УДК 539.32: 622.023 Технические науки/ 2.Механика
Masanov Zh.K.1, Azhihanov N.T, Turimbetov T.A.2, Aimeshov
Zh.A.3
1Kazakh Academy of
Transport and Communications named after M. Tinishbaev, Almaty, Republic of
Kazakhstan.
2Caspian State
University of Technologies and Engineering named after Sh.Eseno, Aktau, Kazakhstan.
3Internetional
Kazakh-Turkish University named after H.A.Yassaui, Turkistan, Kazakhstan.
Mathematical modeling of diagonal fossils’, that have
different forms, flexibly-movable condition in anisotropic environment
This
article concerns with the numeral investigation of flexibly-movable intensity
condition of double diagonal fossils that have been weakened with double
periodic chinks.
We know about the researching
works that deals with the modeling of the hole cleaning efficiency is an
important criterion that should be well determined during drilling operations.
The carrying capacity, the ability of transporting the drilled particles to
surface, is one of the major roles of drilling fluids. Especially during
underbalanced drilling operations in horizontal and deviated wells, flow
behavior of the two-phase fluid should be well determined in order to improve
the hole cleaning efficiency. Otherwise, an improper hole cleaning may result in
differential pipe sticking, increased torque and drag and hence a severe
economical loss.
They determined the slug
interval by considering the slug frequency and the gas phase velocity. Then the
flow pattern transitions were estimated from the slug intervals. They developed flow pattern maps for vertical air
and water mixture through various noncircular conduits including concentric
annuli. From these flow pattern maps, they concluded that the channel geometry
has very little effect on the flow pattern transitions (1st
picture).
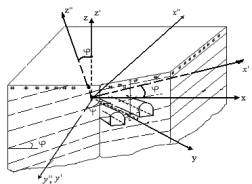

1st
picture. Drawing of area of the account
It was concluded that the flow
patterns of cuttings are dependent on the total flow rate of the liquid and gas
phase. It was also concluded that in order to avoid the formation of a
stationary cuttings bed, an approximate boundary of minimum flow rate of each
phase can be determined. The minimum requirements for gas and liquid flow rates
were found to be always in the intermittent flow regime.
![]() (1)
(1)

1st
picture. Environment weakened by two-period beams
The carrying capacity of the aerated drilling fluid
was evaluated by using two-phase flow properties and a cuttings transport
model. Moreover, a computer program was developed for the prediction of flow
patterns, circulating pressures, optimum two-phase flow requirements, bit
hydraulics and hole cleaning. It was concluded that dispersed bubble flow did
not develop in the drill string and the annulus, and that the multiphase models
calculated lower bottom hole pressures compared to dispersed model.
![]() ,
, ![]()
![]()
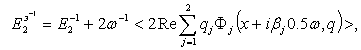 (2)
(2)
![]()
Here < > - the sign of medium meanings; ![]() anisotropic settings;
anisotropic settings;
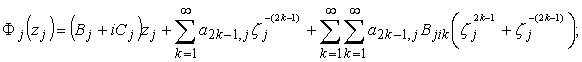
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() (3)
(3)
![]() Transporting alevrolics (
Transporting alevrolics (![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() ) is a equivalent of whole alevrolic flexibility
) is a equivalent of whole alevrolic flexibility ![]() modules and
modules and ![]() anisotropic settings
anisotropic settings ![]() that has been
estimated in a connection of chink.
that has been
estimated in a connection of chink.
During the progress of the
mathematical model, experimental data acquired from multiphase flow loop is
integrated. Flow pattern and pressure ![]() loss estimations are compared
with the experimental data and hence the model’s performance
loss estimations are compared
with the experimental data and hence the model’s performance ![]() is evaluated.
is evaluated.
Moreover,
empirical equations are proposed for friction factor Oxyz determination corresponding
to each flow pattern individually and mutually as well.
![]() (4)
(4)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() - can be find out by coefficient of modeling flexibility.
- can be find out by coefficient of modeling flexibility.
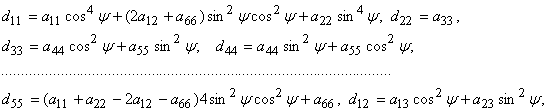 (5)
(5)
![]() (6)
(6)
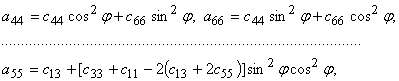
![]()
![]() ,
, ![]() , (7)
, (7)
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]()
Similarly, the air compressor
is used with a volumetric flow meter and an electropneumatic control valve to
deliver required amount of gas into the loop. The compressed air mixed with the
water before entering to the annular section. A pressure regulator is mounted
before the gas flow meter as a safety measure and to keep the air pressure controlled
prior to entering to the test section. The pressure of the gas phase is kept
usually at 25 psi. The pressure of the loop, frictional pressure losses, liquid
and gas flow rates are measured using the data acquisition system. Data logger
and data acquisition software are used to gather and store the experimental
data digitally. The determination of the locations of the pressure transmitters
on the test section was one of the important tasks during setup design and
construction. The data collected should be reliable since the mathematical
model’s performance would be evaluated using the experimental data. Therefore,
entrance and exit effects are calculated for each casing-drillpipe
configuration
using Equations 69 and 70. The
entrance length is calculated by;
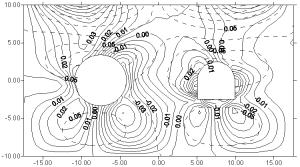

R1=3,5M; R2=2,5M;
H=10M; L=5M; w/a=∞; H=10M;L=5M;y=450; j=0; w/a=∞; - - w/a=3
y=900; j=300;
w/a=6.0; - - w/a=2,5
For practical purposes, frictional pressure losses can be determined using
friction factor correlations proposed separately for each flow pattern and flow
properties of the mixture. A new mixture Reynolds number NRemixl based
on liquid holdup term is introduced for intermittent flow.
When this wide range of
application of two-phase flow in petroleum engineering is considered, the
importance of the appropriate determination of flow parameters of two-phase
fluid systems is remarkable. Several studies4-26 have been carried out for
understanding the flow mechanism of two-phase fluid systems through pipe.
References
1.
Ержанов Ж.С., Айталиев Ш.М., Масанов Ж.К. Устойчивость горизонтальных выработок в наклонно-слоистом массиве.
Алма-Ата, Наука, 1971, 160с.
2.
Ержанов Ж.С., Айталиев
Ш.М., Масанов Ж.К. Сейсмонапряженное состояние подземных сооружений в
анизотропном слоистом массиве. Алма-Ата: Наука, 1980 – 210с.
3.
Масанов Ж.К.,
Атымтаева Л.Б., Жолдасова Ш.А., Жоламанова З.К. Упругая, упругопластическая состояние
полостей в анизотропном
массиве. / труды 1–го Центральноазиатского геотехнического симпозиума "Геотехнические
проблемы строительства, архитектуры и
геоэкологии на рубеже 21–го века"7 Астана, 2000. Том–1, –с. 240–2427