Economics / Business Economics
SAGYTOVA g.
Kazakh Economics University named after T.
Ryskulova,
Republic of Kazakhstan
evaluation OF HIGHer SCHOOL COMPETITIVENESS in the
REPUBLIC of KAZAKHSTAN.
Resume: The methology formation of complex
evalution of higher school competitiveness in the Republic of Kazakhstan is considered in the article.
Key words: competitiveness of educational
services, educational area, the financial stability of educational services
(institutions).
Modern educational system, having actively joined the
market model of functioning some years ago, nowadays is saturated competitive environment.
The educational market services of the higher professional education is rigidly
structured by organizational-legal forms of educational institutions (national,
state, joint-stock, private sector), by the "goods" supply or
merchandise offer (profiles, directions, terms and forms of studying), by the
territorially-legal status (local higher schools, branches and representations
of other cities) and etc.
According to marketing rules the densely
"populated" market niche actualise the competition problem of
educational structures. Herein, the competitiveness management can be considered
as a strategic objective for higher schools development.
The competitiveness in general is understood as the
potential of the institution providing the maximum satisfaction of consumer
requirements and distinguish ing it among the others. The competitive structure
always possesses certain advantages that provide a demand for offered services.
Within the limits of higher education the competitiveness finally is defined by
demand of students for educational services of a certain higher school (the
primary, nearest indicator) and by demand of graduates in the labor market (the
secondary, final indicator).
The competitiveness of a higher school includes a number
of features providing certain position in the educational system:
•
quality of education
•
intracorporate environment
•
external image
•
marketing factors
•
demand of graduates in the labor market
With presence of formal-status recognition
(accreditation) the competitive evaluation can be performed with following
parameters:
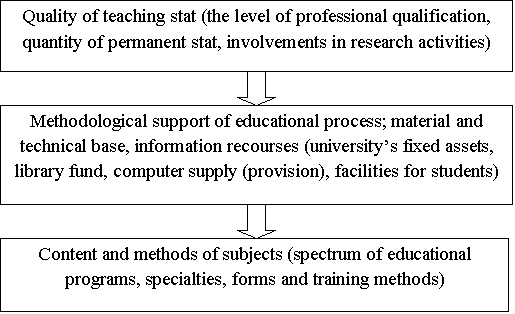
The definition of
"competitiveness of educational services" should be presented as an ability of educational services to maintain the
given competitive advantages over lifecycle and permanently compete on the
educational services market by continuous improvements.
Evaluation of competiveness
for University“ IAB”
Financial analysis was conducted based on data from the non-governmental education institution
"International Academy of Business" (further referred as “IAB”)
on bookkeeping reporting forms (1,2). The following data was gathered necessary
for the “IAB” competiveness evaluation estimation and characteristics.
Table 1 – Liquidity and
solvency evaluation of the “IAB”
|
# |
Indicators |
2009 |
2010 |
Changes from 2009 to 2010 |
|||||
|
+,- |
% |
||||||||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|||||
|
1 |
Most realisable assets |
2786 |
3158 |
+372 |
113 |
||||
|
2 |
Quick assets |
6579 |
6843 |
+264 |
104,0 |
||||
|
3 |
Slow assets |
27040 |
36600 |
+9560 |
135,0 |
||||
|
4 |
Fixed (sticky) assets |
41680 |
44540 |
+2860 |
106,0 |
||||
|
5 |
Most advance commitments (time liabilities) |
11590 |
12830 |
+1240 |
110,6 |
||||
|
6 |
Current liabilities (short-tecm) |
15843 |
17320 |
+1477 |
109,3 |
|
|||
|
7 |
Long-term liabilities |
3600 |
4900 |
+1300 |
136 |
|
|||
|
8 |
Fixed liabilities |
47052 |
51173 |
+4121 |
108 |
|
|||
|
9 |
Coefficient of absolute liquidity col.1/( col.5+ col.6) |
0,101 |
0,104 |
0,003 |
102,9 |
|
|||
|
10 |
Coefficient of quick liquidity (col.1+ col.6)/( col.5+ col.6) |
0,341 |
0,331 |
-0,01 |
97 |
|
|||
|
11 |
Coefficient of current liquidity ( col.1+ col.2)/ col.6 |
1,9 |
2 |
0,1 |
105,2 |
|
|||
|
12 |
Coefficient of complex liquidity ( col.1+(0,5* col.2)+(0,3* col.3)/ ( col.5+(0,5* col.6)+0,5* col.7 |
0,68 |
0,66 |
-0,02 |
97,0 |
|
|||
Table 1shows:
·
Increase of
the coefficient of absolute liquidity (recommended value is 0,2) it indicates that university intends to pay
off the current liabilities in near future.
·
The coefficient
of quick liquidity (optimal value is 1) indicates that university is able to pay
off its current liabilities by monetary means (funds).
·
The coefficient
of current liquidity shows that the current assets cover the current
liabilities which indicate stability of balance.
·
The coefficient
of complex liquidity (optimal value is <0,9), shows the ratio of total current assets.
The analysis on financial stability was conducted
based on the «IAB» data (balance
sheet 001).
Table 2 – Indicators of the “IAB” financial stability
|
# |
Source
of money |
Recommended
value |
2009 |
2010 |
|||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
||||
|
1 |
Authorized
capital |
- |
9000 |
9000 |
|||
|
2 |
Surplus
funds |
- |
1800 |
2680 |
|||
|
3 |
Supplementary
capital |
- |
49220 |
56048 |
|||
|
4 |
Retained
income |
- |
39170 |
44974 |
|||
|
5 |
Long-term
debt |
- |
8700 |
10500 |
|||
|
6 |
Accounts payable (credit
indebtedness) |
- |
16350 |
21050 |
|||
|
7 |
Deferred
income |
- |
930 |
1025 |
|||
|
8 |
Advanced
capital |
- |
81370 |
97672 |
|||
|
9 |
Equity
capital (ovner’s equity) |
- |
52750 |
60497 |
|||
|
10 |
Debt
(borrowed capital) |
- |
61970 |
68552 |
|||
|
11 |
Equity
to total assets |
0,5-0,6 |
0,645 |
0,809 |
|||
|
12 |
Total
debt to equity |
0,4-0,5 |
0,4 |
0,5 |
|||
|
13 |
Financial
leverage ratio |
1 |
0,86 |
0,90 |
|||
|
14 |
Financial
stability index |
0,8-0,9 |
0,94 |
0,95 |
|||
Having analyzed indicators from the
table 2 it is possible to draw a following conclusion:
·
Equity
to total assets in 2010 was 0,809 (normal range
is 0,5-0,6), therefore financial independence and financial stability will remain.
·
Total
debt to equity is within the normal range and
the university is independent from external sources.
·
Financial
leverage ratio indicates that the part of university’s assets are financed at its
own expenses.
· Financial stability index increased to value 0,850 by 2010.
The
calculations show that the University “IAB” is
financially viable and
sustainable, independent and competitive by
85% in comparison with the rivals.
One of the criteria
of an educational institution’s competitiveness estimation is an extra value of
the educational products that is offered in the market of such services. It is
reached by changes in the content and structure of educational products, by
implementation of fundamental and applied science progress in educational
process.
Table 3– Specification of
competitive positions of departments at the “IAB” and “Eurasian Market
Institution” LLP
|
Value |
Specification |
Department
specification value |
|
|
“IAB” |
“Eurasian
Market Institution” LLP |
||
|
0,3 |
Quality
of education |
Good 8 |
Satisfactory 5 |
|
0,2 |
Reputation |
Good 8 |
More
likely good 7 |
|
0,05 |
Internal
environment |
More
likely good 7 |
Satisfactory 3 |
|
0,01 |
Technological
innovations |
Excellent
10 |
Not
quite satisfactory 4 |
|
0,02 |
Structure
of the educational goods (external and internal); |
Excellent
10 |
Good 8 |
|
0,01 |
Marketing
factors |
Satisfactory 6 |
Excellent
10 |
|
0,2 |
Financial
status |
Excellent
10 |
More
likely good 9 |
|
0,2 |
Demand
of graduates in the labor market |
Good 8 |
Not
quite satisfactory 5 |
|
0,01 |
Material,
technical and information base |
Good 8 |
Satisfactory 6 |
|
|
TOTAL: |
6,58 |
6,15 |
Validation scale
|
Quality standards |
||||||
|
Excellent |
Very good |
Good |
Satisfactory |
More likely Bad |
Not quite satisfactory |
Bad |
|
10 |
9 |
8 |
5 |
3 |
4 |
3 |
|
Quantitative values, points |
||||||
Based on data in the table 3, the analysis of the “IAB”
and its competitor - “Eurasian Market Institution” LLP
on rendering of educational services has been carried out; these specifications
were collected from poll of students.
Each specification
was calculated on validation scale and led to total value. Table 3 shows that
total influence on competitiveness estimation constitutes:
·
“IAB” - 6,58;
·
“Eurasian
Market Institution” LLP - 6,15.
These values
satisfy the requirements of General rating conducted by Independent Kazakhstan Agency
for Education Quality Assurance (IKAEQA).
SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses,
Opportunities and Threats) is the most common method of analysis (Table 4).
Table 4 - SWOT-analysis of the “IAB”
|
Opportunities O: - finding partners for joint quality of educational
services; - to develop the sectorial standard «Quality
management System. Special requirements on application of ISO 9001:2000 in
the higher professional education institutions»; - to implementa harmonization and an actualization
of available standard-legal base in the educational sector in compliance with
international norms and rules |
Threats T: -new competitors in the market of educational
services -change in tax rate - inflation |
|
Strengths S: -experience -non-material results of education - continuity of educational processes and
consumption of their results; - duration and labor input of educational process,
and its integrated approach (50-60 various subjects); - significant amount of specialities; - consumers are the state, employers, students; -absence of sectorial requirements to Quality
Management System of higher schools; -government support |
Threats T: -new competitors in the market of educational
services -change in tax rate - inflation |
Table 4 indicates good position of the institution in the market. Growth
of educational services and changes in the market share of the university are
possible only with presence of the following factors:
·
experience;
·
continuity of
educational processes and consumption of their results;
·
duration and
labor input of educational process, and its integrated approach (50-60 various
subjects);
·
significant
amount of specialities;
·
employers and
students;
·
sectorial
requirements to Quality Management System of higher schools;
·
government
support;
Performed analysis
of activities indicates that the University
“IAB” is competitive in educational services in the local market.
Thus, the complex
evaluation of competitiveness based on indicators of education quality,
intracorporate environment, external reputation, marketing efforts and
conformity to labor market requirements will allow to develop correcting management
strategies of development of certain higher school that will generally promote the
increase of competitive environment development and strengthening of higher professional
education system.
Literature
1)
Vasilyev Yu.S. Economy and organization of higher school management: textbook / Yu.S. Vasilyev, V.V. Gluhov, M.P. Fedorov; editing
Dr. V.V. Gluhova. – 2-d eddition, corr. and add. –St. Petersburg 2001. – 543p.
2)
Minazheva G.S. Development, implementation
and improvement of quality management system in higher educational institutions
of Kazakhstan: scientifically-practical edition / G.S. Minazheva. - Almaty: Kazakh
university, 2009. - 111 p.
3)
Gorshkova L.A, Poplavskyi B.N. Innovative
component of strategic management. - Access mode: http://nauka.vvags.ru/