systems
to changing parameters of the channel. This is particularly important in the
construction and operation of critical digital communication systems (digital
TV and radio broadcasting, cellular systems, satellite communications, control
of space objects, etc.)
In connection with this, a formula that takes into account non-binary
codes metric is obtained based on the Golomb formula [2]. In this case, the
maximum value of the minimum code distance ![]() in
the working code sets is twice the number of codewords of length n:
in
the working code sets is twice the number of codewords of length n: ![]() = 2n.
= 2n.
In this case, the probabilities of coincidence and discrepancy of bit
code sequence with the bits of its phase shift are determined by the following
formulas:
![]() ,
, ![]() , (2)
, (2)
and the normalized autocorrelation coefficients may be determined by the
formula:
![]() , (3)
, (3)
where ![]() – the number of
matching bits of the original code sequence with the bits of its cyclic shift –
the minimum distance of the source sequence and its cyclic shift.
– the number of
matching bits of the original code sequence with the bits of its cyclic shift –
the minimum distance of the source sequence and its cyclic shift.
3. ESTIMATION OF THE
SPECTRAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE CODES REPRESENTED BY THE NONBINARY PR-SEQUENCE
An important statistical characteristic of the code is its energy
spectrum. From previous work of authors [3] should be that the calculation of
code sequences metrics directly from their spectral estimates is extremely
difficult, so it is convenient to calculate the parameters of the frequency
spectrum by the values of the signal correlation function. Using the
relationships of Wiener-Khinchin, an algorithm for calculating the spectral
characteristics of non-binary PR sequences with the introduction of a metric is
obtained:
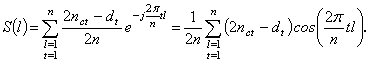 (4)
(4)
(In (4) l and t are summation indices).
So, formulas (3) and (4) may be used for the calculations of the normalized autocorrelation coefficients and the spectral characteristics of non-binary PR sequences with the introduction of a new metric. These results allow to have the new possibilities for the estimations of other important characteristics of information channels and systems, which are more effective, then traditional metrics and methods of their estimations.
4. RESULTS
Thus, the main results of the work are:
a)
calculation of metric characteristics of
non-binary code PR-sequences that are different from the classic ones by the
higher effective;
b)
algorithms for calculating the correlation
and spectral characteristics of the non-binary code PR sequences with the
proposed code metrics.
References:
1. V. A.
Kotelnikov Theory of Optimum Noise Immunity, Gosenergoizdat, Moscow, 1956. –
156 p. [in Russian].
2. Claude E.
Shannon The Mathematical Theory of Communication. Univ of Illinois Press, 1949.
– 55 p.
3. Dunn,
Patrick F. Measurement and Data Analysis for Engineering and Science. New York:
McGraw–Hill, 2005.
4. G. E. P.
Box, G. M. Jenkins, G. C. Reinsel Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and
Control. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice–Hall, 1994.
5. M. B.
Priestley Spectral analysis and time series. London, New York: Academic Press,
1982.
6. Donald B.
Percival, T. Walden Andrew Spectral Analysis for Physical Applications:
Multitaper and Conventional Univariate Techniques. Cambridge University Press,
1993.
7. R.
Jurgenson Immunity digital transmission systems telemechanical information,
1971. – 250 p.