Borzienkova S., Ladieva L.
The National Technical University of Ukraine “Kyiv Polytechnic
Institute”
The
evaporation control in the thermal cracking process
Thermal cracking or dry distillation
under pressure was designed for processing heavy fuel-oil residues and
distillate materials. This method contributes to a significant increase in
selection depth of light oil-products from oil.
Dry processing based on decomposition of hydrocarbon molecules and is the most
common way of chemical processing of oil-products. The destructive distillation
process of fuel oil and tars was invented to increase gas-oil fractions
resources – the cracking plants feedstocks for hydrocarbons mixture with
different structure (distillate yield increased by almost 35% compared with
conventional distillation). The peculiarity of the process is a combination of
a raw distillation with a tarry residue thermal decomposition in the
evaporator.
 Fig.1.
Technological scheme of installation for destructive distillation of fuel oil
and tars
Fig.1.
Technological scheme of installation for destructive distillation of fuel oil
and tars
Installation with single continuous
passing of material is showed in Fig. 1. It consists of the high-temperature
section (oven, evaporator), the fractionation (stripping and rectification
columns, etc.) and the cooling (refrigerators, etc.) sections.
Gas-oil fractions principally formed
on the evaporator. It`s a part of the high-temperature section, which works at
medium (420 ... 425 °C) temperatures and low overpressure (0.2 ... 0.3 MPa).
The formation takes place under the live steam influence: a mixture of fuel oil
with a small amount of water vapor and cracking gases enters the bottom of the
evaporator. There the mixture begins to be purged by heating steam and
decomposes into heavy resinous residue and volatile mixture of cracked gases.
Fluid level and overpressure are the
main parameters of the evaporator operational condition.
Next control system (Fig.
2) was created to ensure the management of the evaporator. It includes
feedforward and error-closing control.
Pressure control is carried out by superheated steam with using a cascading
control system. The internal control loop consists of flowmeter of water vapor
(6-1), normalizing converter (6-2), the regulator (6-3) and the actuator (6-4).
The external loop includes a pressure meter (4-1), the regulator (4-2) and
summator (4-3), which forms internal tasks for regulator. The signal from the
disturbances compensation loop is applied to summator. Compensation loop
consists of flowmeter for cracking gases (5-1), normalizing converter (5-2) and
the dynamic equalizer (5-3).
Fluid level control is carried out by feeding liquid fuel oil. It used a
similar system to control. The internal control loop includes flowmeter (3-1),
normalizing converter (3-2), the regulator (3-3) and the actuator (3-4).
External circuit: level gage (1-1), the regulator (1-2), summator (1-3), which
receives the signal from disturbances compensation loop. It consists of
measuring the flowmeter for severe cracking residue (2-1), normalizing
converter (2-2) and the dynamic equalizer (2-3).
Additionally, the solvent supply control loop was provided to reduce the impact
of speed removal of heavy residue. It consists of the viscometer (7-1), the
regulator (7-2) and the actuator (7-3).
Besides the temperature control
loops of all incoming and outgoing flows were introduced monitoring of the
evaporation process (8-11 contours).
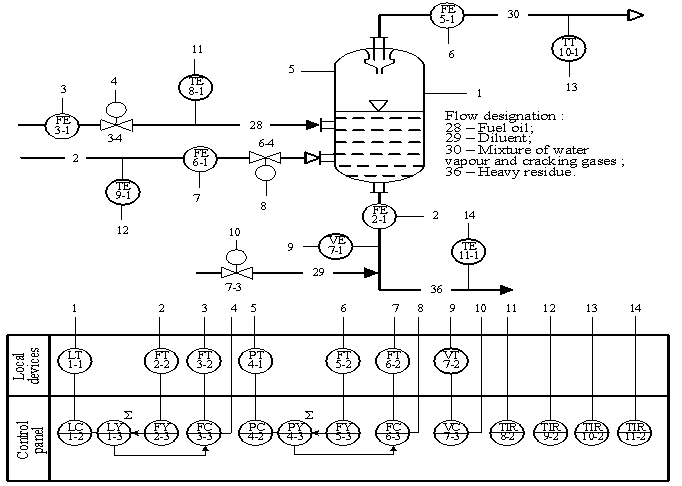
Fig.2. Automation scheme of evaporators work
The relevance of fuel-oil dry
distillation technology is recycling and using products of primary oil processing.
Also, the designed scheme of
vaporizer automation control enables to increase the accuracy of measurement. Therefore the process control is going to be better.
But the main advantage of this scheme is reducing the support resources. And it
is economically profitable.