Geography and hydrology / 3. Hydrology and Water
Resources
K.-agricultural
sciences., Yust N. A., k., k. agricultural
sciences., Shelkovkina N.S.
Far Eastern State Agrarian University, Russia
The
impact of wastewater on the state of
in
rivers in Amur oblast
Surface
water resources of the Amur region is 171 km3 / year. The region
takes 2,628 rivers longer than 10 km, including 31 over 200 km and more than 41
thousand rivers and streams up to 10 km. The largest rivers of the region
longer than 500 km: the Amur, Zeya, Bureya, Selemdzha, Giluy, Olekma, Nyukzha
[1].
Surface
water bodies are used mainly for power generation, drinking and industrial
water supply, mining, sewage, shipping. The main pollutants fall into rivers of
the Amur oblast by means of the
wastewater discharge.
Wastewater
formed in the Amur oblast,
consist of the organic pollutants, ammonia nitrogen, phosphates, petroleum
products, phenols, iron. Structure of sewage pollution degree: Pollution-free
cleaning – 2,74 million m3 (10,2%), insufficiently treated – 75,28
million m3 (1,26%), the regulatory net – 0,08 (38,5 %), regulatory
peeled – 4,57 million m3 (14,4%) [1].
Dynamics
of wastewater discharged into surface water bodies to the degree of
contamination So, from 2009 to 2012, the volume of polluted wastewater
decreased from 83,45 to 78,02 million m3. (Chart 1).
In terms of the
largest number of river basins of wastewater discharged into the river basin.
Zeya – 48,9 million m3, where the most concentrated gold mines and
industrial centers of the region (gg.Zeya, Szymanowski Free, Belogorsk).
Maximum load on the distance from the river. Selemdzha to the mouth, 60% of the
wastewater entering the basin. Zeya, accounted for Erkovetsky coal mine.
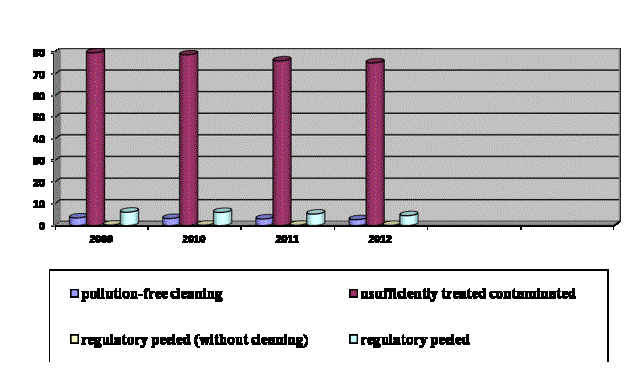
Chart 1 - Dynamics of
wastewater discharged into the river
The structure of the wastewater
discharged by the degree of purification compared to 2011 is shown in Table 1.
Table 1
Volumes of wastewater discharged into the
river Amur region, million m3
|
Wastewater |
Amur Oblast |
|
|
Total |
2011 |
84,7 |
|
2012 |
82,66 |
|
|
% |
-2,4 |
|
|
Normative net |
2011 |
0,13 |
|
2012 |
0,08 |
|
|
% |
-38,5 |
|
|
Regulatory purified |
2011 |
5,34 |
|
2012 |
4,57 |
|
|
% |
-4,4 |
|
|
Insufficiently cleaned |
2011 |
76,18 |
|
2012 |
75,28 |
|
|
% |
-1,2 |
|
|
Without purification |
2011 |
3,05 |
|
2012 |
2,74 |
|
|
% |
-10,2 |
|
The volume of discharge
of pollutants in the composition of wastewater in 2012 decreased as compared to
2011 by 12,7% and amounted to 9,63 tonnes, taking into account the dry residue
– 25,819 tonnes Weight relief within the established standards amounted to 83%
of the total discharge of pollutants [2].
Wastewater formed
in the Amur region, are formed by organic pollutants matter (BOD), ammonia
nitrogen, phosphates, petroleum products, phenols. Heavy metals are typically
present in wastewater within the standards and are mainly due to their content
in natural water source. Regulatory effluent decreased due to the enterprises
zototodobyvayuschey industry, which corresponds to a total reduction of waste
water in the industry due to the reduced volume of sand washing. Thus, combating
pollution of surface water resources is necessary in order to improve sewage
treatment plants, adjust the volume of wastewater discharged into water bodies.
Analysis of the data showed that the volume of wastewater discharged into
surface water bodies in 2012 amounted to 82,66 million m3, which is 2,4% less
relative to 2011, when it was dropped 84,66 million m3. A steady decline in the volume of wastewater is observed.
References:
1. Gosudarstvenny report on the protection of the
environment and the environmental situation in the Amur region in 2011 the
Ministry of Natural Resources of the Amur Region, 2012
2. Information bulletin on the state of water bodies,
bottom, banks of water bodies, their morphometric features, water protection
zones of water bodies, quantitative and qualitative indicators of water
resources, the state of water sistempo Amur Basin District relating to the area
of operations of the department of water resources of the Amur Amur BWI region
for the year 2012.