Òåõíè÷åñêèå íàóêè / 6. Ýëåêòðîòåõíèêà è
ðàäèîýëåêòðîíèêà
Doctor of Sciences Artyushenko V.M.1, candidate of
Sciences Volovach V.I.2
1Technological
University, Korolev, Russia
2Volga
Region State University of Service, Togliatti, Russia
Research and analysis of statistical characteristics of
useful signal reflected from an object with spatially-distributed reflective
elements
Lead. The article
shows that in the analysis and implementation of radio-technical devices
operating at close ranges, one should be aware of the extensive nature of the
detected object, multipath nature of the reflection of signals from the object,
etc.
In the article we examine the
results of experimental studies of the statistical characteristics and of the
parameters of the Doppler signal spectrum for different models of extended
objects. Analysis and generalization of the obtained results was carried out based
on a big selection of fragments of the Doppler signal spectrum that allows us
to consider these results as statistically reliable. It is shown that
acceleration motion of the extended object has the greatest influence on the
width of the spectrum of the Doppler signal and, consequently, on the accuracy
of the measurement of its speed of movement.
Key words. The
short-range radar systems (SRRS), the extended object, the vehicle, the spectrum of the Doppler
signal, the effective width of the spectrum, scattering cross-section, the speed of the
motion, the acceleration of the motion.
Introduction. Short-range
radar systems (SRRS) are widely applied in various systems of measurement of
movement parameters, protection systems of various objects, classification
identification systems use the principle of short-range radar-location. [1,2]. Consequently, they
should also use other characteristics than those applied in the theory of long
range radio systems.
Doing the theoretical justification
and practical implementation of any devices belonging to the class of SRRS, for
example, measuring device of motion parameters of various objects, you should
consider a number of specific features for short range, such as the extended
nature of the detected object, the comparability of geometric dimensions of the
object with the distance to it, multipath nature of the reflection of signals
from such objects, etc.
As a result, it is necessary to analyze the
characteristics of reflection of the sounding signal, to define the width of
the Doppler spectrum of the signal, to select the method of definition and experimental
determination of the scattering cross-section, and also to create on their
basis mathematical models corresponding the real physical phenomena in SRRS
taking into account the extended nature of the detected objects, constantly
changing range, various laws of instantaneous detection probability, a priori
uncertainty about the position of the object and its motion parameters [1,2].
Body. A priori
knowledge of the statistical characteristics of signals and disturbing
influences allows us to formulate more accurate mathematical models of the
reflected signal as well as interferences influencing this signal and
reasonable approach to the development of devices of SRRS. Previously the
authors [3] have selected and justified models of disturbing influences on
electronic detection devices (EDD) of high frequency type, which is a special
case of SRRS taking into account multipath nature of the signals reflected from
extended objects. It was noted that the probability density of the
envelope of such a signal is well approximated by the PDF of Nakagami, and the PDF
of the instantaneous values at specific values of the distribution parameters
is clearly bimodal.
One of the objects of
detection, changing motion parameters, ensuring traffic safety in the group,
etc. SRRS are various vehicles of railway transport and road transport, which
by their structure can be attributed to the extended objects of complex shape. Particularly interesting
is the study of the above mentioned vehicles in connection with the special
character of the reflections of the sounding signal coming from them. It is known [4,5] that
a vehicle as an object of detection is a complex spatially distributed radar
target. Characteristics of the signal reflected from such a target, not only
affect the range of SRRS, but also largely determine the number of other
important indicators for such systems as: the accuracy of measurement of speed,
resolution and other.
As is known, when we measure the
motion parameters of any extended object with radio methods, the speed of its
movement is determined by the Doppler frequency offset of the signal:
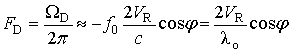 , (1)
, (1)
where VR – is the radial velocity of movement of the detected
extended object; λî – is the wavelength of the
probing signal; j – is the angle between the direction of the axis of
the main lobe of the antenna directional diagram and the direction of movement
of the extended object.
One of the most important
statistical characteristics of the signal reflected from the extended object,
affecting the accuracy of measurement of speed of its movement, is the spectrum
of the Doppler signal (SDS). The main parameters of the SDS are the average
frequency of spectrum FD.A,
the shape of the envelope, the effective width DF and power ÐD.
The effective width of the SDS
is determined by the resulting pattern of the directivity of the antenna in the
plane of the angle j. As noted by the authors previously [4] the effective
width DF, is also affected by the correlation interval. The
interval characterizes the rate of change of a random process in time:
![]() , (2)
, (2)
It is also shown that at a
certain mutual arrangement of radio-technical sensor (RS), measuring the speed
of the object and the vehicle, when the vehicle moves in the direction RS, the
width of the Doppler spectrum of the received signal can be estimated by the
formula
![]() , (3)
, (3)
where 2Da – is the angular size of the vehicle (in horizontal
plane).
Determination of the parameters
of the reflected signals, including the spectral parameters can be used in
various applications [6-10].
Next, let us proceed to study
results of SDS parameters.
It should be noted that the
methodology we use now was proposed by the authors before [1,2,10]. Also
earlier on the basis of the proposed method the authors experimentally
determined the average values of scattering cross section (SCS) sV, the width of the SDS is DFV and root-mean-square deviation of the SCS on the
example of different types of vehicles. To summarize the obtained results it was interesting
to carry out the research of more extended objects such as vehicles of railway
transport, as well as the study of the influence of acceleration of these
objects on the parameters of the SDS.
An experimental study of the
parameters of the SDS reflected from extended objects (train rolling-stock,
single cars, in some cases for a shunting locomotive), was performed using
microwave oscillations of serial rate meter RIV-V2 with wavelength l = 8 mm. Analysis
and generalization of the study results of the parameters of the spectrum
produced from the numerous fragments of the Doppler signal reflected from the
vehicle of the same model. The number of the considered fragments from the
vehicles of each type was 380...400.
All of the spectra of the
reflected signals can be divided into three groups. The first group will include the SDS under
irradiation of the vehicle (train rolling-stock) at an angle close to zero when
the vehicle is at a relatively large distance of about 50...60 m. For this case
is characteristic the spectrum of the reflected signal, potentially providing a
good accuracy of measurement of speed and, consequently, acceleration and high
resolution. The spectral width at the level of 0,707 is ΔF = 8…10 Hz.
The second group of spectra
corresponds to positive angles of irradiation of the vehicle α0
≥ 17î. In this case, the width of SDS increases significantly
and is ΔF = 20...25 Hz, which corresponds to the location the vehicle at
relatively small distances of about 10...20 m from the RIV velocity meter. The
angular dimensions of the vehicle often exceed the beam width of the antenna.
Moving vehicle rapidly changes its angle, which is accompanied by rapid
fluctuations of reflecting centers, which leads to the expansion of the SDS,
the deterioration of the accuracy potential of the velocity meter and frequency
resolution. In addition, this case is characterized by a sharp decrease in the scattering
cross-section (SDS) for some types of cars caused by the oblique fall of the ray
on a smooth surface of the vehicle (mirror reflection), as well as some
decrease of scatter of the values of SCS for different types of cars, due to the fact that the narrow
beam of antenna irradiates only a part of the surface (projector mode).
The third group of spectra
corresponds to the deceleration mode of the vehicle from the trigger point to
the moment of release the car retarders. In this case the body of a railroad car as
well as the velocity meter is exposed to strong vibration. In this case the
spectrum of the reflected signal is expanded so that its width reaches ΔF = 30…40 Hz. Under these conditions the
accuracy of the velocity measurement is the worst.
A significant expansion of the
range is observed in Doppler signals reflected from shunting locomotives, because
their body continuously vibrates from the running engine. Moreover, SDS does
not only expand, but also has a "parasitic" harmonics, the amplitude
of which is comparable with the spectrum of the main signal, which
significantly affects the measurement accuracy, and can lead to errors in the
velocity measurements.
The results of processing of
the experimental data show that when rotating wheels of the vehicle or its oscillating
parts (for example, the rear and side doors, hatches, covers and accessories
for fastening cargo) are irradiated, in the spectrum of the reflected signals
appear additional components. Moreover, the frequencies of these components can
be both above and below the frequency of the main signal, and their level is 10...40
dB below the main signal. It should be noted that the results obtained in this
part of the study are absolutely identical to the earlier obtained results of study
of similar parameters of SDS for road transport [5]. At low speeds of rolling
of the vehicle the spectrum of the reflected signal is exposed to stronger
"parasitic" effects than the spectrum of the signal reflected from
the vehicle at a higher speed. This is because at low speeds of rolling of the vehicle
the spectrum of the reflected signal falls within the frequency domain of
additive noise, whose spectrum and the SDS "overlap". As a result of
this not only the expansion of ΔF
can occur, but its "splitting" as well, which greatly reduces possibility
of accurate measurement of the Doppler frequency signal.
As a result of experimental
studies it has been shown that the vehicle movement acceleration has the
greatest influence on the width of the SDS and, consequently, on the accuracy of
speed measurement of the extended object movement (railway cars, vehicles in
general). Moreover, the bigger is its absolute value, the wider is the energy
spectrum of the reflected signal, which is fully consistent with the
theoretical analysis.
Conclusions. Considering
a good compliance between theoretical and experimental results we can draw the
following conclusions. The average value of the acceleration of railway cars rolling
into brake
position is within (+0,45)…(+0,55) ì/ñ2. At the time of braking, the acceleration is in the range of (–1,9)…(–2,1)
ì/ñ2; respectively, in the output of the moderator it is (–0,05)…(+0,05)
ì/ñ2. It should be noted that while technically implementing
the tracking velocity meter for increasing
accuracy of measurement of the average frequency of spectrum of the reflected
signal, the time constant of the measurement must be chosen from the condition
of minimum width of the Doppler reflected signal at the maximum possible acceleration
value of the vehicle, taking into account the required processing speed of the
meter in receiving and issuing information about velocity of the vehicle
movement. As can be seen from the presented results, the time constant of the
measurement must be within 80...120 ms.
References:
1. V. M. Artyushenko, Research and development of the radar measuring instrument of
parameters of movement of extended objects (monograf), Moscow, NOU VPO FTA,
2013. – p. 214.
2. V. I. Volovach, Methods and analysis algorithms of
short-range radio engineering devices, (monograf), Moscow,
Radio and communication, 2013. – p. 228.
3. Artyushenko
V. M., Volovach V. I. Statistical Characteristics of
Envelope Outliers Duration of non-Gaussian Information Processes. In the Proceedings of IEEE East-West Design & Test Symposium (EWDTS’2013),
pp: 137-140.
4. V. M. Artyushenko, V. I.
Volovach, “The analysis of parameters of a range of the signal reflected from
extended object”, News of higher education institutions. Instrument making. –
2012. – 9 (57). – , pp. 62–67.
5. Lu N. H.,
Bruce A. Eisenstein. Detection
of Weak Signals in Non-Gaussian Noise // IEEE Trans. – 1981. – Vol. IT-27, 6. –
Ð. 755-771.
6. Prokopenko N. N., Serebryakov A. I., Budyakov P. S. Perspective high-frequency
correction in differential and broadband amplifiers. In the Proceedings of Papers – 5th European Conference on Circuits and
Systems for Communications, ECCSC'10, art. no. 5733875, pp: 135-139.
7. Budilov V. N., Volovach V. I.,
Shakurskiy M. V., Eliseeva S. V. Automated Measurement
of Digital Video Cameras Exposure Time. In the Proceedings of IEEE East-West Design & Test Symposium (EWDTS’2013),
pp: 344-347.
8. Shakurskiy M. V., Shakurskiy
V.K., Ivanov V. V. Digital converter of frequency deviation based on three
frequency generator. In the Proceedings
of IEEE East-West Design & Test Symposium (EWDTS’2013), pp: 316-319.
9. Anfalov
K.V., Volovach V. I. Comparative
Analysis of Coding Effectiveness in Telecommunication Systems with ARQ. In the Proceedings of IEEE East-West Design &
Test Symposium (EWDTS’2013), pp: 320-324.
10. Volovach V. I. Accumulating
probability of detecting the objects in the control zone of radio security
devices // Electrical engineering and information systems. – 2011. – 1, v. 7. –
pp. 17-20.