Current state and development
trends of food industry of the Republic of Kazakhstan
Gaukhar Sakhanova
Abai Kazakh National
Teachers’ Training University
Dostyk str. 13,
Almaty, Kazakhstan
E-mail:
ecolady@mail.ru
Annotation: Kazakhstan came into new period of
development – stage of economic growth. In economic policy there appeared new orientation
points related to gradual withdrawal from “raw” model of development and
creation of competitive and diversified industry. Economic growth achieved at
the account of extensive use of natural resources seldom has sustainable
character. Therefore development of sectors and industries providing growth of
added value becomes of big importance.
Among these sectors is food industry.
Food industry allows more rational use of rich natural potential of country,
developing it on the basis of production with higher added value and, as the
result, providing the sustainability of economic growth.
JEL Classification:
L000, E660, E690
Key words: food industry, food safety, state
support, agroindustrial complex
UDC: 330.341.1:62(574)
Introduction
Food safety of country is one of the
factors of state security. It defines economic stability and political independence
of state, it’s possibility to fulfill the primary needs of it’s citizens
without damage to national and state interests.
National interests of the Republic of
Kazakhstan in agriculture production sphere may include: provision of adequate volume
of domestic production of food products; keeping the specified level of state
food reserve; provision of correspondence of quality of produced and realized
food products to standards of quality and safety on food products; provision of
adequate living wage, level and high quality of healthy life for population; expansion
of production of competitive food products with orientation for export; performing
state control of food market (including account and control of production, foreign
and domestic supplies, food reserves).
Therefore, strategic aim in sphere of
food and processing industry in middle-term period is increase of
competitiveness of processing sites based on principles of sustainable
development of the Republic of Kazakhstan. According to data of Statistical Agency
for January 1, 2009, in Kazakhstan output of production of food industry is
performed by approximately 3,0 thousand sites, where 69,1 thousand of people
work, that is nearly 17 per cent of all employees in processing industry.
Average annual rate of increase of
sphere for the lat five years made 108,4 per cent.
Analysis of output of
food products in the republic
Food industry is a combination of
industries producing food stuff, belonging to the primary spheres of life
support and takes one of the first places in sustainable development of the
economy of country. Production of food stuff is intensively developed sector of
processing industry of Kazakhstan [1].
In conditions of crisis the more dashing,
if compared to other industries, increase of prices for food stuff is explained
by their primary importance and necessity. Due to this increase rate food industry
follows the industries of natural monopolies.
Development of domestic food industry,
turning it to highly effective and high-yield economic sector is the main
factor of providing of food safety of country, affecting the interests of all
economic system of state.
Food industry plays significant role
in development of agriculture and essentially affects the development of such
related sectors as electrical energy, transport, production of packaging materials.
It plays key role in formation of social prosperity of population [2].
The message of President of the Republic
of Kazakhstan «New decade – new economic upsurge – new possibilities for
Kazakhstan» says that the important segment of diversification of the
development of agriculture-production complex, which shall be performed due to
three main directions:
1. Increase of labor productivity;
2. Providing the food safety;
3. Realization of export potential.
Labor productivity in agriculture
sector makes approx. 3 thousand dollars for one employee per year. In developed
countries this marker is 50-70 thousand dollars. Therefore the task is aimed to
increase the productivity in agriculture sector at least twice. To deal with this
task is possible only with agriculture-industrial diversification, that is
rapid increase of production of agriculture raw materials, new equipment, new
technologies and approaches in agriculture. International experience shall be applied;
it shall be rapidly embedded into our agriculture. By year 2014 more than 80
per cent of domestic market of food stuff shall be comprised of domestic food
products [3].
According to estimations of Ministry of economy and budget
planning of RK, actual increase of GDP in 2009-2010 makes 1-3 per cent. Inflation
rate at the end of 2009 and 2010 is planned within the limits of 7-9 per cent.
Strategic aim in sphere of food
industry at midterm period is the increase of competitiveness. Due to this, maximum
efforts are aimed at creation of favorable conditions for increase of
competitiveness of processing sites and providing food safety.
Data of Statistical Agency show that
within recent years volume of production in food industry of the republic had
reduced, particularly in 2009 it reduced for 1,8 per cent and made 792 billion
tenge in current prices (table 1). Decrease happened to be less deep that in
several other sectors of processing industry of country, yet preconditions for
decrease of production were substantial enough:
• compression of customer demand of population;
• deficiency of turnover assets;
• decrease of possibility to attract
credit resources;
• loss of competitive price
advantages by certain food products.
Table 1 – Volume
of production of food industry
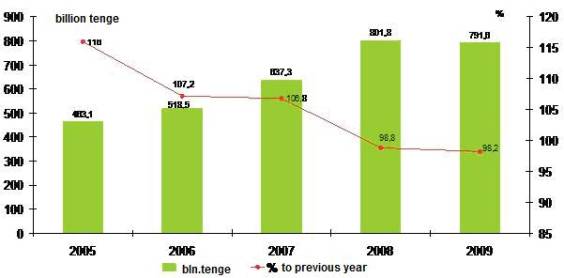
Source: according
to data of Statistical Agency. www.stat.kz
In year 2009 there appeared the significant
growth of such trends as production of vegetable oils, meat and meat products,
juices. The biggest decline, affecting on the whole the markers of sector, was
shown by manufacturers of sugar and milk products (table 2). The output of non-alcoholic
and soft drinks reduces insignificantly. Beer production remained actually due
to the level of 2008.
Table 2 – Production of food stuff
in RK
|
Year |
2005 |
2006 |
2007 |
2008 |
2009 |
|
Meat and food subproducts, mln. tonnes. |
85,6 |
91,4 |
110,2 |
113,5 |
122,2 |
|
Cereal, rough grinded flour mln. tonnes. |
26,1 |
35,9 |
40,2 |
43,2 |
42,1 |
|
Pasta, mln.tonnes. |
85,1 |
104,1 |
124,8 |
122,4 |
127,2 |
|
Vegetable oils Refined and non-refined, mln. tonnes |
167,0 |
212,7 |
237,3 |
188,9 |
206,7 |
|
Processed milk - liquid and Cram, mln. tonnes |
179,7 |
225,8 |
258,7 |
266 |
235,2 |
|
Solid forms of milk, mln. tonnes |
4,3 |
4,4 |
3,8 |
3,0 |
2,8 |
|
Butter, mln. tonnes |
19,7 |
18,6 |
19,7 |
17 |
14,7 |
|
Cheese and curd, mln. tonnes |
14,9 |
17,0 |
17,1 |
16 |
13,9 |
|
Fruit and vegetable juices, mln. litres |
99,5 |
129,9 |
168,0 |
122,5 |
132,2 |
|
Canned fruits and vegetables, mln. tonnes. |
5,2 |
5,2 |
6,3 |
6,9 |
4,0 |
|
Sugar, mln.tonnes |
528,7 |
490,2 |
392,3 |
508,5 |
385,1 |
|
Wine, mln.litres |
52,8 |
36,8 |
19,4 |
13,3 |
11,7 |
|
Cognac, mln.litres |
5,4 |
6,3 |
6,1 |
4,3 |
4,4 |
|
Vodka and
liquor-vodka products, mln.litres |
65,6 |
64,4 |
63,6 |
61,2 |
59,9 |
|
Beer, mln.litres |
323,5 |
363,8 |
410,9 |
360,7 |
360,8 |
|
Soft drinks (including soda), mln.litres |
777,5 |
904,3 |
1112,2 |
1094 |
1005 |
|
Tobacco products, bln. pieces |
30 |
30,8 |
31,5 |
28,5 |
26,7 |
Source: according
to data of Statistical Agency. www.stat.kz
The last year was especially problematic
for development of milk and sugar industry in Kazakhstan. Negative dynamics in production
of milk stuff was experienced during all year, and production of sugar showed
increase only in November and December. The main reason of this situation is
rise of price of raw materials.
For milk industry this factor became
the major, as in conditions of limited effective customer demand and high price
competitiveness on the part of Russian manufacturers, rise of prices for end
products is limited. The previous year, due to created favorable conditions for
import milk products, volumes of supply of it’s certain types in the territory
of country exceeded markers of the preceding year. Thus, compared to 2008, in
Kazakhstan there were imported for 6,2 per cent more cheese and curd, for 5,2
per cent – butter milk, yogurt and kefir, for 28,3 per cent – milk and non-concentrated
cream, for 30 per cent - butter.
In sugar production factor of price
rising for raw materials in 2009 was partially compensated by price rising for
end products (almost for 30 per cent compared to 2008), which became possible
due to introduced regime of limited import of white sugar in the territory of
country. Nevertheless, as in 2008 production of sugar cane in Kazakhstan
reduced for 58 per cent, factor of two-fold price rising of import raw material
still affected the decrease of output volume of sugar by domestic plants.
Table 3 – price index of food industry
products, in per cent to the previous year
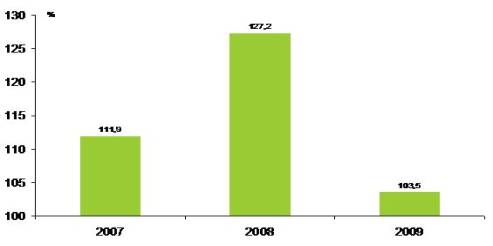
Source: according
to data of national Bank of RK
Prices of domestic manufacturers of food
products increased in 2009, but their growth rates substantially slowed. Thus,
if in 2008 price index made 127,2 per cent, then in 2009 – 103,5 per cent. The most
rise in price was of sugar – for 29,8 per cent, tea and coffee – 27,4 per cent,
tobacco products – 23,7 per cent, meat of poultry and rabbits - for 21,5 per
cent. The reason was price rising of raw materials. Only in December 2009
compared to December 2008 price for sugar, tea and non-processed tobacco,
purchased by industrial plants for further reprocessing, increased
correspondingly for 44,5 per cent, 38,3 per cent and 36,1 per cent (table 3).
Increase of prices for poultry appeared
on the background of increase of it’s production and is related, most probably,
to price rising of corn – main feed for poultry, of electric energy and of
import vaccines and premixes.
At the same time in 2009 due to
decrease of price for raw materials vegetable oils reduced it’s cost for 18,8
per cent, flour and cereal - for 12,9 per cent, spices and flavors – for 3,7
per cent.
Kazakhstan began to export wheat to
China approx. 3 mln. tons, and through China to Japan, Korea and countries of
South-Eastern Asia, that will affect the export markers of country.
According to data of Ministry of Agriculture
of RK, average annual volume of consumption of wheat in China is nearly 100
mln. and each year demand for wheat in China increases for 2 mln. tons.
Table 4 – Investments to capital stock in food
industry
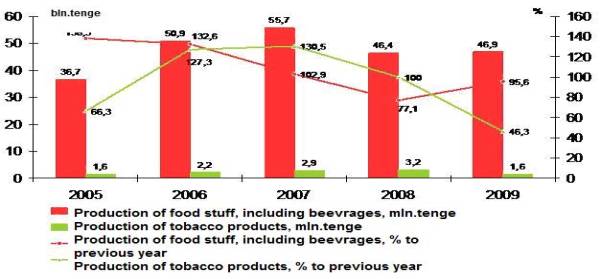
Source: according
to data of National Bank of RK
In this year investments to capital
stock in food industry continued to reduce. Compared to 2008, they reduced for
7,6 per cent, while in 2008 ã. - for 21,8 per cent. In conditions of shortage of financial assets for
realization of current activity of entities, investments to capital stock
reduced at the account of owned assets. So, investment share at the account of
owned assets decreased from 81 per cent in 2008 to 76 per cent in 2009. (decrease
in nominal terms made 8,5 per cent to 2008). At the same time, there increased
the ration of loan assets from 13,2 per cent to 19,4 per cent (nominal increase
made 42,8 per cent), and budget assets from 0 to 0,9 per cent (table 4) [4].
Therefore, in 2009 conditions of
functioning for agriculture-processing productions were complicated enough. Partially,
it was based on devaluation of tenge, which became the reason of increase of
prime cost of domestic end product due to rapidly increased cost of imported
complete parts (machinery and equipment, accessories, raw materials), share of
which in food industry of Kazakhstan is rather large. Besides that, the higher levels
of devaluation of national currency performed in countries – main trade
partners of Kazakhstan – in Russia and Ukraine created competitive advantages
in the domestic market for imported food stuff from these countries. As result,
lower prices offered by Russian and Ukrainian manufacturers at impossibility to
devalue them by domestic manufacturers, made certain types of Kazakhstani
products non-competitive.
However state support of
agriculture-processing productions allowed escaping the deep degradation of
sector.
Kazakhstan has all possibilities for
realization of reserves aimed at increase of volumes of production of food
stuff of higher quality. Large-scale implementation of scientific-technical
progress into production will allow to develop food industry.
For most Kazakhstani entities the main
goal is the cooperation with international manufacturers, which became possible
on the basis of their innovation development. In many cases the most effective
became the strategy of long-term cooperation, participation in alliances with
worldwide leaders as the alternative to independent approach to foreign
markets. Level of cooperation of Kazakhstani companies with foreign partners
shows that as they move further on the way of understanding problems and
advantage of approach the worldwide market, the more effective their financial
and economic status becomes.
As we can see from table 5, general goods
turnover in 2009 made 4 067 066,2 thousand dollars on agriculture
products, 1 274 512, 2 thousand dollars on processed products,
2 792 554 thousand dollars, that is 1 989 976 thousand dollars
less if compared with 2008, i.e. for 32,8 per cent.
Goods structure of Kazakhstani
export and import from 2000 till 2009 did not undergo great changes in
direction of improvement.
Thus, in structure of Kazakhstani
export raw materials still prevail.
Table 5 – General foreign turnover
of RK for the period January - December 2008-2009, thousand USD
|
Products |
Turnover |
2008 |
2009 |
2009 to 2008, per cent |
|
In general |
General goods turnover |
6 057 042,2 |
4 067 066,2 |
67,2 |
|
Export |
3 140 634,4 |
1 702 834,1 |
54,2 |
|
|
Import |
2 916 407,8 |
2 364 232,1 |
81 |
|
|
Balance |
224 226,6 |
-
661 398 |
74,6 |
|
|
Agriculture products |
Turnover |
2 343 273,2 |
1 274 512,
2 |
54,3 |
|
Export |
1 901 779,4 |
805 618,1 |
42,4 |
|
|
Import |
441 493,8 |
468 894,4 |
103,2 |
|
|
Balance |
1 460 285,6 |
336 724,0 |
23,1 |
|
|
Processed products |
Turnover |
3 713
769 |
2 792
554 |
75,2 |
|
Export |
1 238
855 |
897
216 |
72,4 |
|
|
Import |
2 474
914 |
1 895
338 |
76,6 |
|
|
Balance |
-
1 236 059 |
-
998 122 |
80,7 |
Source: according
to data of Statistical Agency. www.stat.kz
Insufficient competitiveness of
processing industry leads to increase of import of goods with high degree of
processing.
At present time status of
agriculture sector shows signs of growth. Volume of gross output of agriculture
for the last years increased 3,6 times. At that, prices for this period
increased almost 2,9 times. Gross harvest of cereal crops in 2009 reached 20,8 mln.tons,
which allowed fulfilling the domestic needs of country and export potential
(including flour).
In 2005 Kazakhstan, having exported
931, 9 thousand tons of flour, became the first in the world as exporter of
flour per capita, and since 2007 — the world’s first on physical volumes of
exported flour. In 2009 Kazakhstan, for the first time bringing into market
more than 2 mln.tons of flour (approx. 2,2 mln.tons of flour (that makes in
crop equivalent more than 3,1 mln.tons of , grain) (record volumes in history
of Kazakhstan)) will for the third time take the leading position in worldwide
rating of flour exporters.
Up to date the republic export more flour
than it is consummated within the country (56 per cent of produced). Thus, nearly
80 per cent currency earning from sale of processed agriculture products in the
republic consist of exported flour. The main consumers of Kazakhstani exported
flour are Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, Afghanistan. It shall be mentioned
that among the goals of milling industry – bringing the volumes of export of
flour from republic to 2, 5–3, 0 mln. tons, and among plans on development of
export are Iran, India, China. The last two countries present strategic interest
for export, as in further decade population of these countries will increase
for one billion of citizens, and possibilities of increase of production of
cereals as at the account of extensive approaches (increase of cultivation
areas), so as at the account of intensive approaches (increase in productivity)
are extremely limited. Besides, recently population of these countries changes
the structure of nutrition, including into ration more and more cereal products,
which also enlarges the demand [5].
The offered conditions of development
of national food market, including the improvement of organizational-economic
mechanism of market regulation, will lead to creation of impulses for the
further development of offer and increase of population welfare on level
adequate for healthy and active life. Along with that, there will be changed the
parameters of market itself, which will acquire the higher characteristics of
effective sustainable development in perspective.
State support of
agriculture-production complex in the republic
State support of APC aimed at it’s
effective development and dealing with utmost important tasks, that is
providing the sustainable increase of production and processing of agriculture products,
food safety, stimulating social-economic development of rural areas, creation
of conditions for Kazakhstan to enter WTO [6].
Competitiveness of agriculture products
of Kazakhstan and products of it’s processing is the main parameter of development
of APC, included in various state, regional programs and strategic plans for
development of APC: Concept for sustainable development of
agriculture-production complex of the Republic of Kazakhstan for years
2006-2010 [7].
The problem of capital raise for agriculture
demands substantial state regulation. At present time state support of
agriculture sector provides subsidizing the expenses for purchase of
material-technical resources, use of short- and long-term bank credits; leasing
of agriculture machinery; purchase of agriculture products and regulating
cereal market with the help of purchase and trade interventions; support of
insurance of harvest of agriculture products; tax benefits and financial
recovery of agriculture entities, etc.
At present time financial support of
agriculture sector of economy is performed through: JSC «National holding «KazAgro»,
which includes share companies «Agriculture production corporation», «Mal
onemderi corporatsiyassy», «KazAgroFinans», «Agriculture credit corporation», «KazAgroGarant»,
«Fund for financial support of agriculture», «KazAgroMarketing»; microcredit
organizations; commercial banks. Budget assets are provided for holding events
under programs, which are defined in Budget Code [8], namely:
- increase of productivity in agriculture sector
based on use of high-yielding technologies;
- organization of medium- and large-sized trade
entities;
- processing of agricultural products;
- implementation of innovation technologies;
- stimulating the initiative of rural population.
«KazAgroFinans» performs the financing of
perspective projects in six directions of development of agriculture in country:
creation and development of modern large-sized dairy farms, network of poultry
factories, hothouse entities, greenhouses; organization of production for
assembling of agriculture machinery and implementation of drop irrigation technology
at production of horticultural products.
Total sum of financial support of
APC by holding «KazAgro» for years 2009-2011 will be 283,9 billion tenge, of
which:
In 2009 141,5 billion tenge (realization
of investment projects – 17,6 billion tenge; financing of agriculture
manufacturers during spring field and harvest works – 68,8 billion tenge; purchase
of grain – 55,1 billion tenge).
In 2010 90 billion tenge (realization
of investment projects – 50 billion tenge; purchase of grain – 40 billion tenge).
In 2011 52,4 billion tenge (realization
of investment projects).
Thus, based on results of analysis
by republic budget there was provided financing of agriculture in 2009 in
amount of 111 227 mln. tenge. In 2010 there will be forwarded 114 672
mln.tenge, 114 005 and 128 047 mln.tenge in 2011 and 2012
correspondingly (Table 6).
Table 6 – State support of
agriculture-production complex for years 2009 – 2012.
|
Year |
2009 |
2010 |
2011 |
2012 |
|
Republic budget expenses (RB),
total, mln.tenge |
3178048 |
3702354 |
4031182 |
4257080 |
|
RB expenses for small-sized
agriculture, total, mln.tenge |
157762 |
162964 |
166816 |
177936 |
|
Including: |
|
|
|
|
|
RB expenses for APC, total, mln.tenge |
111227 |
114672 |
114005 |
128047 |
|
Including: |
|
|
|
|
|
Direct state support of APC |
42325 |
51888 |
49219 |
61902 |
|
Indirect support of APC |
68902 |
62784 |
64786 |
66145 |
|
RB expenses for other (woodland,
water, fish industry, land relations), mln.tenge |
46535 |
48292 |
52811 |
49889 |
|
APC share in RB expenses,
per cent |
3,5 |
3,1 |
2,8 |
3,0 |
|
Share of direct state
support of APC in RB expenses, per cent |
1,3 |
1,4 |
1,2 |
1,5 |
Filed according to data of Law
of the Republic of Kazakhstan «On republic budget for 2009-2011» dated 04.12.2008
ã. and Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan
« On republic budget for 2010-2012» dated 07.12.2009.
Share of financing of agriculture
sector in expensive part of republic budget made in 2009 - 3,5 per cent; 2010– 3,1
per cent, 2011– 2,8 per cent, 2012– 3,0 per cent. Share of direct support is
provided by republic budget from 1,4 per cent in 2010 to 1,5 per cent in 2012.
Direct state support includes
current transfers to oblast budgets, budgets of Astana and Almaty cities for
development of agriculture and state support for development of APC.
As the result of financial support,
in republic there formed favorable conditions for development of stock farming
and land farming, which were significantly stimulated by state investments to
APC. Thus, wheat production per capita in 2007 reached 1058 kg, which allowed
Kazakhstan to become the worldwide first on this marker, leaving behind
Australia, and on wheat export – 7 place worldwide. In 2009 total cultivated
area made 21,6 mln.hectares, which is 1,6 mln.hectares or 8,2 per cent more
than level of 2008. At that, cereal crops were located on area of almost 17 mln.hectares
or 4,9 per cent more than level of 2008 (wheat was disseminated on area of 14,5mln.hectares).
Oil-bearing crops accommodated 1076,4 thousand hectares, or 18,9 per cent more
than level of 2008. Feeding crops were located on area of 3,1 mln.hectares,
which is 32,9 per cent more than level of 2008. Potato was seeded in area of
170,2 thousand hectares, sugar cane -19,2 thousand hectares, cultivated areas
of vegetable-vine crops stabilized at level of the previous year and made 112,1
thousand hectares.
In 2009 number of cattle stock increased
for 2,4 per cent compared to 2008, in 2008 – for 2,9 per cent compared to 2007.
In all categories of farms there increased the cattle stock of sheep and goats
for 3,9 per cent, horses for 5,8, camels for 5, poultry for 6,4 per cent. Still
it is necessary to point that pig stock decreased for 1,2 per cent. For 2009 realization
for slaughter of all types of stock and poultry in live mass in all categories
of farms increased if compared to the previous year for 2,8 per cent, milk
production - for 1,6 per cent, chicken eggs – for 19,5 per cent.
Food safety
Food safety is a situation when all
people at any time have physical and economic access to adequate in quantity
relation safety food, necessary to lead active and healthy life. «Roman declaration
on worldwide food safety» says about obligation of any state to provide right of
each person for access to safe and full-value food products according to right for
adequate nutrition and right for freedom of starvation [9].
Food safety is one of the main goals
of agriculture and economic policies of state. In it’s general view it forms
the vector of direction of any national food system to the ideal condition. In
this sense, strain after food safety is uninterrupted process. At that, while
reaching it there often happens the change of priorities of development and
mechanisms of realization of agriculture politics [10].
Food safety of country is provided
in case if it’s economy produces not less than 80 per cent of consumed products, or in case if country specializes
in production of stuff, which export allows it to get the positive balance of
external trade balance on production. Food safety is considered to be provided
if beside production of necessary quantity of products there performed it’s
additional output in volume of compensated reserve stock in period of 60 days
or in 17 per cent of annual volume of consumption. In case if certain types of products
are not produced in country or their production is limited, need in them is
fulfilled by purchase from other countries. Whereas it is important not to
allow the appearance of production, political or other dependence from
exporting countries due to lack of products.
All developed countries protect
product markets from import: in the USA it does not exceed 17 per cent. Self-sufficiency
level in the USA and in France makes 100 per cent, in Germany – 93 per cent, Italy
– 78 per cent, Japan – 50 per cent [11].
The necessary condition to provide
food safety is physical and economic accessibility of food products for
population.
Upon physical accessibility of
products we shall understand the presence of food products in the whole
territory of country at any time and in adequate assortment. Here it should be accounted
that, as food products of own production have high ratio in consumption structure
of Kazakhstani population, physical accessibility of products is defined not
only by presence of goods in market, but also by possibility to produce them in
private farm holding.
Formation of worldwide production
resources is characterized by systematic crisis of production and sale of
agricultural products, presenting a serious threat to sustainability of
production supply of population. United Nations Organization (UN), World Bank (WB),
International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Food Program (WFP) and Food and
Agriculture Organization (FAO) in March 2008 declared international production
crisis. In April it already spread over 39 countries of the world, impending
the further spread. Starvation problem began to perceive especially acute when in
2007 and 2008 in 22 countries there rushed the wave of «product revolts», in
course of which many people suffered or died.
Director General of FAO Jacque Diouf
at world summit on November 16-18, 2009 mentioned that when 20-30 per cent of
population in country are starving or constantly lack food, the growth of the
whole economy is slowed. Considering that there are more than 40 such countries
and that quantity of starving people already exceeds 1 billion, that is 105
million more than in 2008, and every 30 seconds 5 children die of starvation worldwide,
then it surely will raise serious concern of international community. At the same
time development trends of international product market with account of many restricting
factors exciting deep contradictions in world economy, do not allow to predict
very high rate of growth of product and raw resources even in long term
perspective.
Estimates of long-term forecasts, made
in cooperation by specialists of Organization for Economic Cooperation and
Development (OECD) and FAO, gives the evaluation of markets of main
agricultural products 10 years ahead. If we take as hypothesis that in later
perspective there will remain the same trends and level of influence of various
factors on each other, then we can predict the scenario of development of
situation in worldwide agriculture sector based on existing forecasts.
Russian institute on agricultural issues
and informatics named after A.A.Nikonov in cooperation with Russian-German high
school of management of Academy of National Economy there were developed
variants of forecasts for development of world and Russian agriculture for period
up to 2050 ã. (study is
performed with support of project ¹08-02-00008à of Russian Humanitarian Scientific Fund). As prerequisites
for this forecast, there were proposed four hypothesises.
The first. Cultivation areas for
main agriculture products (wheat, corn, rice) will not be reduced, and will be
even increased. It is one of the main lessons that each country shall learn as
the result of production crisis in 2007-2009. Otherwise many countries and mankind
on the whole condemn themselves for constant repeat of such type of crisis.
The second. In all countries even
more recourses will be wasted on implementation of innovations of
scientific-technical progress into agriculture, thus allowing increasing the
effectiveness of use of resources, first of all land and water.
The third. Developing countries of
many regions will increase consumption of proteins at the account of meat and
milk products. It follows that the more share of grown plant resources will be
used as feeding.
The fourth. In most of the countries
there will remain the tendency to use agricultural resources generally for
production goals. Exception will be made only by those countries where exist
special natural and political conditions allowing them the effective use of
land resources for production of biofuel. To such countries may be referred, at
first, the USA (ethanol made of corn), Brasilia (ethanol made of sugar cane) and
in perspective – several countries of South-Eastern Asia, which can grasp
effective production of biodiesel from palm oil [12].
According to data by specialists on
solving production problem and liquidation of deficiency until 2050 rate of
consumption shall 1,3-1,5 times exceed rate of population growth. At that coincidence
of rates of population growth and cumulative nature of rate of consumption is
predicted only for three planetary regions (North America, Oceania, and Europe).
Negative tendencies of resource formation depressively influence as the product
market on the whole, so as markets of certain countries.
At the end of previous century
nearly 15 countries in the world annually underwent product crisis, in current
century their number increased up to 25. In 2007 in crisis declaration addressing
FAO for extraordinary help signed 47 countries. To fulfill needs in food
provision for planet population, which it is estimated to reach 9,1 billion to
2050, production of food stuff shall increase for 70 per cent, yet with
background of the whole row of problems including climate change and rapid
urbanization.
The main reason for starvation and
lack of nutrition on summit of 2009 was named lack of financing of agriculture
in developing countries. According to estimates of FAO specialists, to reach
the necessary growth dynamics of production, total average annual volume of
investments to primary agriculture (increasing soil fertility, their security,
technique, technologies, stock, etc.) and processing sectors (storage,
realization, processing of products) of developing countries compared to 2007 shall
be increased for almost 50 per cent.
Price rising for food stuff leads to
degradation of life quality in many countries, including developed ones. Nominal
prices index for products filed by FAO doubled for the period of 2002-2008. Increase
of actual prices was less expressed but still significant. After four decades of
relative balance actual price index for food stuff began to increase in 2002 and
rose rapidly in 2006-2007. At mid- 2008 actual prices of food stuff if compared
to 2002 increased for 64 per cent. The feature of tendency is that if earlier after
price rise there happened stabilization and even decrease, then in 2000-s this
process becomes irreversible.
Therefore, each country shall design
proved methodology including complex of strategic and operative measures for
sustainability, security and reproducing of base of food safety. The methodology
which is the reliable basis for stabilization of domestic production and sale, establishing
of effective foreign economic relations at food trading, formation of legal and
economic warranties of sustainable provision of national agriculture-production
independence.
Conclusions
Financial support of APC aimed at it’s
effective development promotes dealing with primary importance issues, i.e. providing
sustainable growth if production and processing of agriculture products, food
safety of country, stimulating social and economic development of rural areas, creation
of conditions for Kazakhstan to enter WTO.
Any
economically developed state has highly developed food industry. Level of development of food industry
characterizes the status of food safety in country. The important role is played by sector at providing
health of population on the basis of proper balanced nutrition. Social significance of food industry is increasing,
as price level for food products in conditions of low paying ability of most of the population defines
social climate in community. Increasing
of it’s investment attractiveness compared to other processing sectors gives it
the possibility to become one of the “points” of economic growth.
This
sector, as “systematically important”, socially important, shall always be
within sphere of state priorities. It shall be eliminated from secondary
status that formed as result of residual financing principle in conditions of command-and-control
economics. Also the sector shall not be brought to such crisis state which was
usual during process of market transformations
and began to threaten food safety of country.
Nevertheless problem of
establishing mutually favorable relations between suppliers of raw materials
and processors remains outside the limits of view of state bodies. Development of
agriculture-production integration demands at first state regulation of price
policy, as it is done in developed countries.
It means that alongside with free market prices in agriculture production there
shall exist prices regulated by state (guaranteed, target, loan, threshold,
interventional).
Together
with economic methods during process of establishing the mutually favorable
relations between agriculture and processing entities exclusively important is
the form of organization of agricultural business. The most appropriate for
Kazakhstan is considered the cooperative form, where function of integrators is
performed by agricultural entities. But cooperation in agriculture is performed
rather slow and for this issue demands the activation of organizational work on
the part of state.
The sector needs
investments, tax privileges and other measures of economic stimulating on the
part of state. There exists acute need in qualified
specialists, who is almost nowhere trained in the republic nowadays.
References
- Urazova R.S. Effectiveness of food industry//Food and processing industry of Kazakhstan. 2005 ¹3. p. 4-5.
- Apssalyamov N. Development trends of food industry in the Republic of Kazakhstan//Transit economics. 2004. ¹5 (44). p. 39-46.
- Message of President of RK «New decade – new economic upsurge – new possibilities for Kazakhstan»//Food and processing industry of Kazakhstan. 2009 ¹6. p. 2-7.
- www.profinance.kz. Food Industry RK finished the
year with almost no loss. http://profinance.kz/2010/02/12/sshhnebya-ishcnyo-u-pbuyiscb-il-yis-gnp-n.html
5. Agroprom.kz. Kazakhstan
in world rating of flour exporters// http://www.agroprom.kz/info/kazahstan-ofitsialno/kazahstan-v-mirovom-reytinge-eksporterov-muki
- Development
strategy «Kazakhstan - 2030». – Almaty: «Parassat» 1998.
- Concept
for sustainable development of agriculture-production complex of the
Republic of Kazakhstan for years 2006-2010.
- Concept
for implementation of system of state planning, aimed at results. – RK
Government Resolution dated November 26, 2007. ¹1297//www.minplan.kz
- Roman
declaration on worldwide food safety.
- Yefimov
A.B. Organizational-economic aspects of maintaining food safety in Russia.
Abstract of dissertation for receiving title Ph.D. in Economics.
11. Kh.K. Makhashov. Food
provision of population of Kazakhstan in conditions of economy globalization//Turan
university bulletin. – 2009. - ¹4. p. 33-36.
12. Development perspectives of world
agriculture up to 2050: possibilities, threats, priorities// "Agriculture
review", November-December 2009// http://agroobzor.ru/article/a-371.html.