Gulnara A.
Shakirova
Vice-rector on Marketing and
Strategic Development of
UIB University
Role of strategic
management in formation
of the Company competitiveness
Maintenance of necessary degree of competitiveness is the integral part of the market economy allowing the company to provide priority position as at intra-firm, corporate or industry level and at regional, national and world market. In the conditions of new economic realities, the main task of any company is working out of the effective management system which strategic
target is development of potential and ability maintenance to compete in
difficult conditions of modern business. According to the theory of competition: “The main task of strategic management is providing of the organization competitiveness which is defined as its ability to keep its market position and to
stand firm against competitors’ actions in the long-term prospect. Depending
on whether it is possible to expect improvement or deterioration of a
competitive position of the company, the decision is made to continue
implemented strategy or to work out new, more effective strategy”. [1] Modern business experience demonstrates the importance of
creating a competitive strategy for all business entities from large corporations to small enterprises.
The
intensification of growth in consumer demand, the arrival of foreign companies to the markets form the need to intensify efforts to develop competitive strategies for the competitive capacity at various
levels. Economic development in high-density market is gradually moving from "sellers market" to "buyers market", thus
companies often respond to these changing of market conditions only with intensified sales policy,
marketing solutions generally lead to temporary improvement
of market
position. In reality, the appropriate response to market needs and the main condition for the formation of the stable position of the company should be the necessity to develop a competitive strategy that ensures an organization's ability to survive in long-term prospect. In this regard, strategic management is a key element in the formation of corporate policy, because, based on the human potential
of the company directing production activity taking into account consumer demand, allows quickly and flexibly to
respond to the time challenges and the state of the environment providing stability and market attractiveness in long-term prospect.
Referring to the background of this question, it should be noted that the concept of strategic planning and later passed in to the concept of strategic management emerged in response to the increasing of dynamism and
uncertainty of the business environment in the late 60s - early70s of the twentieth century. Gradual
displacement of accent from planning to strategy creation has allowed the
companies to pay more attention to firm positioning in the market concerning
competitors. The concept of strategic management was built on the principle:
“future begins today” and complies
with P. Drucker’s quotation:
“Strategic planning deals not with the future changes but with the future of
the decisions made today”. [2]
For today more and
more obvious there is a question that the primary goal of strategic planning
consists in a substantiation of the major purposes and development of correct
strategy of long-term development. In spite of the fact that strategic
management is considered the important condition to provide competitive
advantage and moreover it becomes sharply necessary in modern conditions, there
is an opinion, that strategic planning is pleasure for rich, growing firms, for
small and medium businesses, it
is unacceptable in the conditions of market fluctuations.
Numerous research conducted in this area, confirm the low interest and activity of business entities in the implementation of integrated strategic management system, at a
relatively high understanding from the
companies top managers’ side of the importance of strategic management
tools, a
small percentage of them undertake real steps, but in most cases developed plans have for a formal nature.
According to the analysis of strategic processes at the enterprise level conducted by I.B.Gurkov, Russian researcher of strategic management confirm that, in general,
Russian companies do not take the trouble to draw up detailed strategic plans. In particular, 40% of the largest (with sales
volume more than 10 billion rubles) and 50% (with sales volume from 1 to 10 billion rubles) firms are satisfied with the plan at the level of general ideas,
or even with a set of individual
projects, and in terms of competitive pressure, Russian firms behave
differently, a quarter of companies stop developing of plans, and a third, on the contrary see
salvation from
the competition
in detailed plans. [3]
The experience of doing business in Kazakhstan shows a similar pattern, the need increases to find new methods of management and system planning of activity at the present stage of companies’ development in Kazakhstan. According to
a survey conducted by the author among small, medium
and large businesses,
presented in Picture1, the following is shown: despite
the generated necessity for
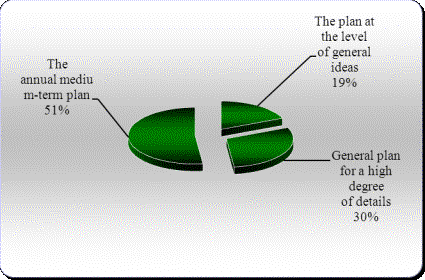
Picture 1 - Analysis of system of activity planning of small, medium and large business
Note: compiled
by the author according to the survey
forward
planning, response to requirements of time more than at 50 % of the
interrogated companies is expressed in development of annual and intermediate
term plans for development. 19 % of the enterprises are limited on working out
of plans at level of the general ideas reflecting the corporate policy. And
only about 30 % of the companies work over detailed plans for development with
forecasting of desirable results in intermediate term and long-term prospect.
Strategic management allows to accumulate a complex of tools of
administrative activity to
ensure and promote competitive
advantages of the enterprise forming a stable market position due to the
ability of adequate reaction to changes in the environment taking into account
internal resources of the company. The sequence and scientific validity of
approaches in the field of strategy planning form the corporate policy on the
basis of the complex approach to the analysis of efficiency of the company
activity, choice of strategic guidelines, implementation of strategic decisions
and regular monitoring of quality of performed processes. The complex and system approach allows to establish steady interrelations
between strategic plans and real actions, for the purpose of application of
timely correcting actions for maintenance of long-term competitiveness of the
enterprise.
In general, schematic process of strategy planning on the basis of the analysis,
forecasting and monitoring of the environment can be represented as
follows:
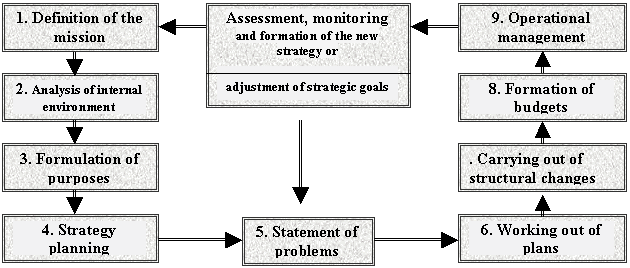
Picture 2 - The scheme of strategic planning
Note: compiled
by the author using source [4]
System planning and effective implementation of corporate policy in the
field of development and business advancement allows to manage in a complex
competitiveness and in the end result serves as an integrated measure to
determine the total potential of the enterprise in all its basic cuts -
scientific and technical, financial and economic, personnel, production and
technology. Adequacy of strategic management to real needs of the
environment taking into account internal resources of the enterprise allows to
estimate objectively possibilities, to predict risks and to make administrative
decisions in interests of the company providing long-term competitiveness as a
whole and in priority directions of activity in particular.
Value of the strategic behaviour allowing firm to survive in competitive
struggle in long-term prospect, has sharply increased last decades.
Acceleration of changes in environment, occurrence of new demands and change of
the consumer’s position, increased competition for resources,
internationalization and business globalization, innovations, development of
information networks doing possible quick spread and reception of information,
wide availability of modern technology, change of a role of human resources,
and also a number of other reasons have led to sharp increase in the value of
strategic management. Influence of all factors on
working out of development strategy put before the company the most complicated
problems to determine the competitive advantages corresponding to real
possibilities. If to address to the theory of the question, all set of
competitive advantages can be divided conditionally into three groups:
- resource, availability of resources of particular quality or quantity (natural or purchased);
- operational,
degree or efficiency of available resources;
- program and strategic, presence of certain strategy for development of the entity-bearer of competitive advantages and quality of this strategy. At the present stage of
development types of advantages become complicated from resource to strategic,
thus, competitive struggle actually turns to struggle of strategy practically
at all levels, and strategic component is the leading characteristic of
competitiveness. [5]
Despite the numerous theoretical and practical experience in strategic planning there is no single model for all companies, as well as there is no
single universal method of strategic management. Every company is unique and specific in its own way,
so the process of strategy developing for each firm is strictly individual
and adjusted to its requirements. In this connection competitiveness of each enterprise depends on the firm's position in
the market, dynamics of its development and potential, competitors’ behavior, characteristics of goods produced by this firm or its services, state of the economy,
cultural environment and many other factors. Nevertheless, the basic
moments noted in this article, allow to apply some main principles to develop
strategy of behaviour and implementation of strategic management without
dependence on a branch orientation of business and specificity of activity of individual economic entity.
The choice of the
purpose and strategy of the enterprise development is a basis of independent
planning and administrative activity in free market relations. In the modern
theory of planning it is accepted to speak about eight basic fields of activity
in which borders each enterprise defines its main goals: company position in
the market, innovative activity, performance level, availability of production resources, degree of
stability, control system, professionalism of the personnel and social
responsibility. Every
company in
the long-term
planning should
itself choose the best strategy for the development or growth in view of its real possibilities and the results achieved at each stage of economic activity, thus degree of rotation of the target interest in the structure of the strategic priorities will
depend on the company's corporate tasks. As the advanced practice testifies,
financial purposes are the most significant in market conditions defining state
of solvency and economic stability of the enterprises, profit reception became
the most priority problem in structure of interests of any company as the
profit serves as the important condition of achievement of all other purposes
which are put in the forefront during the different periods of activity of the
enterprises. At the same
time the profit should not
cover with itself many other things of the purpose of development or firm
activity.
The effectiveness of management is reflected in the dynamics of development not only at the level of business structures, but also on the position and dynamics of the country development on a global level. In the conditions of
globalization any country cannot abstract from world tendencies of development,
the comparative estimation of development in system of world economic relations
turns to one of the major factors defining competitiveness of national economy.
One of such criteria of an external estimation of the countries’ activity is
carrying out of a rating of global competitiveness
conducted annually by the Lausanne International Institute for Management Development (IDM). This rating provides a comprehensive
assessment of the countries’ competitiveness on four factors: economic activity,
government efficiency, business efficiency and infrastructure. For
example, Kazakhstan according to the IDM report in 2011 took 36th place among 59 analyzed countries of the
world losing three points compared to last year. Despite the fact that Kazakhstan continues to outpace the CIS countries (Russia - 49 th, Ukraine - 57th), in general analysis of trends is not reassuring.
And
falling on seven points of two factors of competitiveness became the main
reasons of a weakening of positions: efficiency of business (from 29th to 36
place) and infrastructure (from 39th to 46) on polling and on statistical data (Table 1). Analysis of strengths and weaknesses under competitiveness subfactors of IMD shows that the competitive advantages of Kazakhstan are the indicators of Fiscal policy (10th place), Public Finance (14) and employment (14th place). The least competitive positions in Kazakhstan are the measures of
productivity (46 place), price (47) and financial (51) indicators including indicators of the banking sector and stock market in the country, scientific
infrastructure (55), health and environment (55th place). [6]
At the same time the level of business performance continues to lag behind by 15 points with respect to the level of government efficiency (21st place), despite the fact that many people consider
that the lack of state control system and the imperfection of legislation influence the quality of processes.
Table 1 – Positions and dynamics of Kazakhstan in the ranking of IMD
for 2010-2011 in the context of the factors
|
Factors and
subfactors 2010 2011
Changes of rating for
the year
|
|
|
|
General rating 33 36 -3 |
|
Economic activity 43 35 8 |
|
1. Domestic economy 38 39 -1 |
|
2. International trade 55 39 16 |
|
3. Foreign investments 27 26 1 |
|
4. Employment 23 14 9 |
|
5. Prices 49 47 2 |
|
|
|
Ýôôåêòèâíîñòü ïðàâèòåëüñòâà 20 21 -1 |
|
1. Government efficiency 16 14 2 |
|
2. Fiscal policy12 10 2 |
|
3. Institutional environment 39 41 -2 |
|
4. Business Law 26 33 -7 |
|
5. Social order 24 24 0 |
|
|
|
Business efficiency
29 36 -7 |
|
1. Productivity and efficiency 39 46 -7 |
|
2. Labour market 8 15 -7 |
|
3. Finance 42 51 -9 |
|
4. Practice of management 23 31 -8 |
|
5. Relations and values 18 25 -7 |
|
|
|
Infrastructure 39 46 -7 |
|
1. Basic Infrastructure 33 36 -3 |
|
2. Technological infrastructure 40 42 -2 |
|
3. Scientific infrastructure 44 55 -1 |
|
4. Healthcare and Environment 52 55 -3 |
|
5. Education 40 41 -1 |
|
Note: compiled by the author using source [6] |
The example of definition of a world rating of global competitiveness
clearly shows that dynamics of business development is reflected not only in a
condition of this or that branch, but also at level of social and economic
development of the country as a whole. External indicators of positioning of
Kazakhstan as an example of world ratings indicate the need of cardinal change
in approaches to competitiveness formation, thus questions of strengthening of
positions are first of all in a plane of quality and management efficiency at
various levels. In this
context, the main areas of settlement issues are questions of finding new, innovative ways of corporate governance with a vector direction on issues of science, innovation, social sphere and creation of an
adequate business
environment that will allow to spend consecutive
economic policy of maintenance of competitive advantages of the country at
external level. Moving on to the lines of strategic management will allow to form responsibility in the
decision of questions in the context of factors "business development", "infrastructure" and "government
effectiveness" in the long term prospect in the context of national strategic development of the country. Formation
of strategic
thinking and
responsibility on the part of economic agents, a systematic approach of planning and strategic management
will allow to predict
the future, to define key strengths and competitive advantages, to calculate strategic
risks. All this will enhance the competitiveness of enterprises and their products, their services in the domestic and world markets, which ultimately will improve the social and economic
situation in the
country providing the key importance in achieving goals reflected in the Message from N.A Nazarbayev, the President of the Republic of Kazakhstan “Social and economic
modernization is
the main vector
of development of Kazakhstan”. [7]
The competitive potential allowing to provide achievement of business
purposes in the future is one of end-products of strategic management. Despite
the importance of the role of strategic management in formation of the company
competitiveness in domestic and foreign markets, a variety of types and definitions
of strategy as
well as practical experience in the this area is rather difficult to classify the strategic management system, nevertheless, it is necessary to consider the most essential
classification features that promote to work out strategic development programs
of various companies:
- stage
of life cycle of the
branch;
- relative force of the branch position of the company;
- decision-making level;
- base concept of achievement of competitive advantages;
- the degree of reactivity of the company behavior in the
competitive
struggle, etc.
Along with the obvious advantages strategic management has a number of restrictions on the use and issues requiring careful
consideration, since this type of management, as well as other management systems
does not possess universality of application in any
situations and to solve any problems because of the following points:
- strategic management can not give an accurate and detailed picture of the future;
- strategic management can not be reduced to a set of routine procedures and schemes;
- huge efforts and large expenditures of time and resources are
required in order to start strategic
management process in the organization;
- negative effects of the errors of strategic foresight are possible;
- realizing strategic
management it is often the emphasis becomes on strategic planning instead of implementation of the strategic plan.
At the strategically-focused approach to management it is necessary to pay
special attention to other factors too which critically influence qualitative
working out of the strategic plan for development, among them the most prominent factors of influence are the following:
- the influence
degree of environment on the choice of the company strategy;
- staged and temporal dynamics of doing business;
- conformity of the chosen strategy to condition
and requirements of the environment;
- conformity
of the chosen strategy to potential and opportunities of the enterprise;
- acceptability of risk inherent
in the strategy;
- appropriateness and feasibility of implementation at all levels.
The increasing role of strategic management in competitiveness formation at
all levels is the obvious fact and time requirement providing efficiency and
viability of activity in the conditions of constantly changing of business
environment. Now the understanding from professional community of necessity of
radical transition to formation of strategic thinking and management actively
grows, that in immediate prospects should promote capitalization of interests
of the enterprises in the field of strategic management and competitiveness
formation at branch and world level.
Literature:
1.
Yu. D. Tursin, S. Yu. Lyapina,
N.G. Shalamova Strategic management, Tutorial. Ì.: Infrà-Ì, 2003.
2. P.
Drucker Management Challenges for the 21st Century/ Translation from English, M,
2003
3. I.B. Gurkov the report "Factors of formation and
mechanisms of the implementation of strategic objectives of Russian companies," Economy section
of Social studies Department of the Russian Academy of Sciences, M, 2008
4. R. I. Akmayeva Strategic
management. Tutorial. Ì.: Wolters Kluwer, 2010, p. 50
5. G.Zh. Nurmukhanova Theoretical,
methodological and practical aspects of competitive economy: Monograph. - Almaty:
UIB, 2007, p. 58
6. Ministry of Economic Development and Trade. "Kazakhstan in the ranking of the International Institute for Management Development (IMD) 2011", www.minplan.kz
7. Message from N.A Nazarbayev, the President of the Republic of Kazakhstan “Social and economic
modernization is
the main vector
of development of Kazakhstan”.//Kazakhstanskaya Pravda, http://www.kazpravda.kz/c/1327711976/ January 28, 2012