UDK 541.13
SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH CLEANING WASTE
WATER FROM OIL
Iztleuov G.M.-professor,
Zhusabek A.S
SKSU by M.Auezova
Oil
production is a new industry in Kazakhstan that promotes the economy and makes
noticeable social development. This industry has many environmental impacts
such as air pollution, soil pollution and hazards associated with waste
production. Petroleum products are the most common pollutants. A
large number of these impurities contained in the effluent of motor and car
companies, railway companies and agricultural equipment, tank farms, pumping
stations and loading points. Wastewater treatment, there are certain
difficulties associated with the release of these parts of the emulsified oil
and oil products, which form water
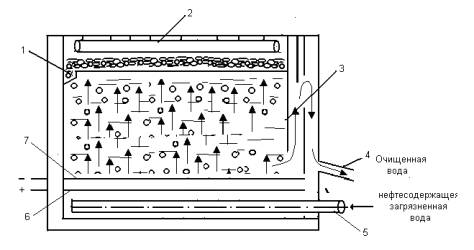
Figure-9. Elektroflotator for cleaning
waste water from oil: 1 pocket charges foam
2- peno device
3- emergents partition
4,5 getting and supply
line, he cathode,6-(titanium),7-an
anode (graphite)
At present, the actual
problem is the development of effective methods of nonchemical intensification
elektroflotatsion cleaning oil and oily water. Positive results were obtained
in the purification of water high effect can be achieved by using a combination
of titanium and graphite electrodes. Concentration of oil in this case
decreases from 350 to 10 mg / l (see Table 1.2)
In Table 1 we studied the effect of current density on the degree of
purification titanium water from oil.
The current density was
varied 25-200 A / m2, and the degree of purification of water has increased
from 69.6% Oil - 89.2%, depending on the salinity of the power consumption of
0.2-1.2 kWh / m3. In Table 2 we studied the effect of electrolysis duration of
the degree of purification of water from oil. Electrolysis time value varied
10-60 minutes while the degree of purification of water from petroleum
increased 89.2% - 99.8%. Use of insoluble electrode-cleaning preferred emulsions, despite this increase
in energy consumption. Increased electrode life, decrease in foam volume and
simplify the technology of its processing compensates for the extra power
consumption. Test installation with such elektroreaktor revealed some features
of cleaning water from oil products. Thus, the cleaning efficiency in floto
depends primarily on the concentration and dispersion of oil particles.
Effect of extraction
increases with their size and quantity without changing the cleaning, the
residual oil wherein the concentration of 1-5 mg / l.
In addition to the electrical parameters, on the degree of extraction of oil
and oil products is greatly affected by hardware design and hydraulic
parameters of the process electroflotation. For example, proposed by "Ford
Motor" elektroflotator countercurrent movement of the water and gas
bubbles, as well as a rotating feed and collection device allows more uniform
distribution of water in the unit volume and to increase cleaning efficiency.
Electroflotation is one of
the most effective ways to purify water from oil and butter, it is carried out
in devices with insoluble or soluble electrodes.
Experiments were carried out special electrochemical cell (Figure 4). Design of
the apparatus for cleaning elektroflotatsion quite simple. The electrodes can
be carried out in the form of plates disposed at the bottom of the unit
horizontally or vertically, occupies almost the entire area of the
bottom to prevent the flow patterns that prevent flotation contaminants
Politkovskaya was found that the efficiency of this method is equivalent to the
treatment of urban wastewater in the aeration tanks to incomplete cleaning,
more efficient and easier to use than biochemical methods of aeration or
biofiltration. When using insoluble electrodes flotation
efficiency depends on the size of recoverable drops. For example, if the
recovery rate of the particle diameter of 18 micrometers is 62.5%, the diameter
of 10 micron - 23.3%. Particle diameter of 5 m oil electroflotation almost
recovered, and a diameter greater than 22 microns are removed effectively
Physical and
chemical processes taking place in the water purification devices
elektroflotatsion include electrolytic generation of gas bubbles, the adhesion
of gas bubbles and dirt particles, transportation of aggregates formed
"gas bubble - particle pollution" on the surface of the liquid to be
treated.
An important and often determined by the stage of the process is
elektroflotation adhesion of gas bubbles and dirt particles, which occurs at
the molecular level. Approximation vesicle particles is effected by external
hydrodynamic forces, and the distance between them is reduced to 10 ~ 6 mm,
molecular forces start to act. In this case, the act of sticking particles to
the bubble is accompanied by a sharp decrease in the surface energy of the
boundary layers and the emergence of forces that seek to reduce the wetted
surface.
The flotation process flows more successfully than the more general surface of
the gas bubbles and the greater area of contact with them
floatable particles. In systems with the same degree of liquid gas filling the
total surface of the smaller bubbles will be greater and the distance between
the particles and smaller bubbles, which enhances the probability of their
collision.
Electroflotation
method has some significant advantages over other methods of flotation
wastewater: ease of manufacturing devices and the simplicity of their service;
possibility of regulating the degree of cleaning fluid depending on a phase
state of particulate contamination by changing only one parameter (current
density) in the process; high degree of dispersion of the gas bubbles, which
provides the efficiency of attachment of insoluble impurities; no moving parts
in the work area devices, ensuring their reliability and precluding mixing
liquid to be treated and grinding it contains suspended particles; additional
mineralization of organic pollutants with simultaneous disinfection of
wastewater generated due to the anode of the electrolysis products - atomic
oxygen and chlorine.
Table 5
Effect of current density on the degree of purification of titanium water from Oil
|
N |
The current density on titanium À/ì2 |
The duration of the
electrolysis, |
Concentration of oil
in the waste water before purification |
Concentration of oil in the waste water after cleaning |
The degree of purification, |
|
1 |
25 |
10 |
350 |
110 |
69,6 |
|
2 |
50 |
10 |
350 |
82 |
77,6 |
|
3 |
100 |
10 |
350 |
50 |
85,8 |
|
4 |
150 |
10 |
350 |
38 |
89,2 |
|
5 |
200 |
10 |
350 |
38 |
89,2 |
LITERATURE
1. Carter, R.
E., MacKenzie, M. D., and Gjerstad, D. H. (1999). Ecological land
classification in the Southern Loam Hills of south Alabama. Forest Ecology and
Management, 114, 395-404.
2. Castaneda, F.
, Collaborative action and technology transfer as means of strengthening the
implementation of national-level criteria and indicators. In Criteria and
indicators for sustainable forest management, ed. R. J. Raison, A. G. Brown,
and D. W. Flinn, 2001, pp. 145-163. IUFRO Research Series No. 7. CABI
Publishing, Wallingford.
3. Castley, J.
G. and Kerley, G. I. H. The paradox of
forest conservation in South Africa. Forest Ecology and Management, 85,1996, pp35-46.
- Caswell, H. Matrix population models:
Construction, analysis and interpretation. Sinauer Associates,
Sunderland,1989, pp 45